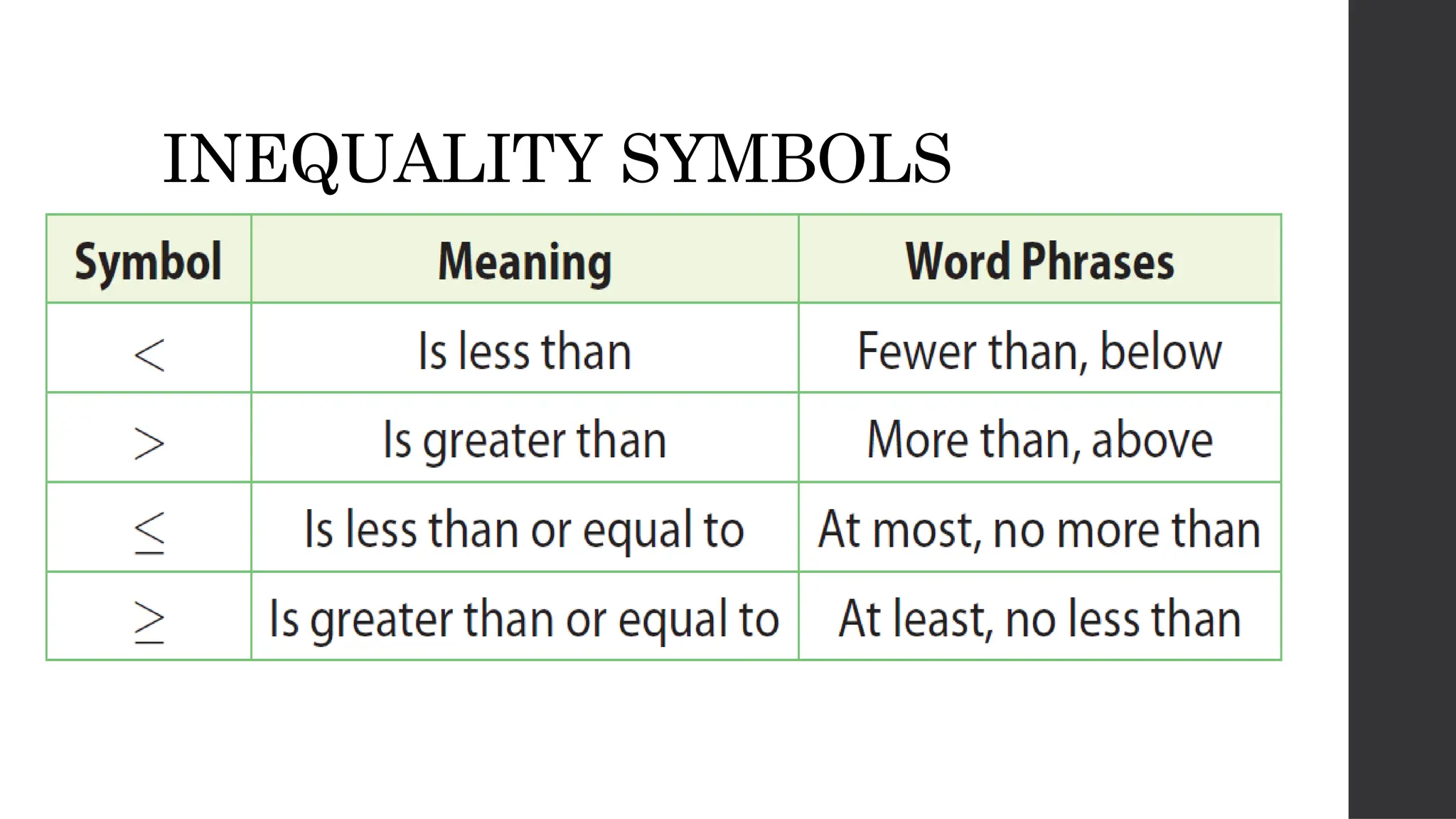
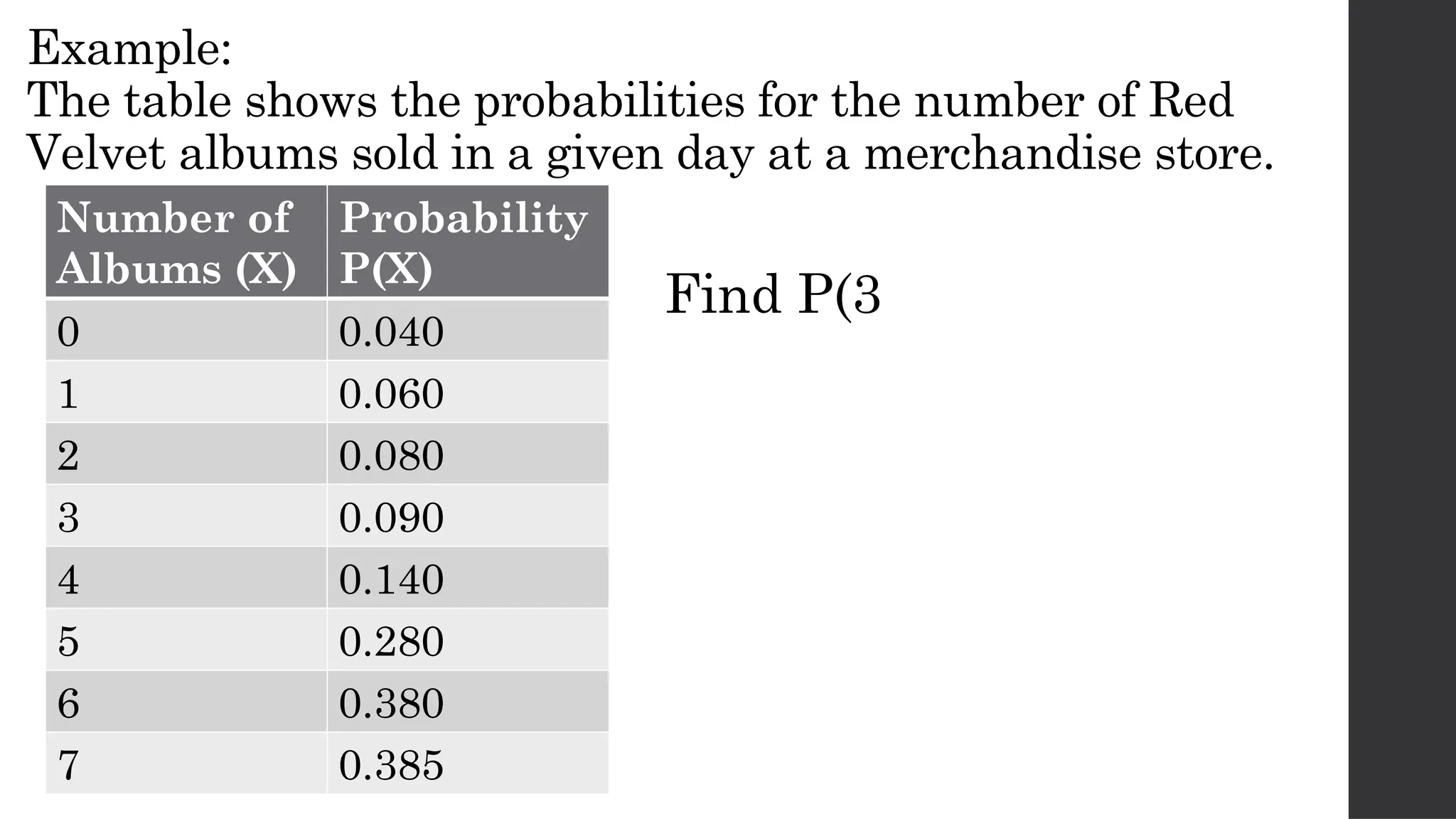
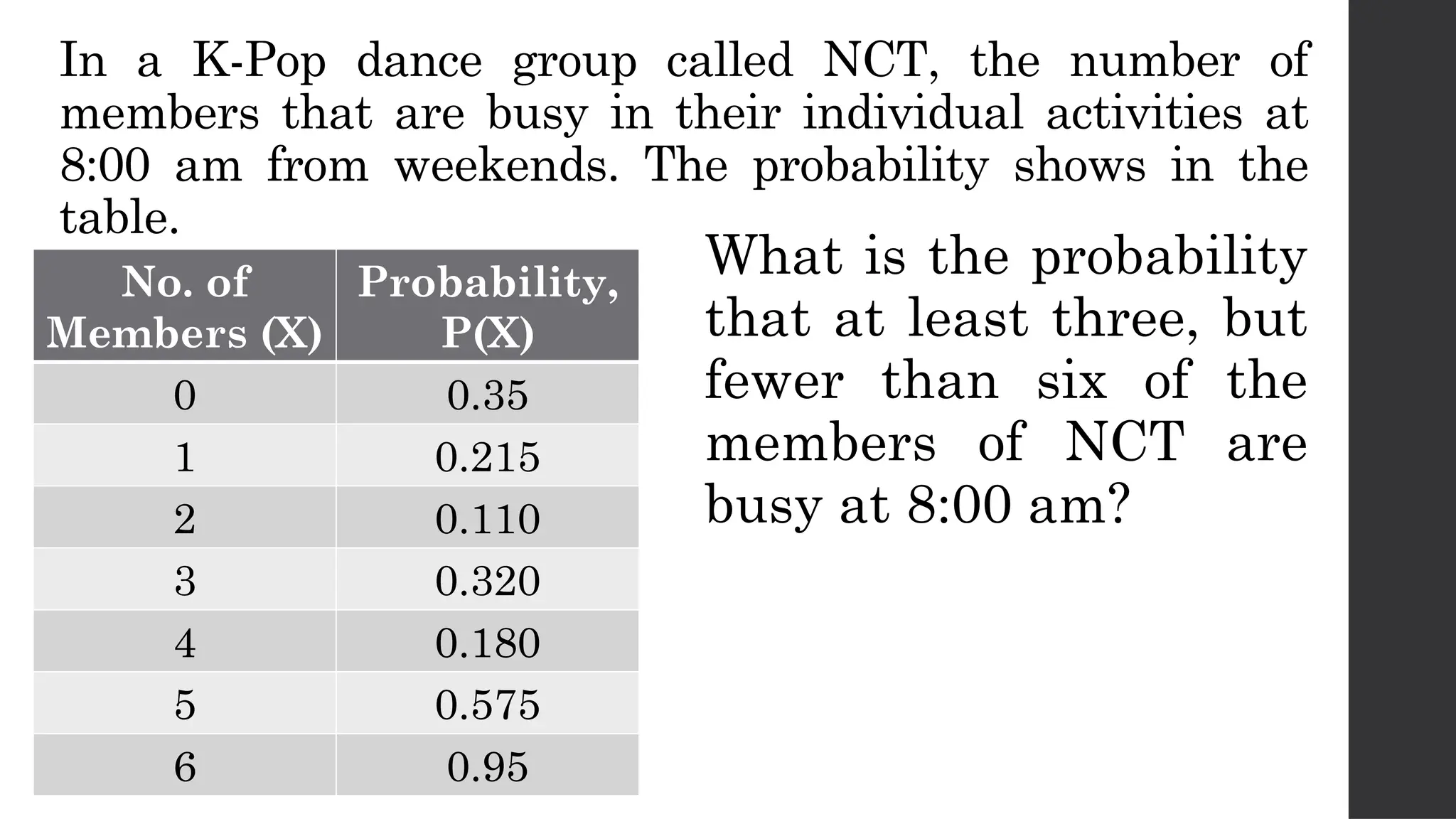
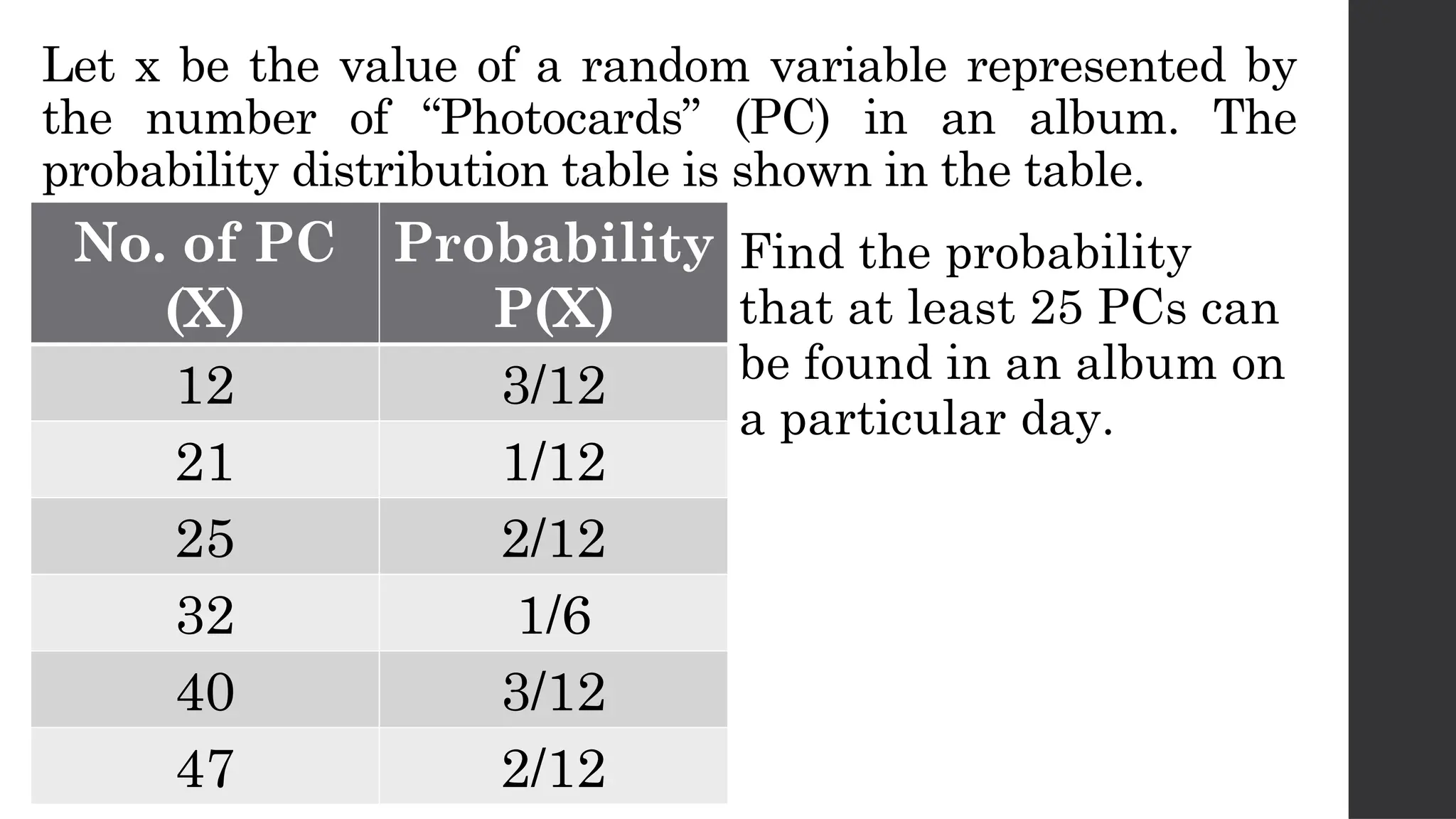
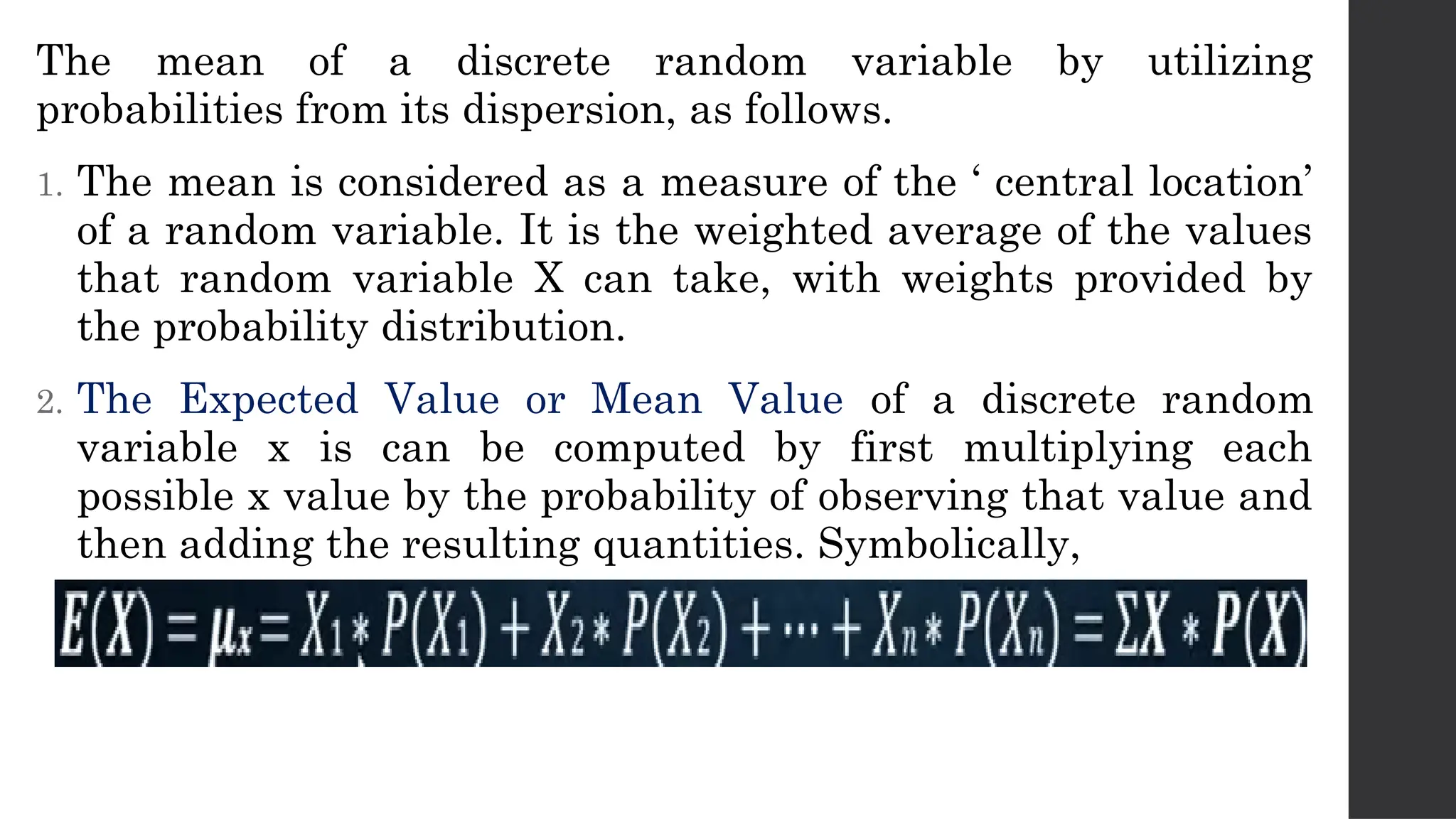
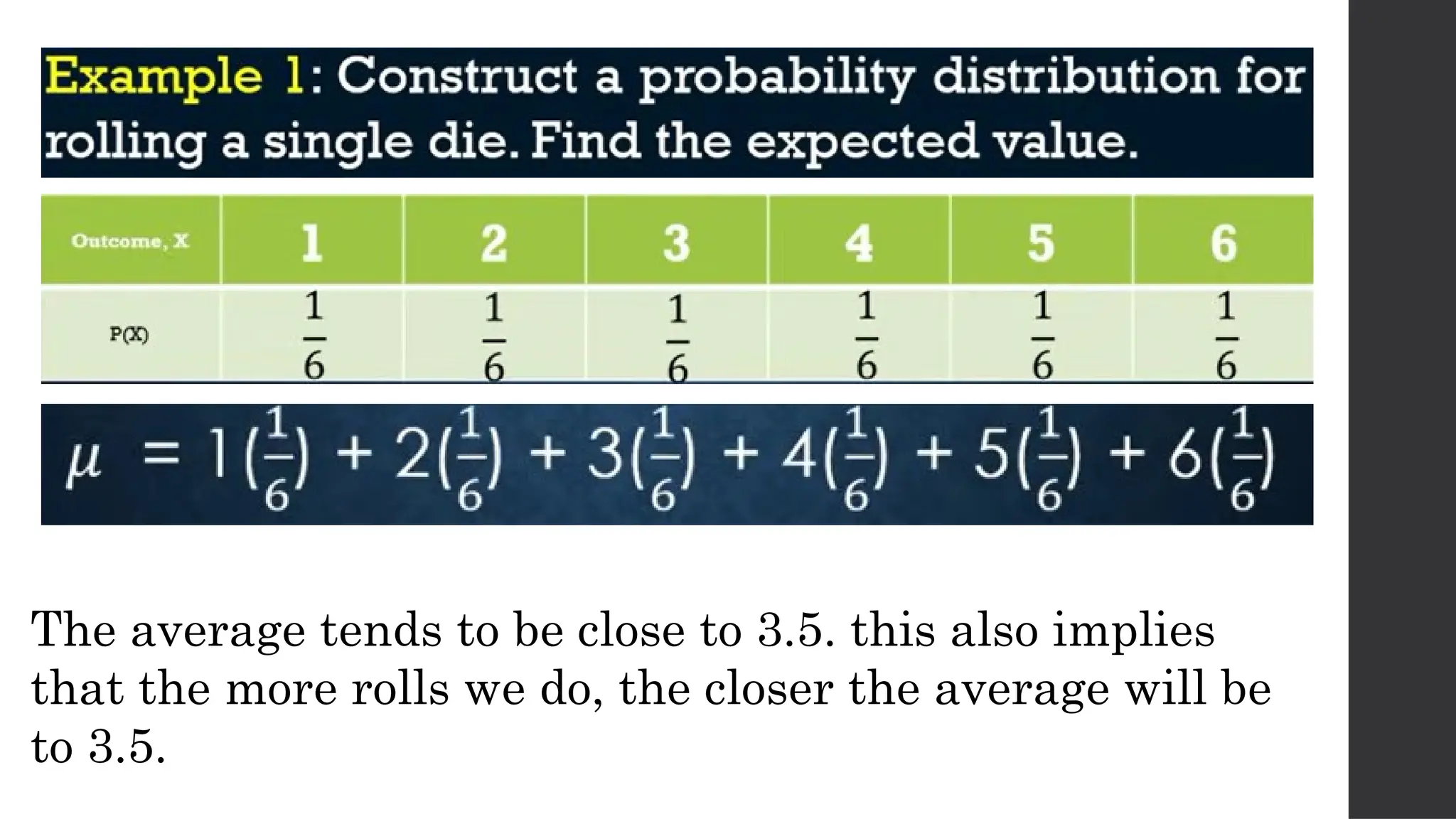
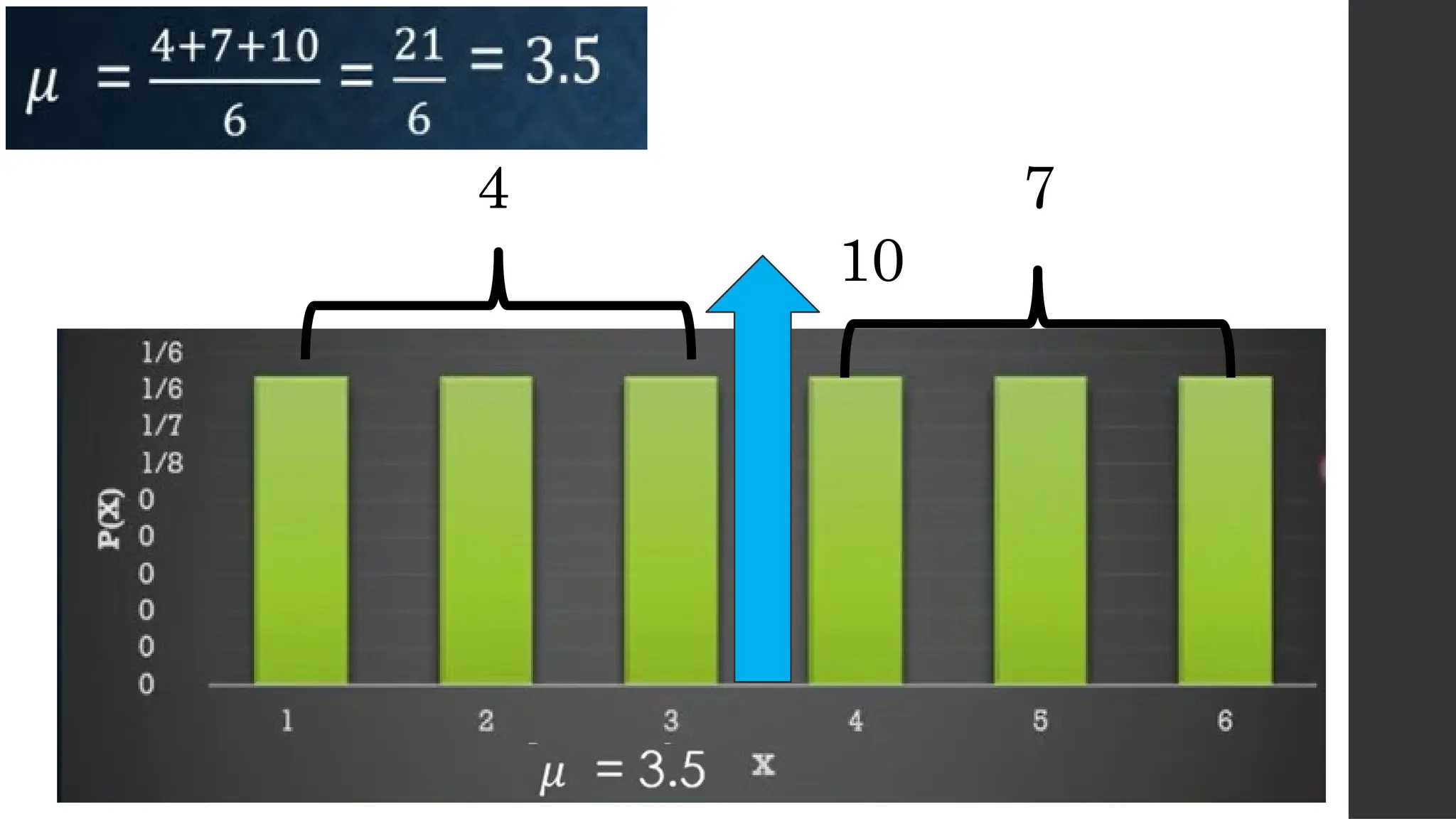
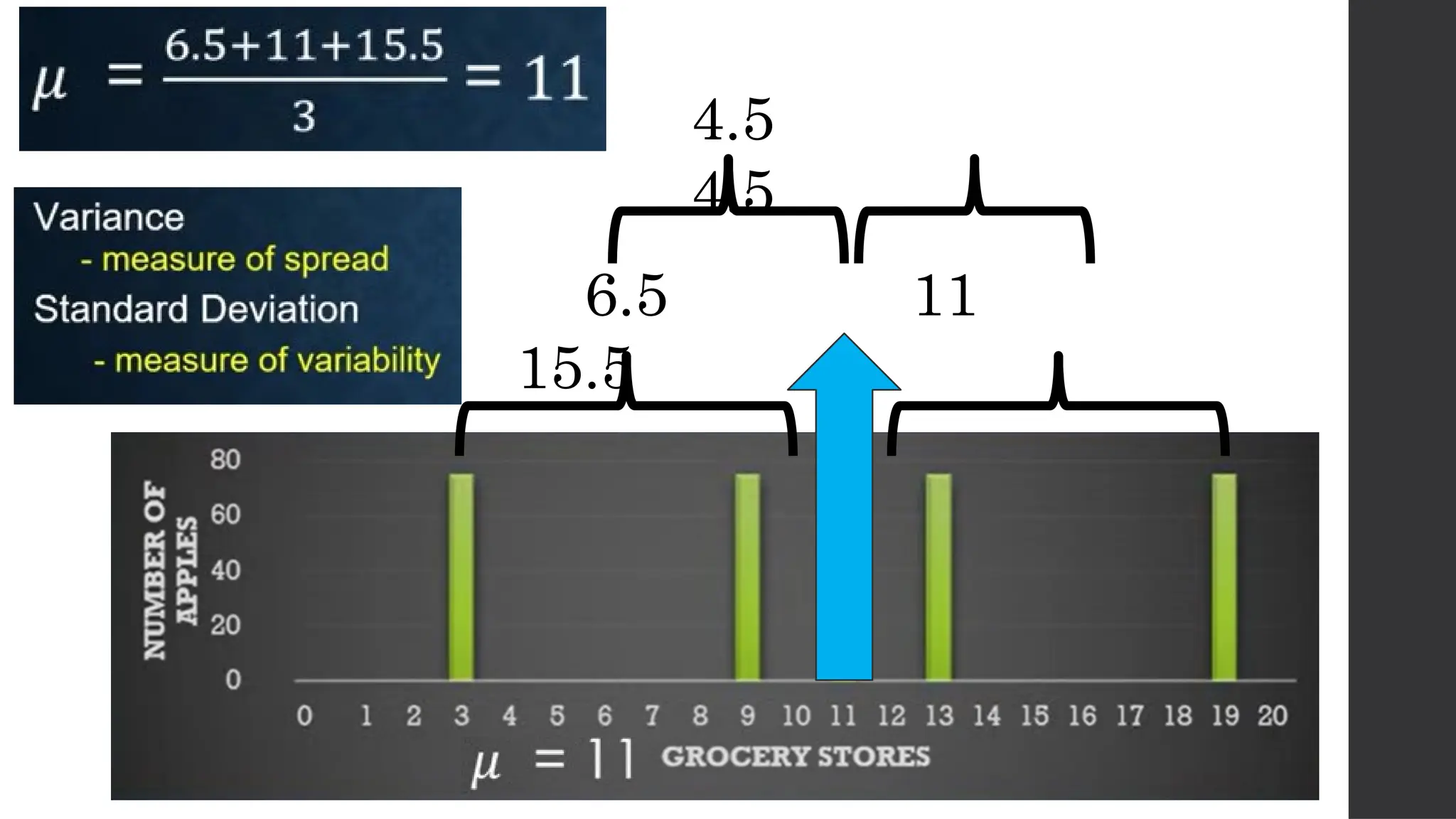
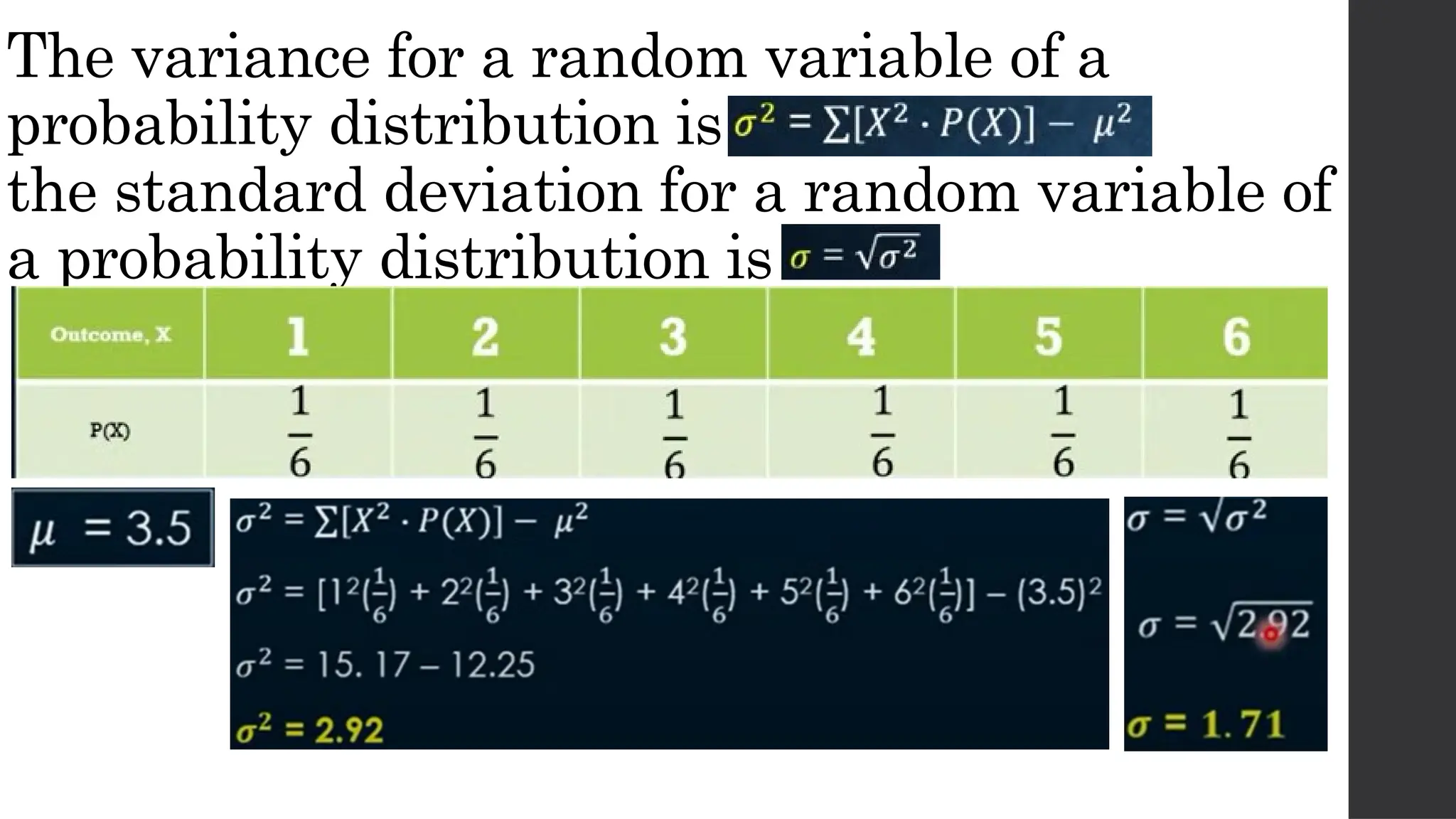
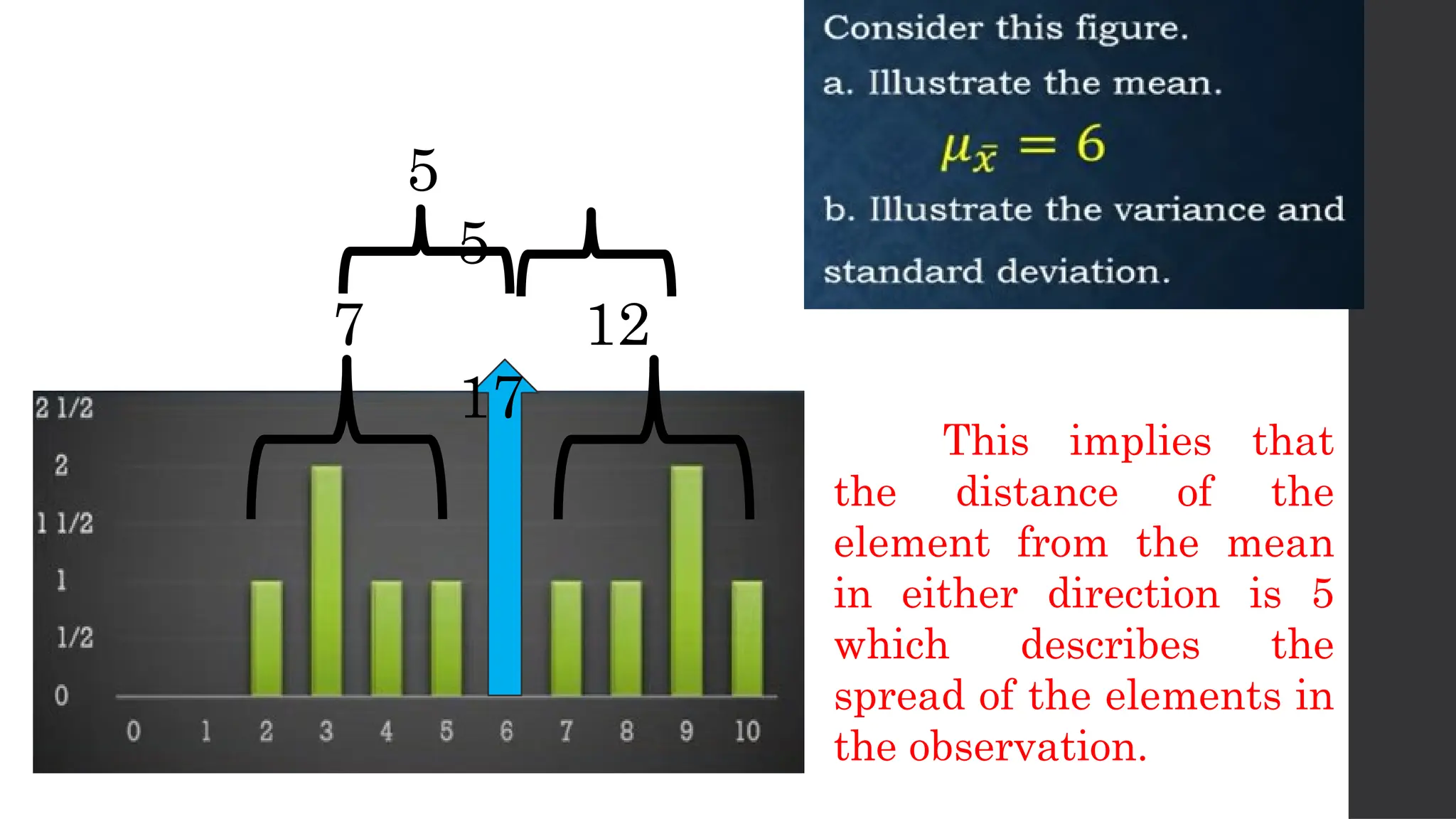
The document discusses probability distributions related to random variables, with examples such as the sales of albums and member availability in a dance group. It covers the calculation of mean and variance for discrete random variables, emphasizing their significance in determining the central location and spread of data. Key points include probability tables for specific scenarios and methods to compute expected values.