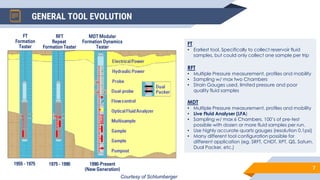
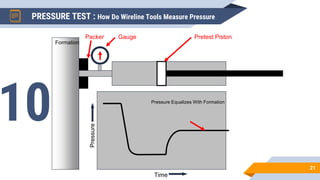
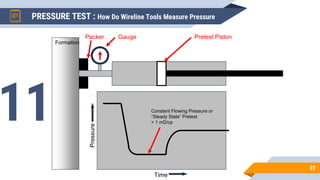
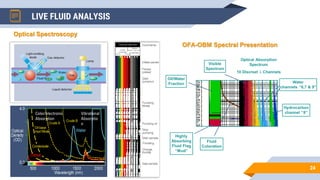
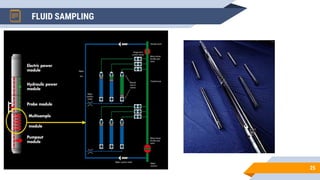
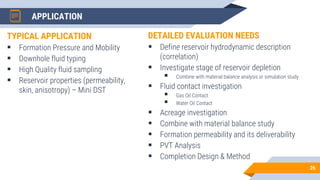
The document discusses the use of RFT (Repeat Formation Tester) and MDT (Modular Formation Dynamics Tester) tools for reservoir evaluation and fluid sampling. These wireline tools are used to measure formation pressure, permeability and obtain fluid samples. The document outlines how the tools work, providing examples of pressure measurement and fluid analysis. It also presents a case study and discusses applications of the tools in reservoir development and contact analysis.