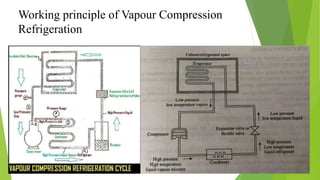
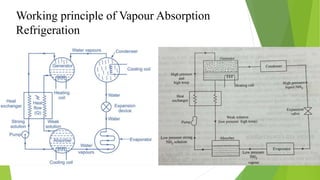
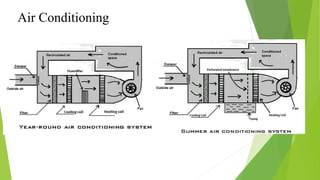
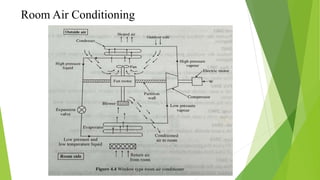
Refrigeration is the process of lowering and maintaining a substance's temperature below the ambient temperature. Refrigerants are working fluids that absorb heat in the evaporator and release it in the condenser while undergoing phase changes between liquid and gas. The two main types of refrigeration systems are vapor compression, which uses mechanical energy to circulate refrigerant, and vapor absorption, which is heat-powered. Vapor compression is more common due to lower maintenance costs, while absorption systems have higher capacities and more consistent efficiency at partial loads.