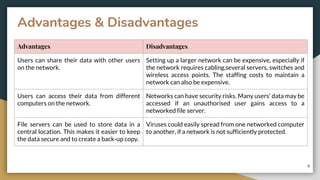
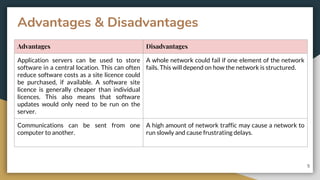
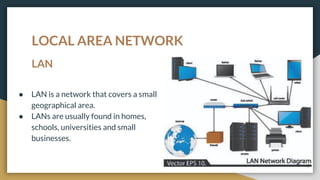
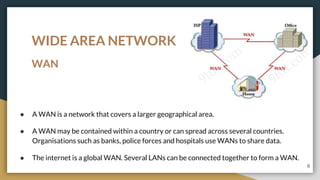
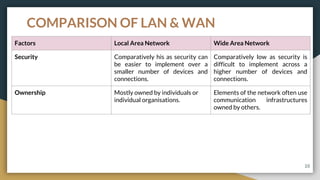
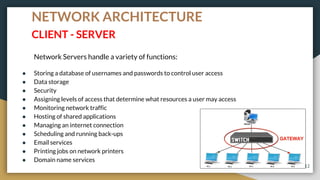
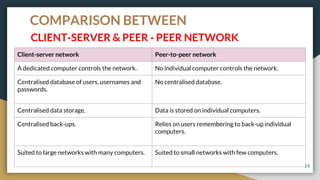
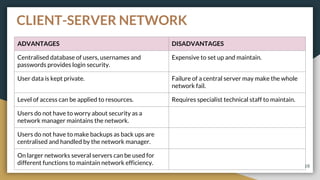
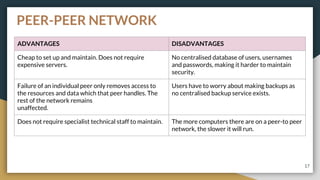
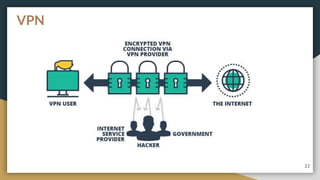
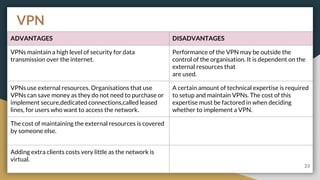
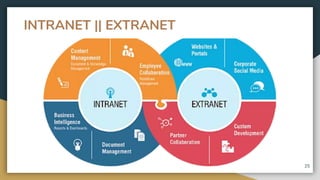
This document provides an overview of computer networks, including their advantages and disadvantages. It defines different types of networks such as LANs, WANs, VPNs, client-server networks, and peer-to-peer networks. LANs cover small areas like homes or offices while WANs span larger distances. Client-server networks have centralized servers that control access and resources, while peers have equal access in peer-to-peer networks. VPNs allow secure remote access to private networks. The document also discusses intranets and examples of network usage.