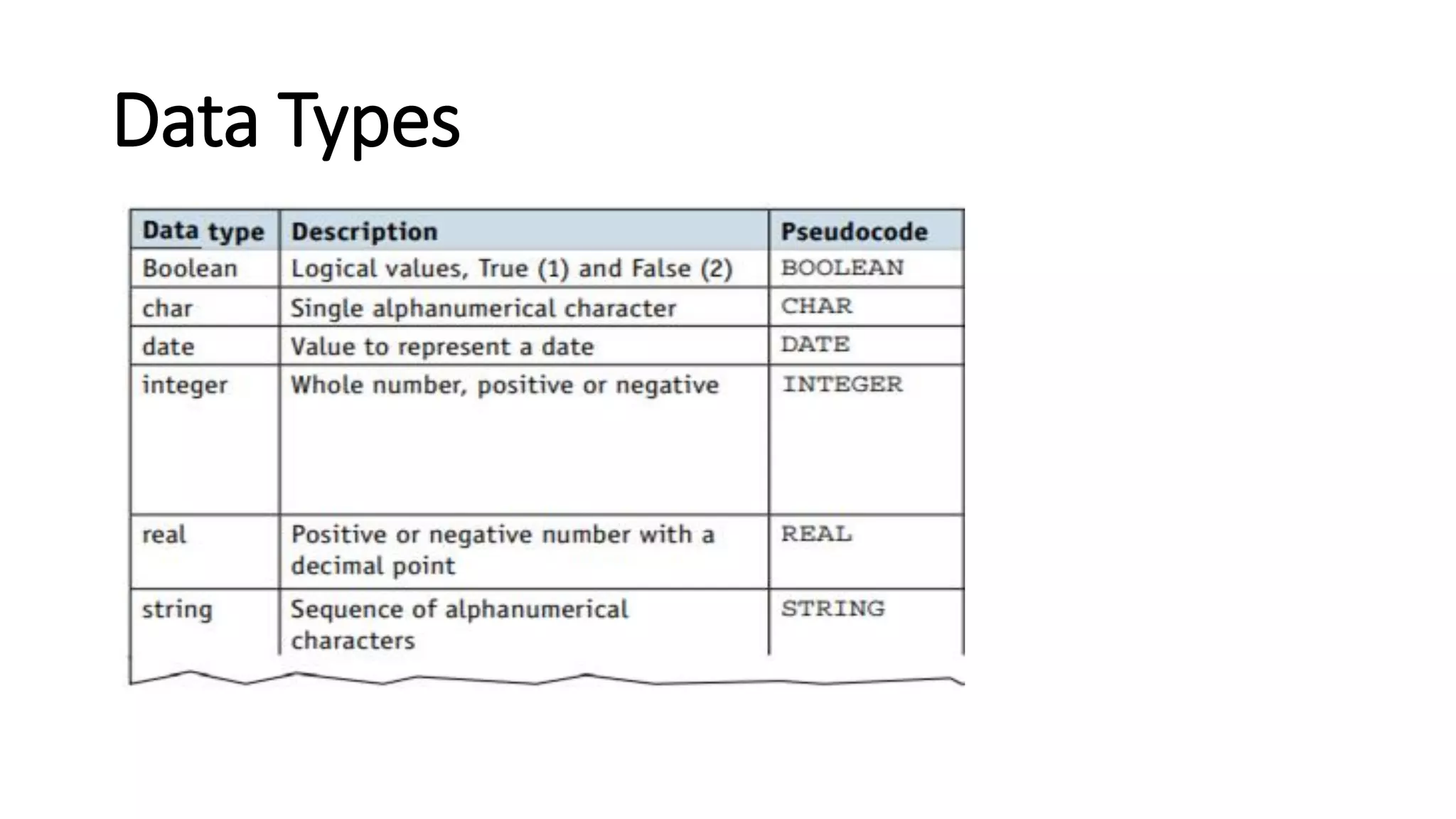
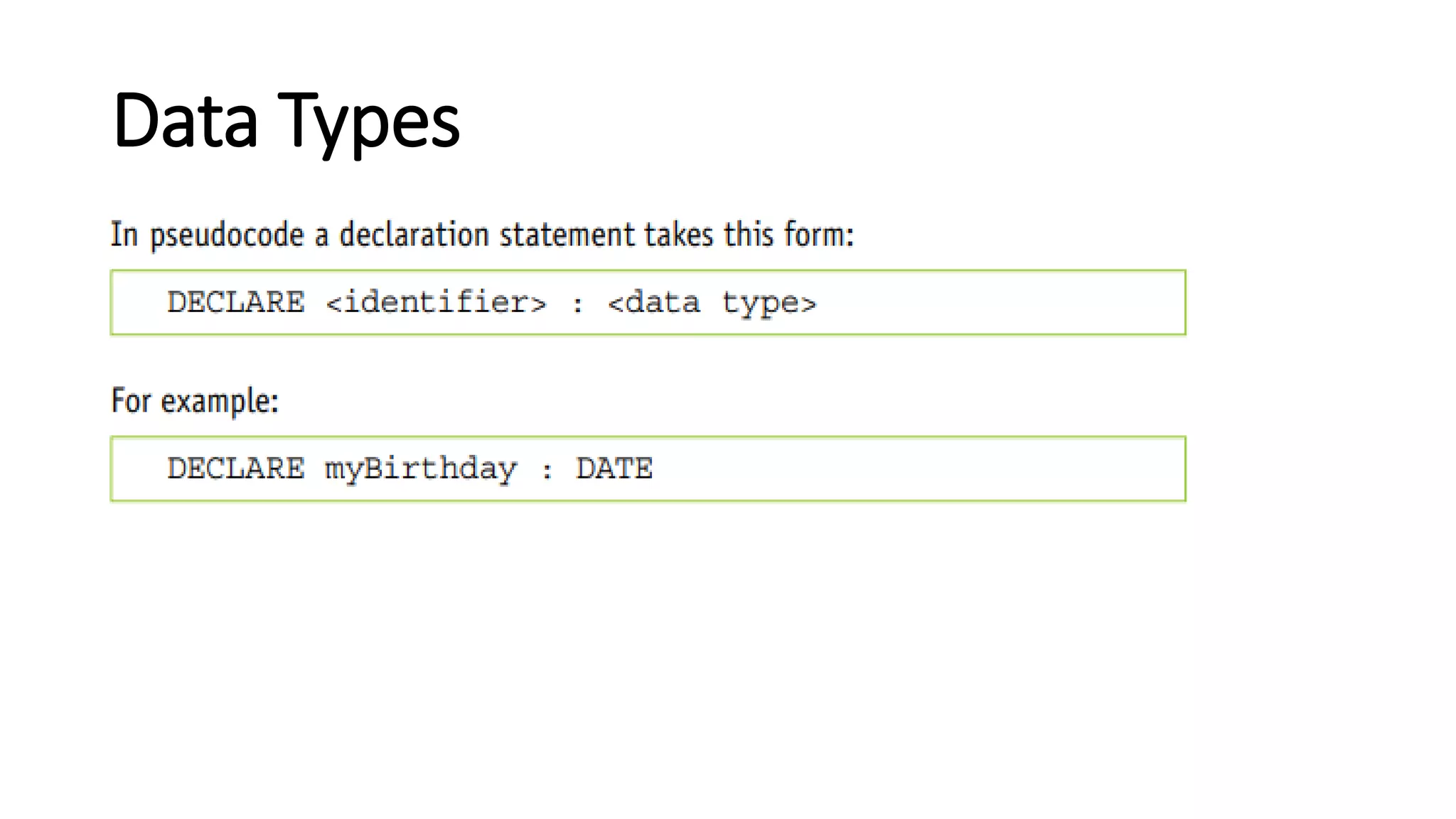
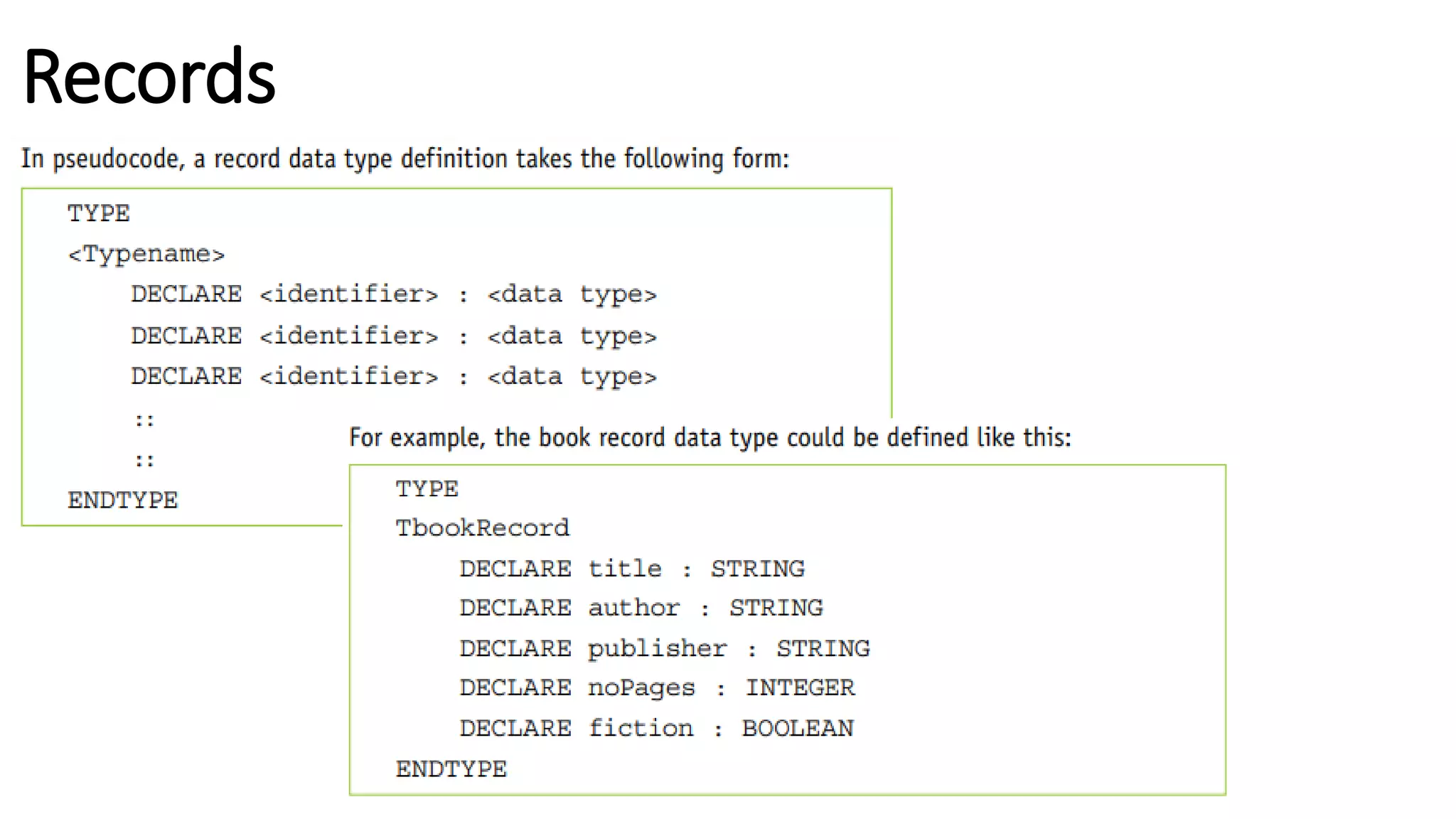
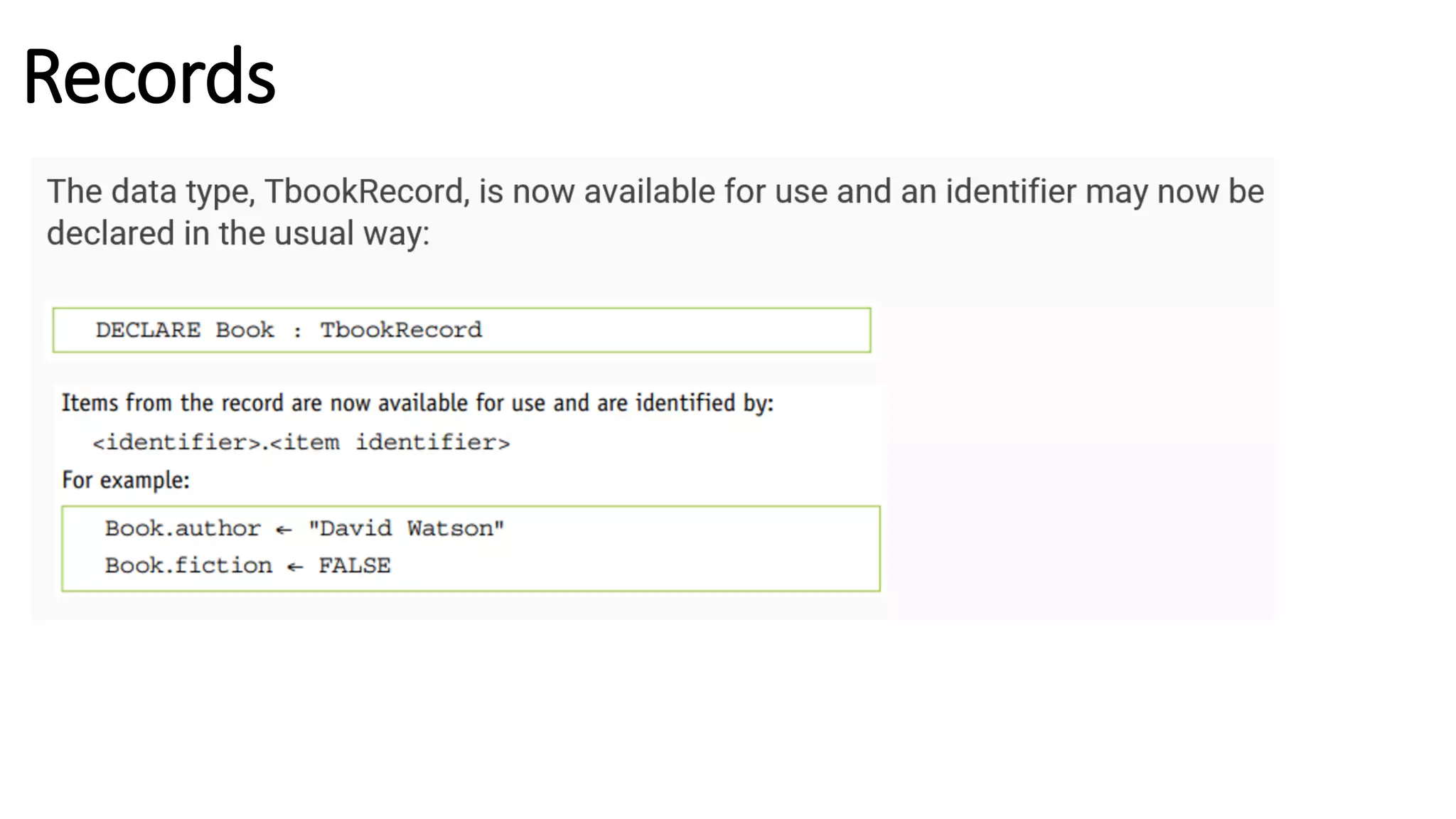
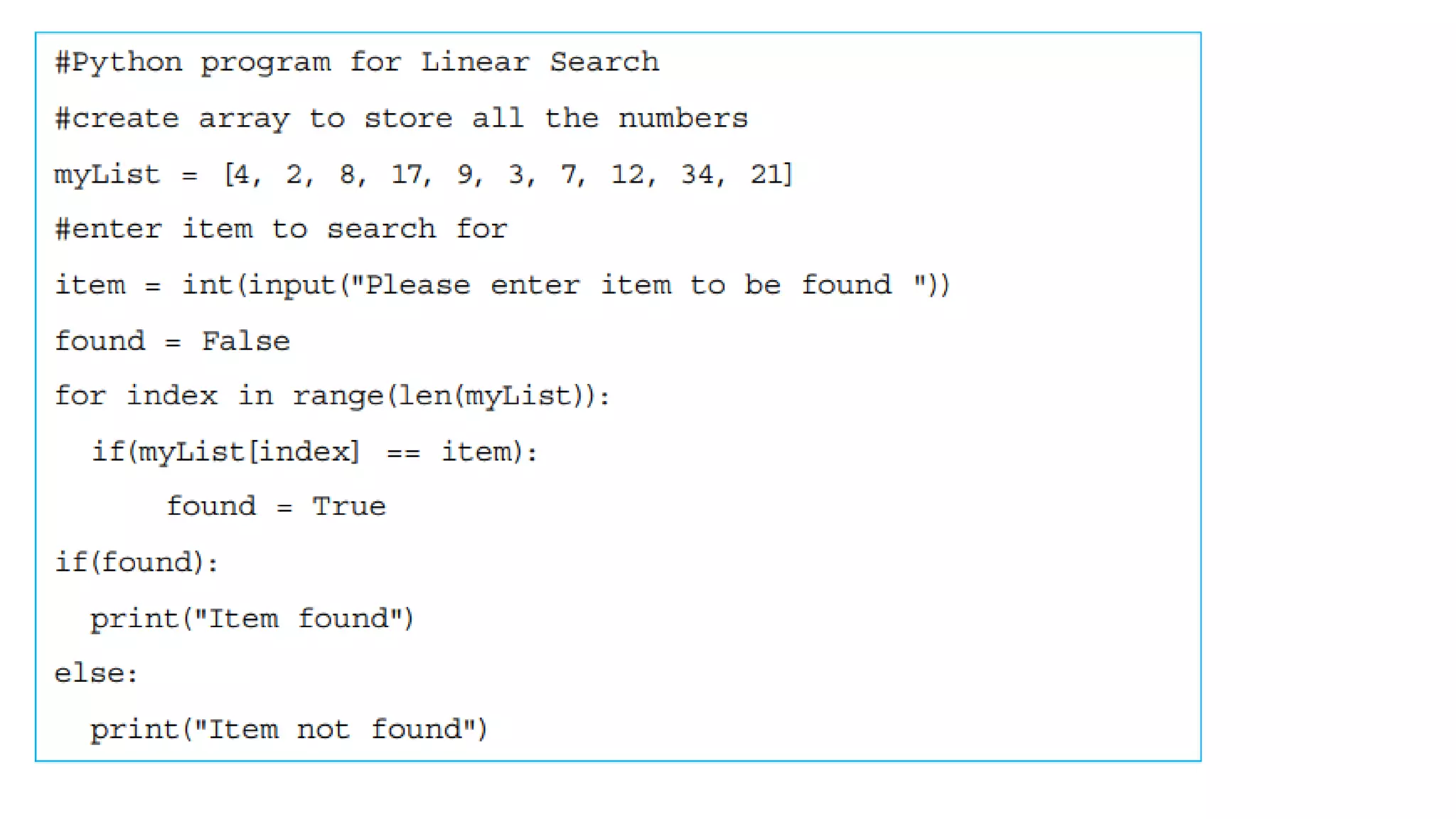
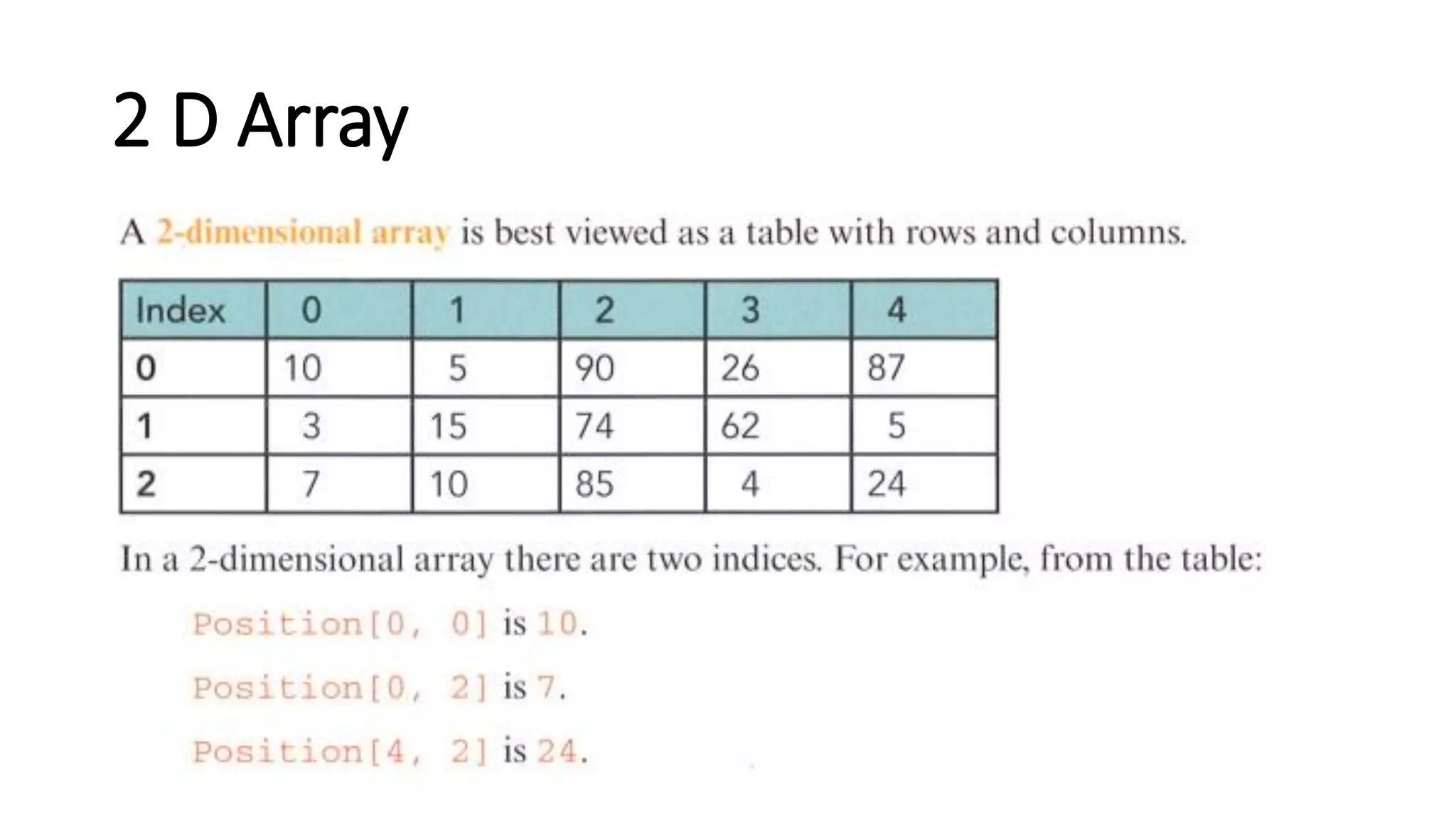
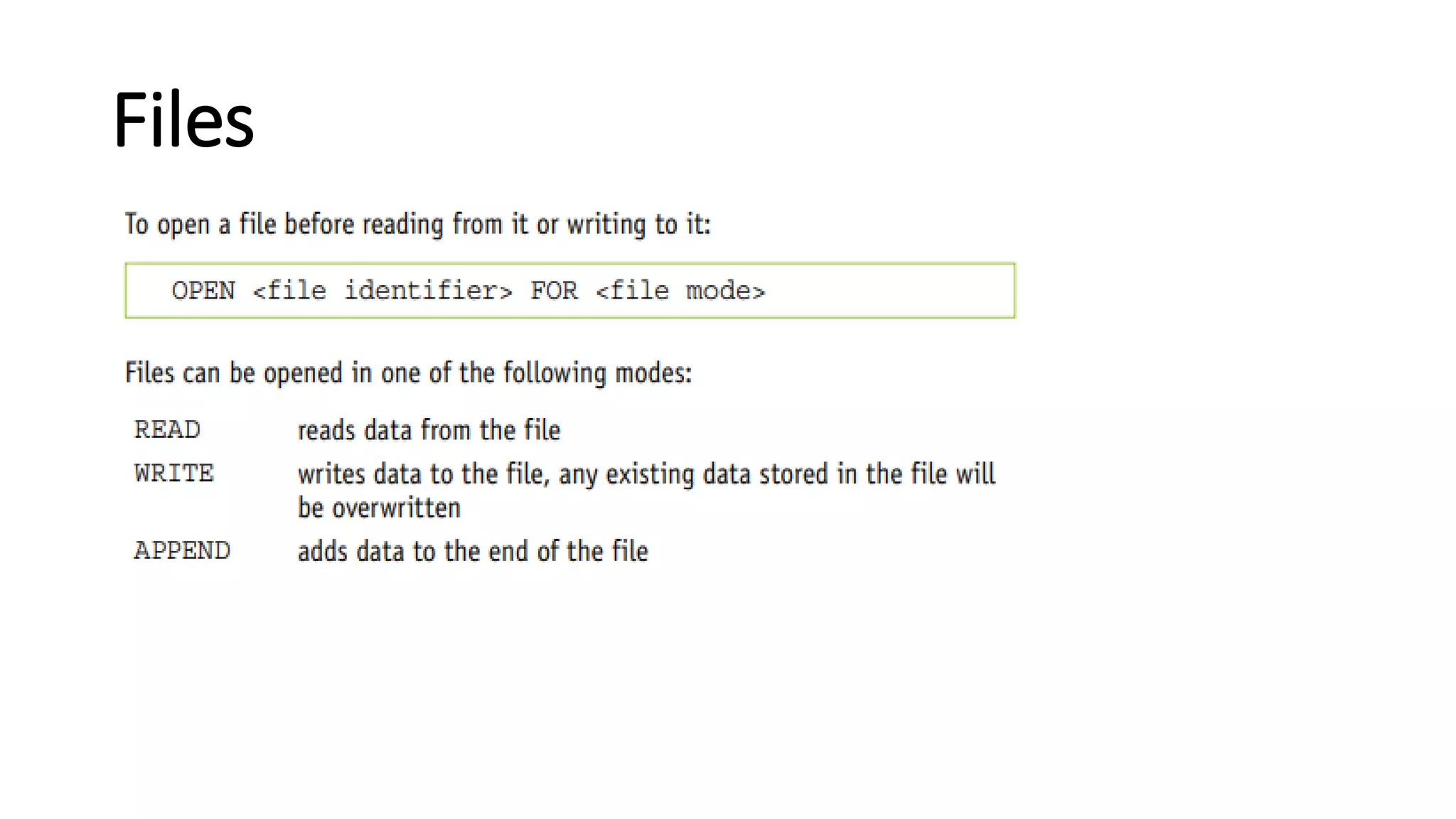
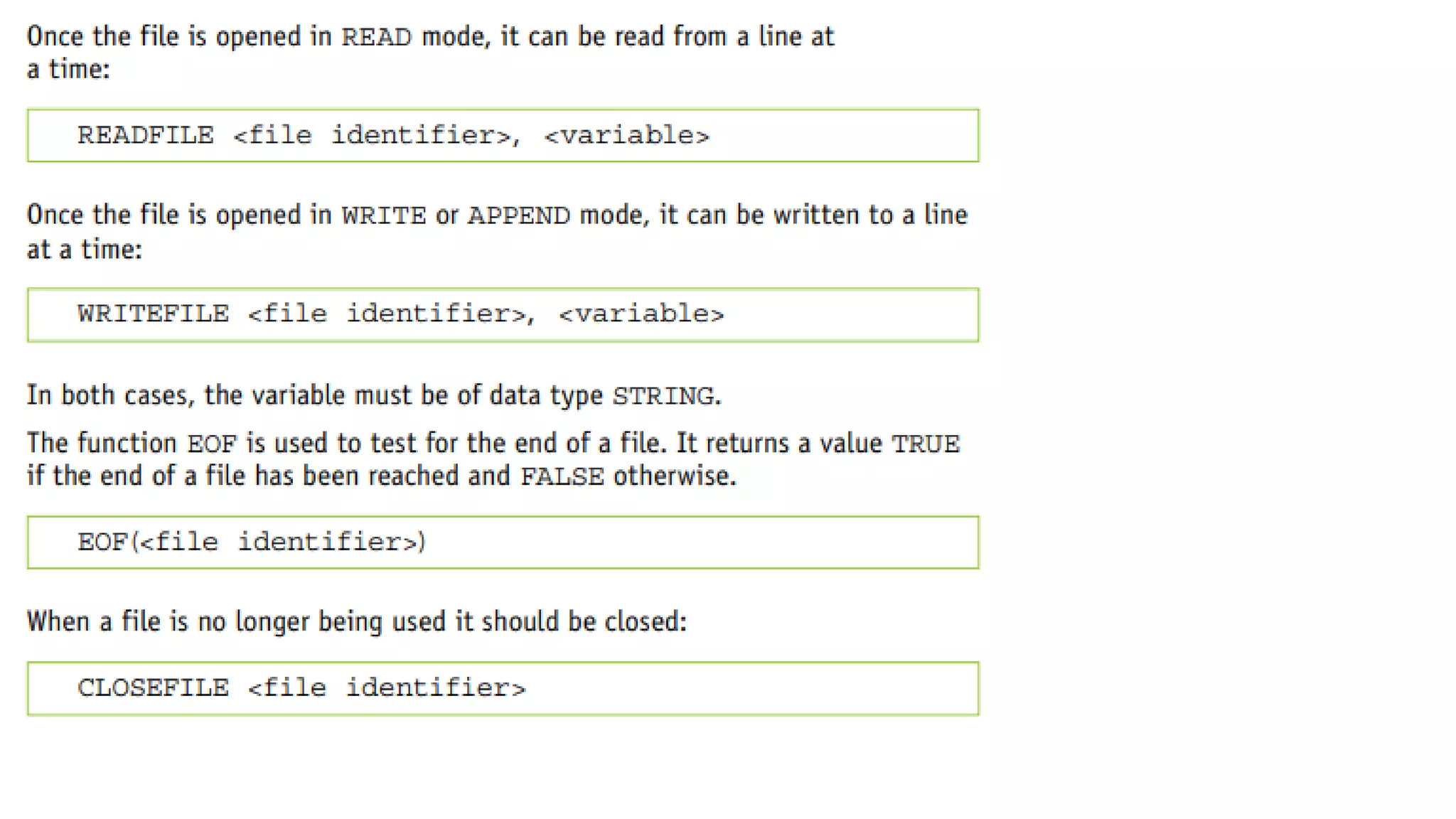
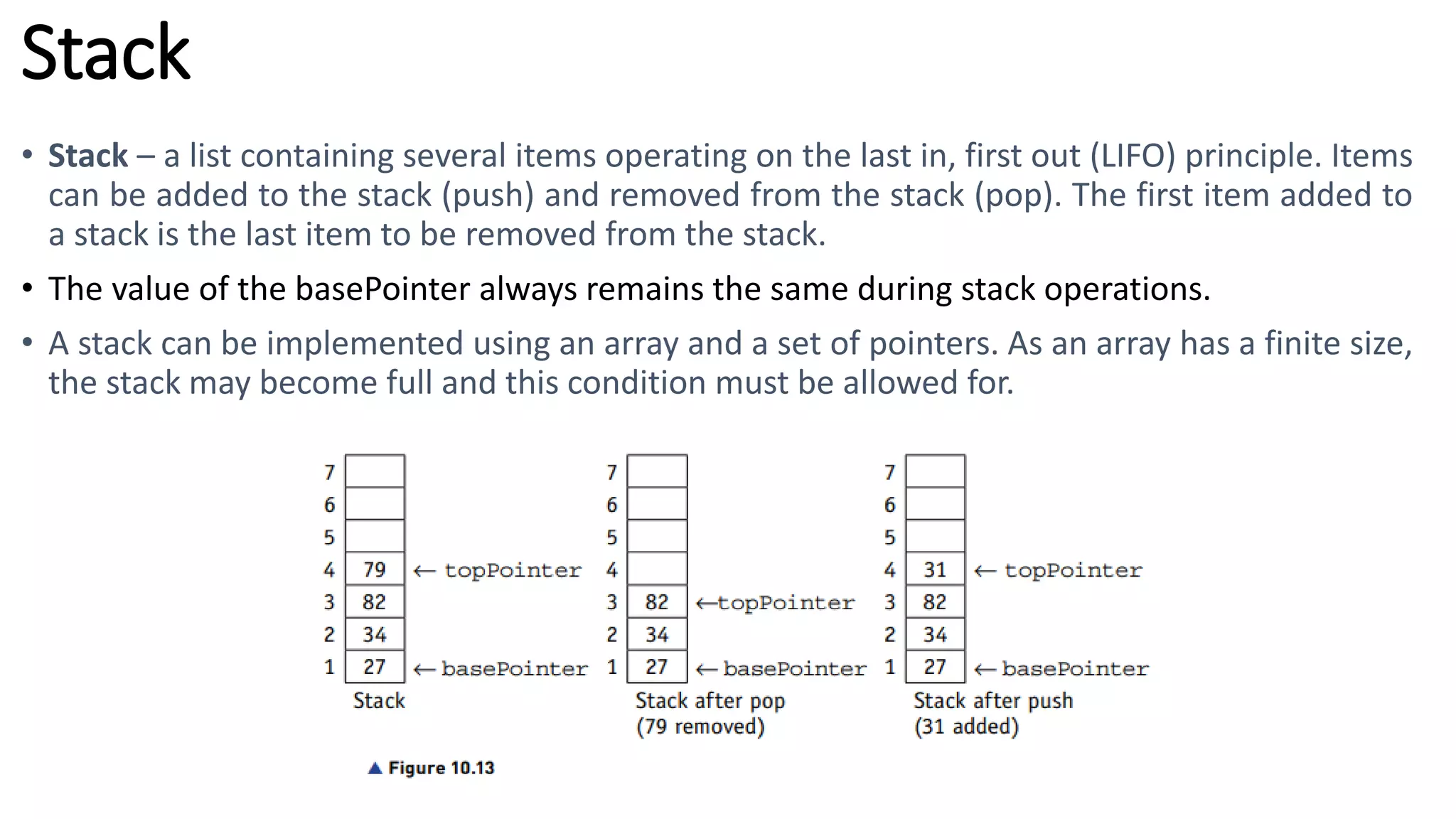
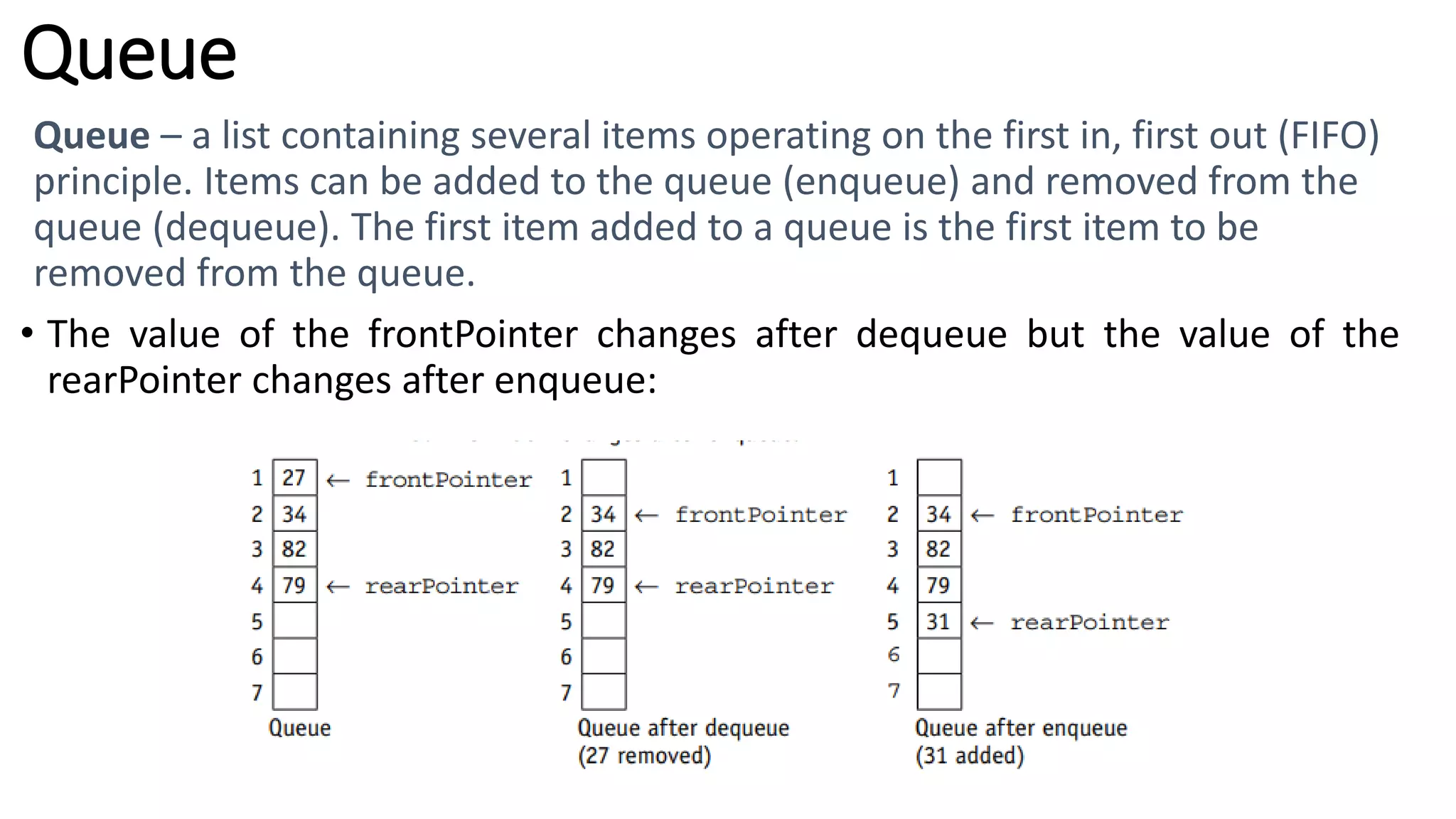
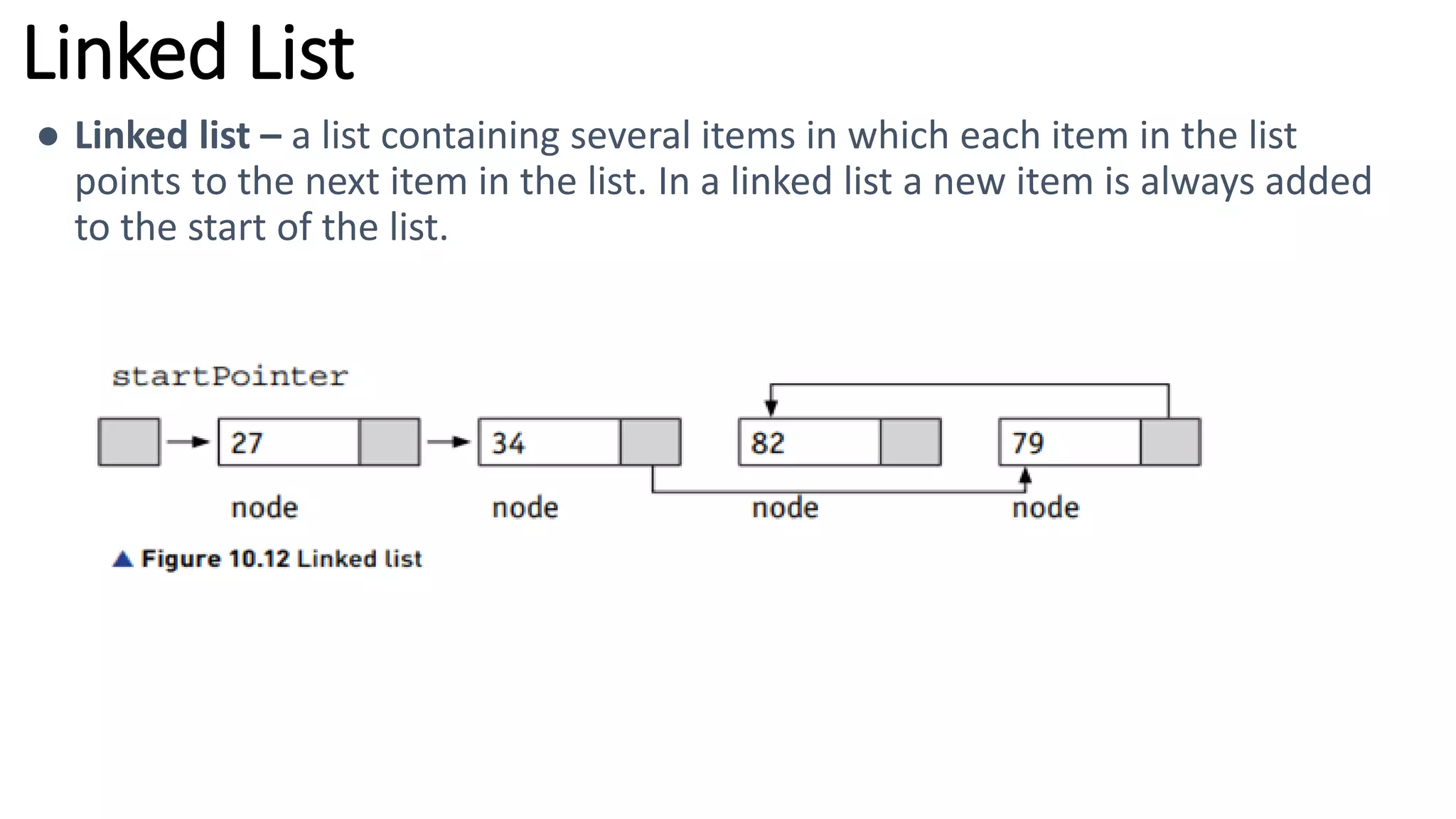
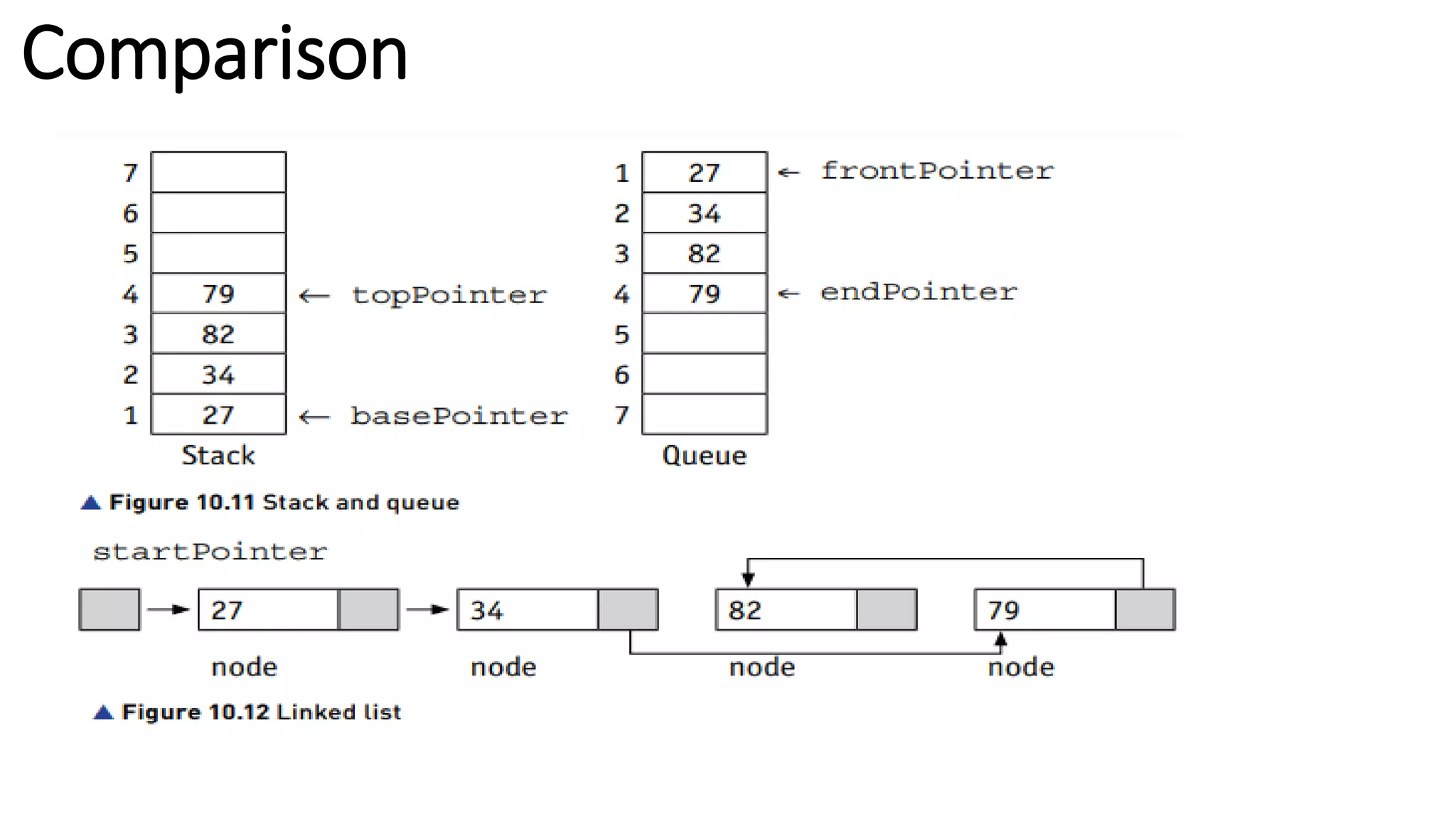
This document provides an overview of various computer science concepts including data types, loops, linear search, bubble sort, 2D arrays, files, stacks, queues, and linked lists. Key algorithms like linear search and bubble sort are explained with examples of pseudocode. Different data structures such as arrays, stacks, queues and linked lists are also introduced along with their core operations.