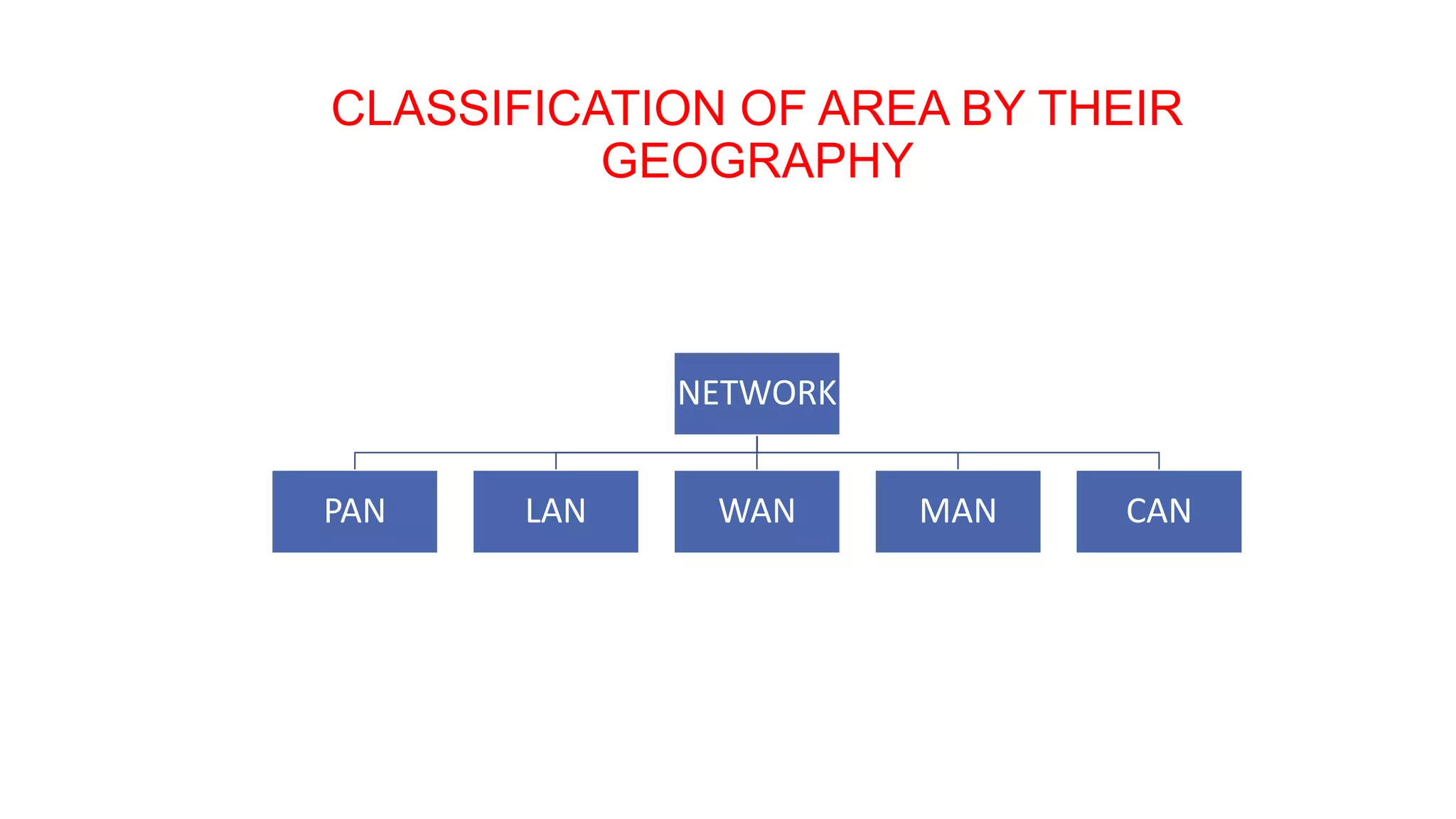
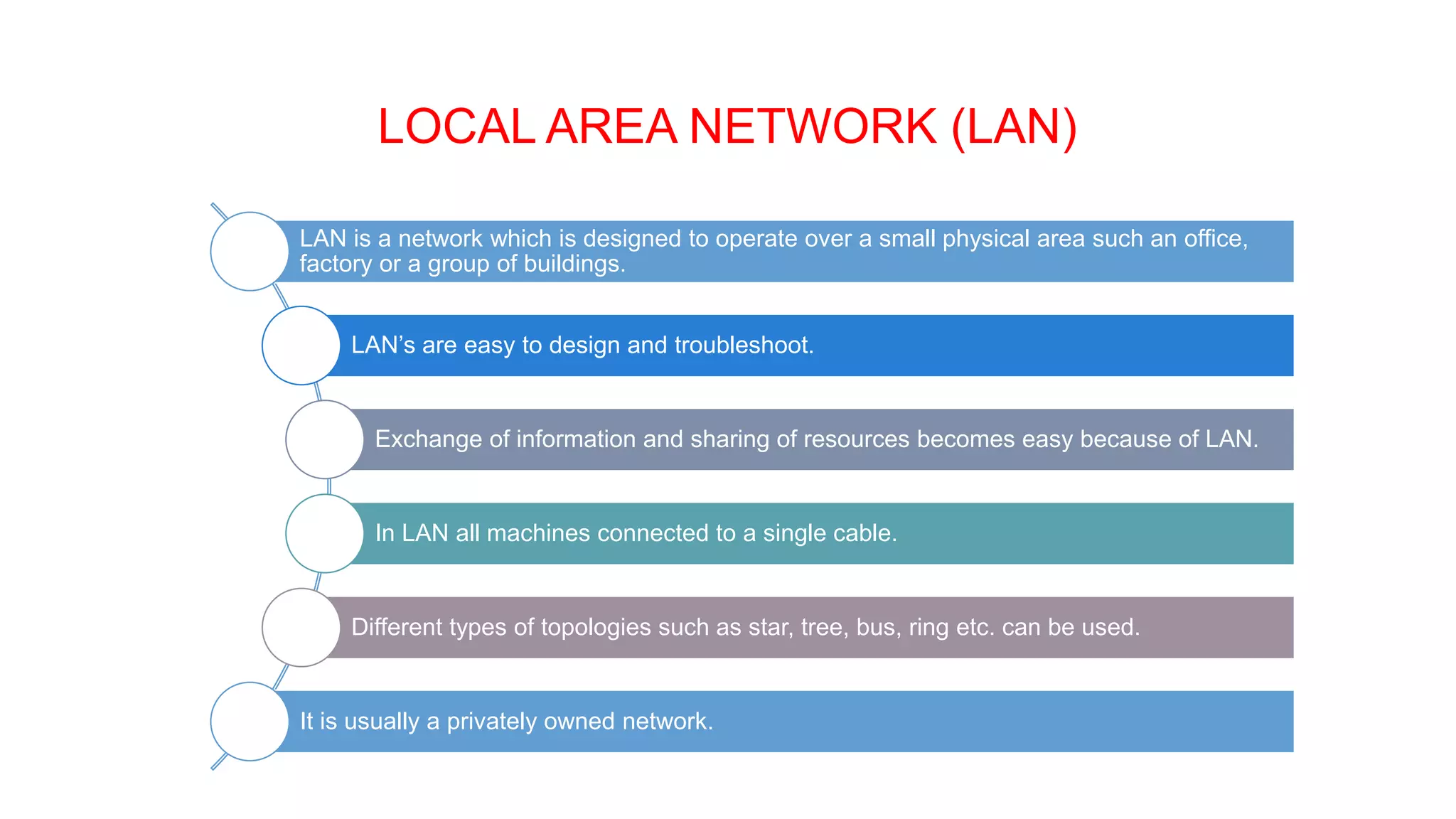
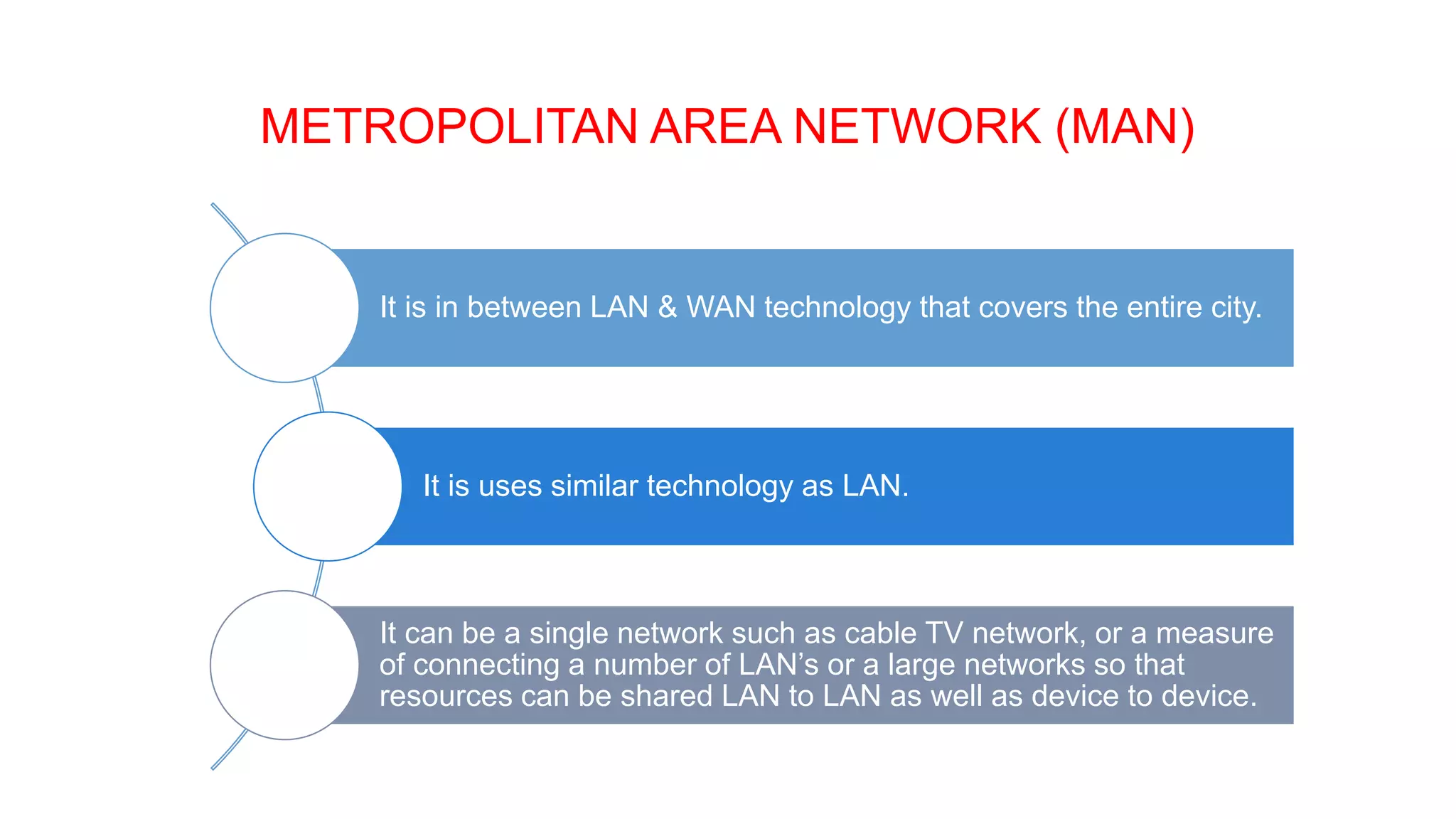
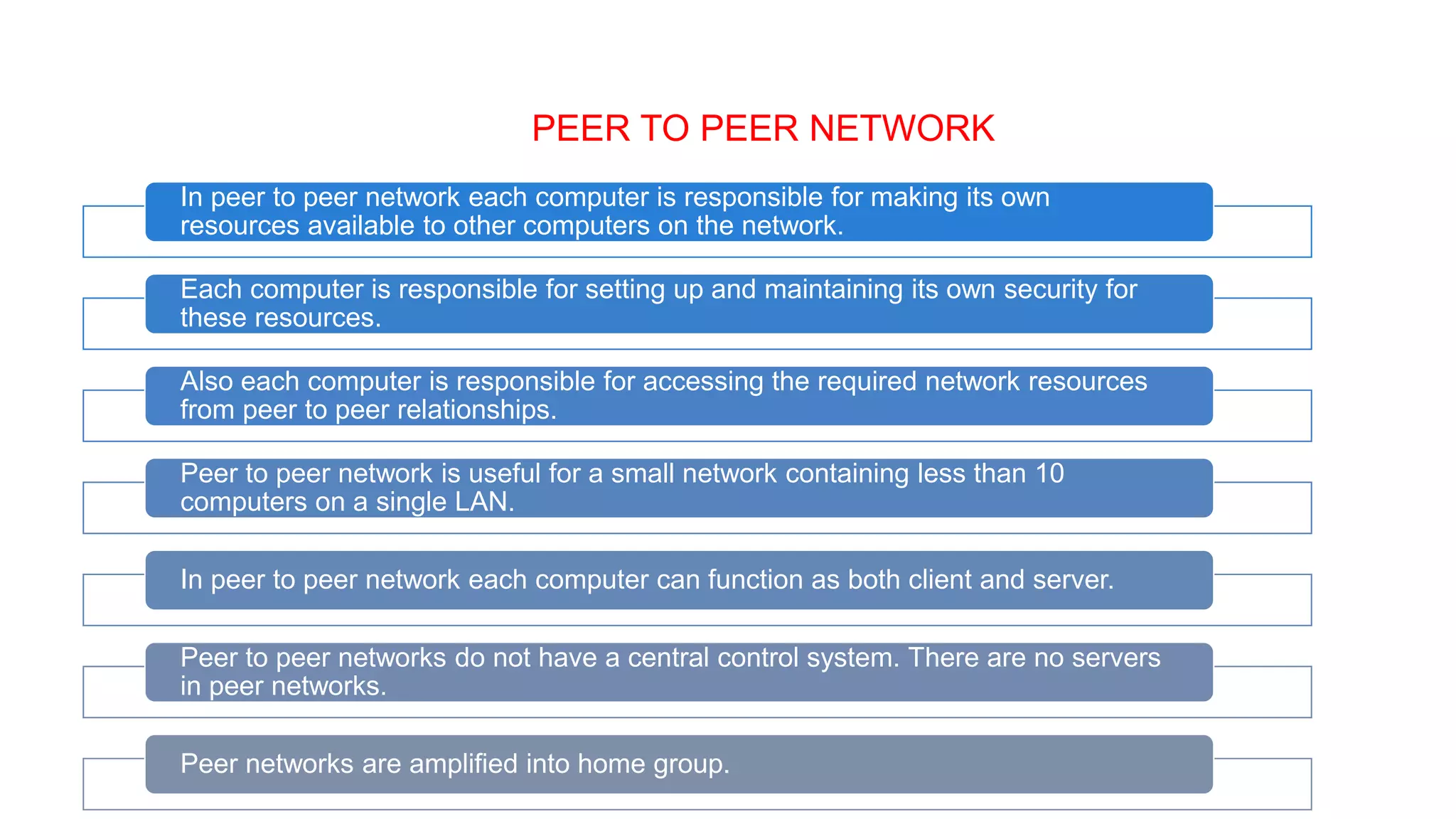
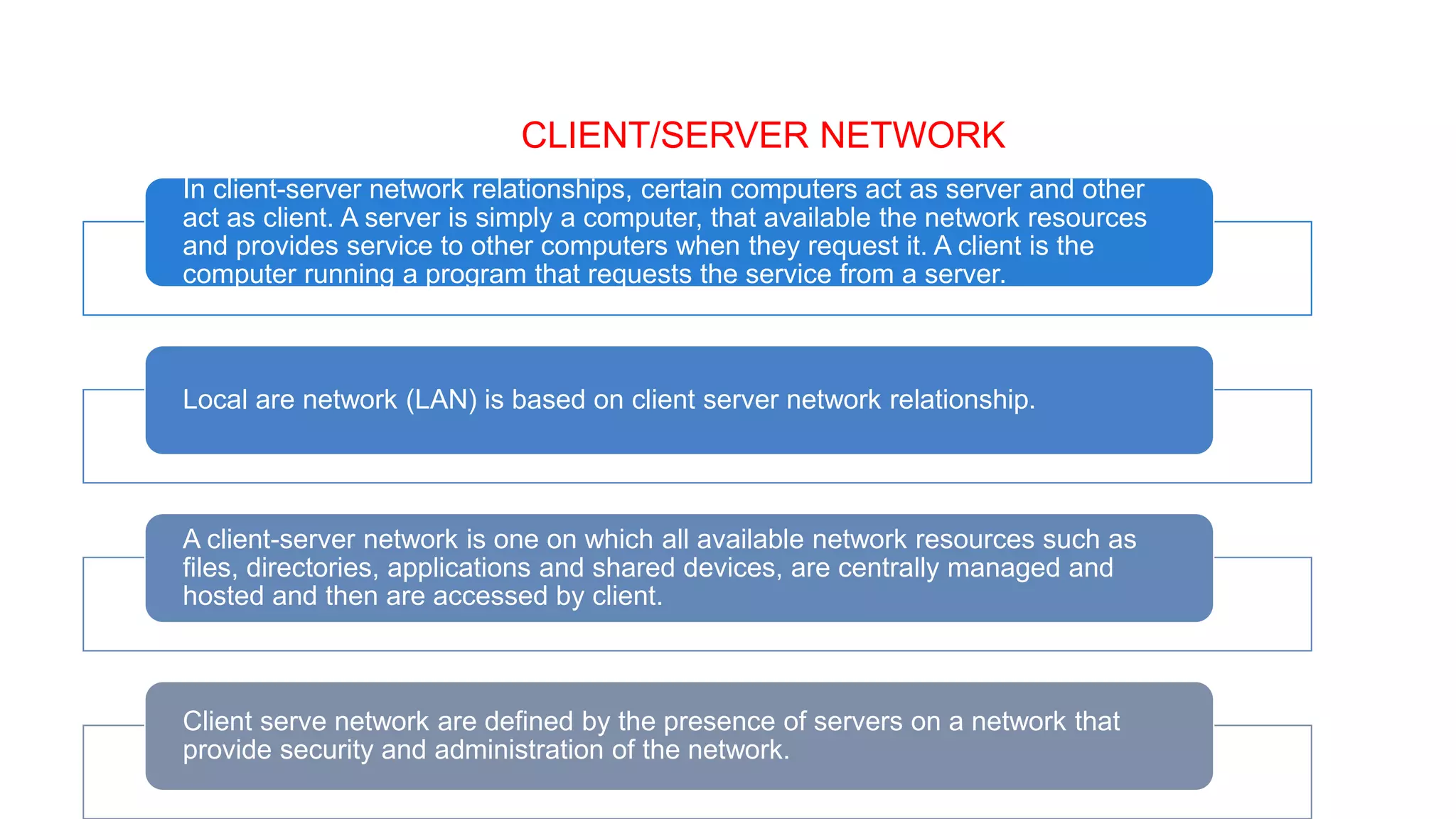
This document provides an overview of computer networks including their definition, components, benefits, disadvantages, classifications by geography and role. It defines a computer network as interconnecting two or more computers to enable communication and sharing of resources. The key components are computers, cables, network cards, switches and operating systems. Networks are classified by their geographic scale such as personal area networks, local area networks, wide area networks, and metropolitan area networks. They can also be classified by their role as either peer-to-peer networks with equal clients and servers, or client-server networks with dedicated server and client computers.