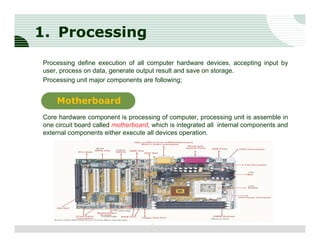
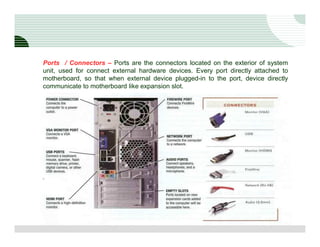
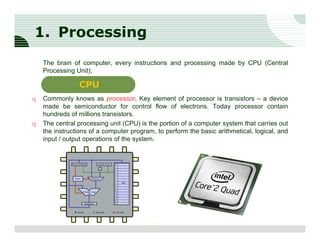
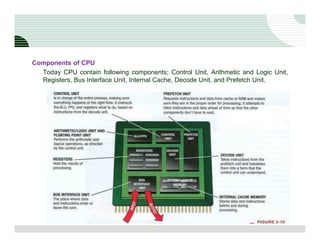
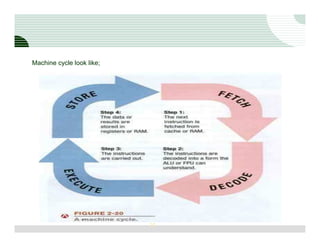
The document discusses the components of a computer hardware system. It is divided into three main sections: processing, storage, and input/output. The processing section focuses on the central processing unit (CPU) and its components. The CPU contains an arithmetic logic unit, control unit, registers, cache memory, and other parts. It executes instructions by performing calculations with data from memory and storage. The motherboard is also described as the main circuit board that connects and allows communication between all the internal computer components.