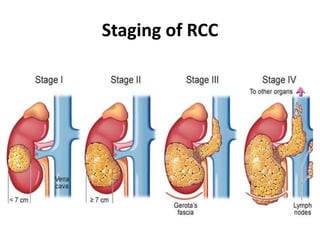
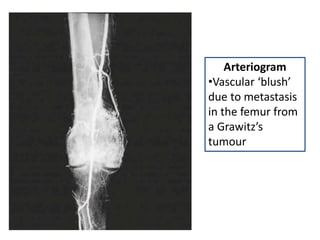
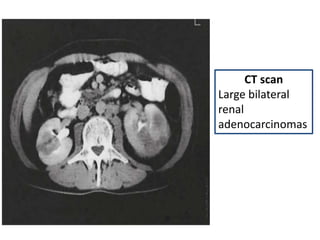
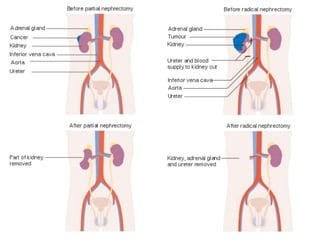
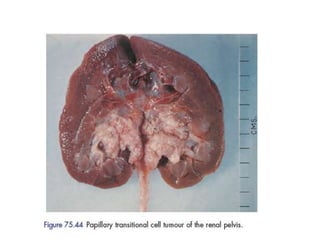
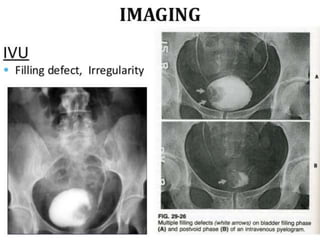
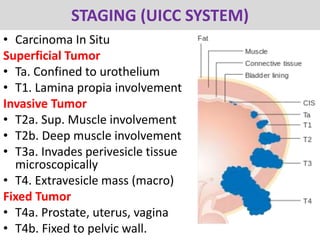
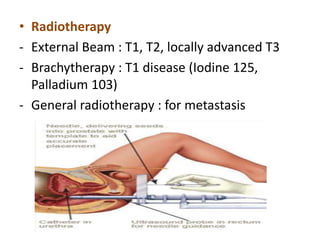
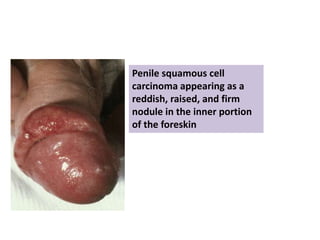
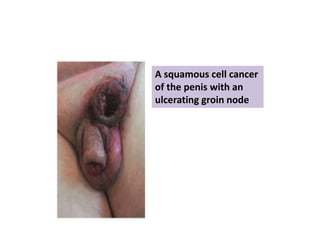
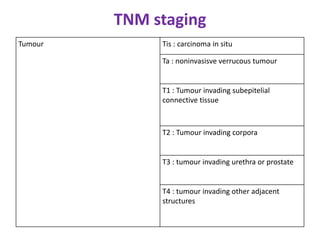
This document provides a comprehensive overview of urologic malignancies, focusing on various types such as renal, bladder, prostate, and penile cancers. It details classifications, clinical features, diagnostic workups, and treatment modalities for each cancer type, highlighting statistical data on incidence, prognosis, and therapeutic approaches including surgery, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy. The document emphasizes the importance of early detection and different staging systems used to assess the extent of these malignancies.