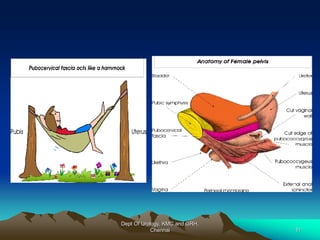
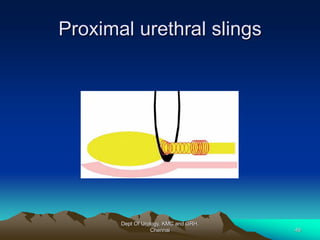
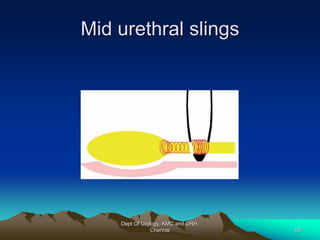
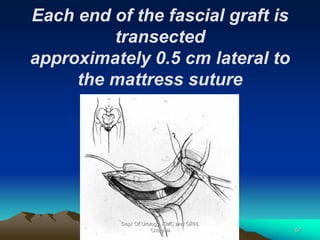
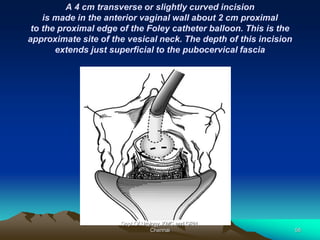
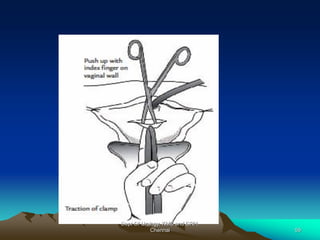
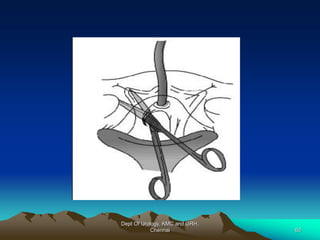
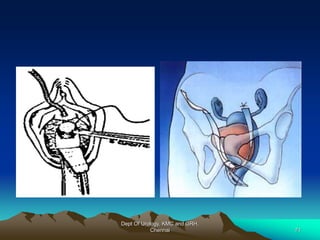
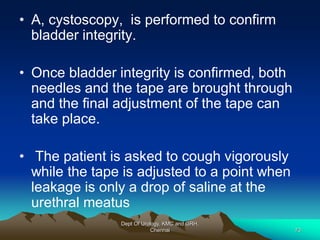
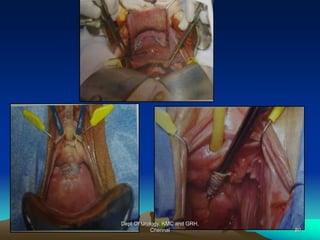
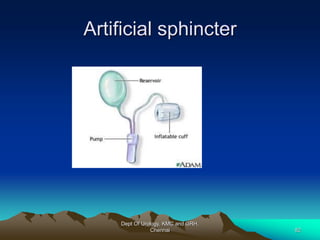
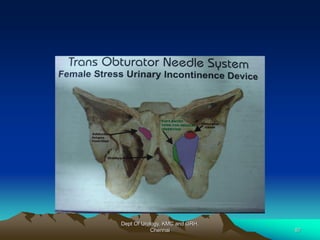
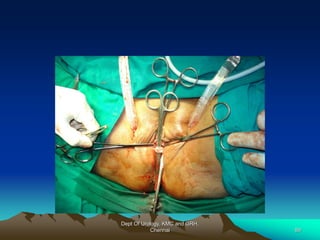
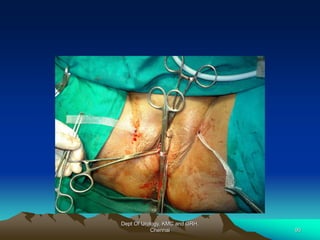
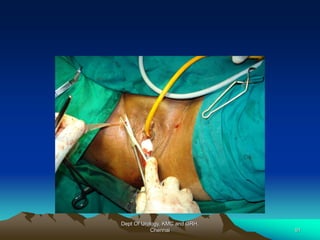
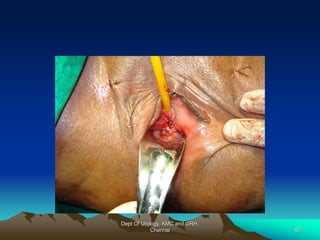
This document provides information about stress urinary incontinence from the Department of Urology at Govt Royapettah Hospital and Kilpauk Medical College in Chennai. It discusses the definition, types, risk factors, investigations including clinical exams, pad tests and urodynamics, and treatments including pelvic floor muscle training, drugs, and surgeries for stress urinary incontinence. The document provides details on conservative treatments like bladder training and surgical treatments depending on the severity of incontinence and bladder neck mobility.