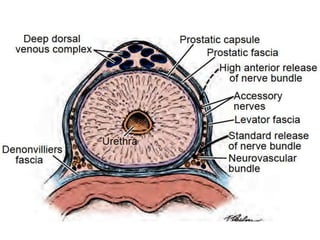
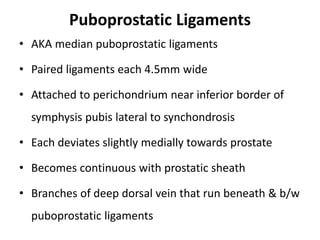
This document summarizes the surgical anatomy of the prostate gland. It describes the prostate's location and relations to surrounding structures like the bladder, urethra, and rectum. It details the prostate's blood supply from branches of the internal iliac artery, innervation from pelvic splanchic and pudendal nerves, and lymphatic drainage routes. The document also outlines important surgical structures like the prostatic capsule, neurovascular bundle, and surrounding fascial planes important for nerve-sparing prostatectomy.