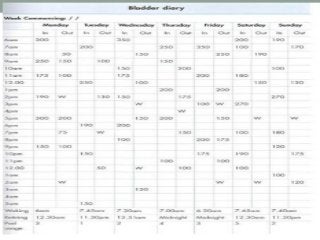
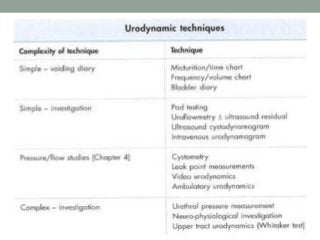
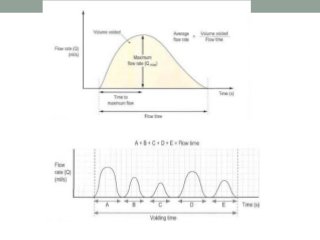
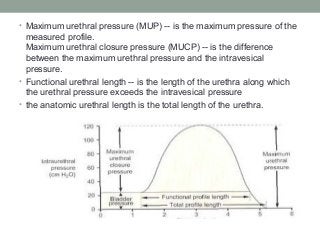
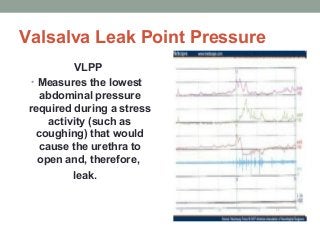
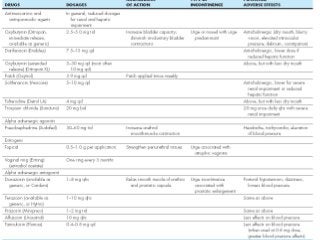
Urinary incontinence is a common condition in older adults that is not a normal part of aging. It can be caused by age-related changes, medical conditions, medications, and environmental factors. There are different types of urinary incontinence including stress, urge, overflow, functional, and mixed incontinence. Evaluation involves taking a history, physical exam, urinalysis, post-void residual measurement, and sometimes urodynamic testing. Management uses a stepped approach starting with conservative treatments like lifestyle changes, pelvic floor exercises, and behavioral therapy. If conservative treatments are ineffective, pharmacologic therapy and sometimes surgical options may be used.