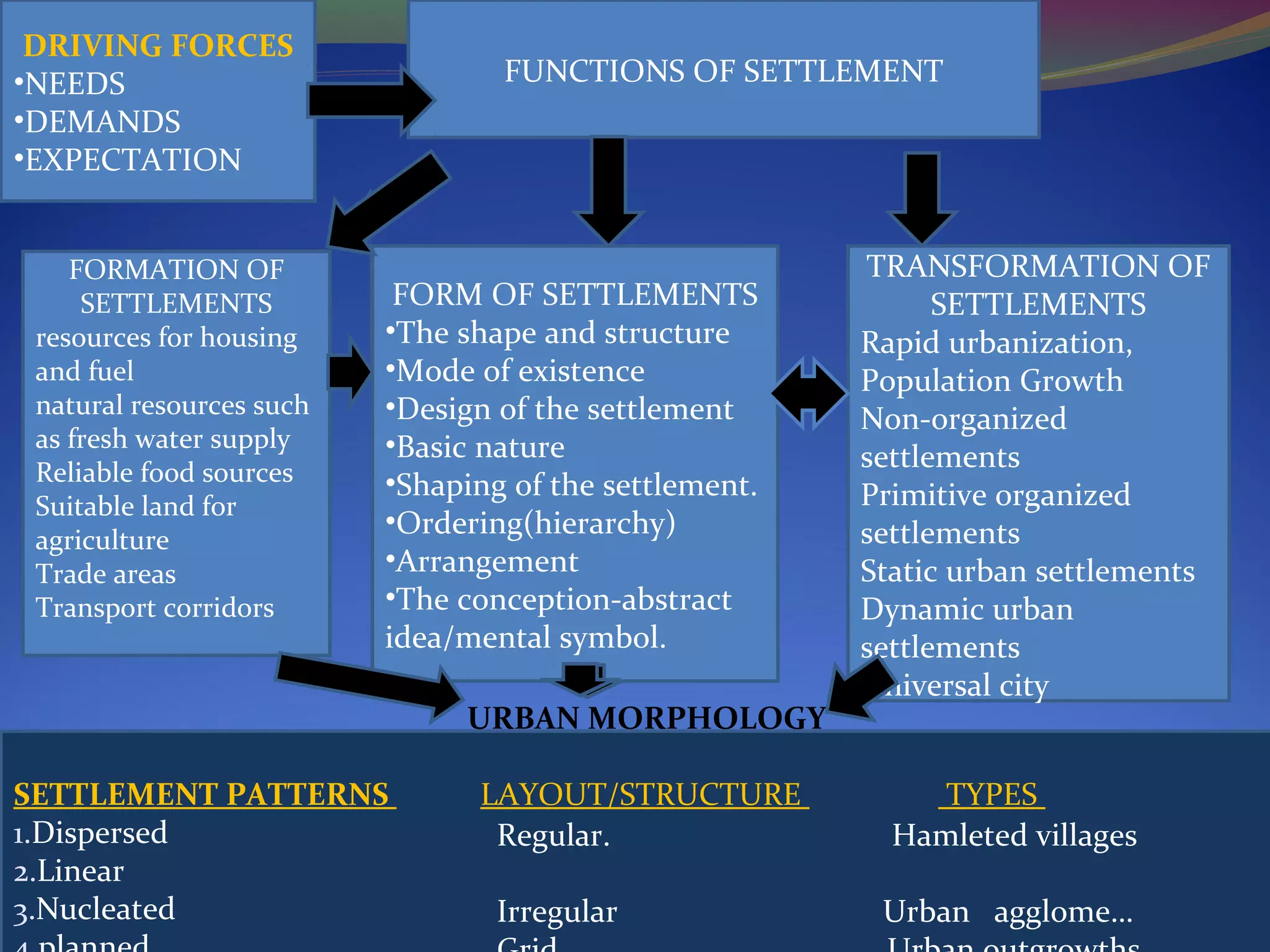
This document discusses the concepts and objectives of urban morphology. Urban morphology is defined as the study of the physical form and development of human settlements. It examines the shape and structure of settlements as well as their transformation over time under various forces. The document outlines different types of settlement patterns, forms, and structures. It also discusses the determinants that influence a settlement's morphology, including physical, functional, social, cultural, economic, and political factors. The objectives of urban morphology include improving comfort, accessibility, diversity and other qualities of urban form.