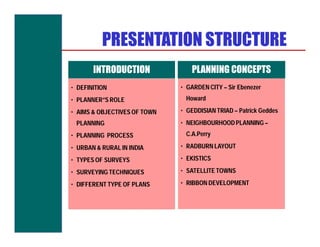
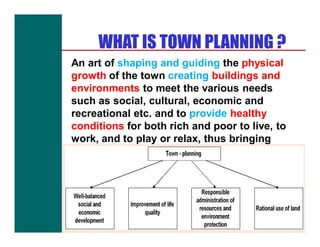
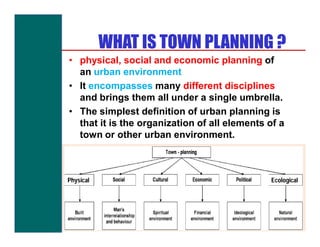
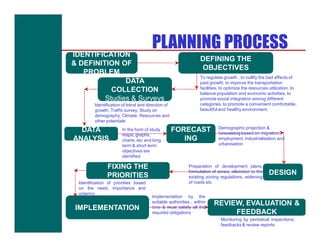
The document discusses various topics related to town planning and planning concepts including:
- Definitions of town planning and the role of planners
- The planning process including identification of problems, data collection/analysis, forecasting, implementation, and review
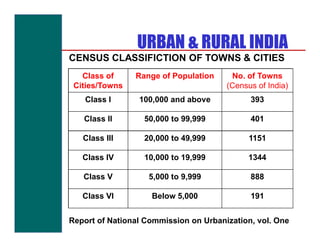
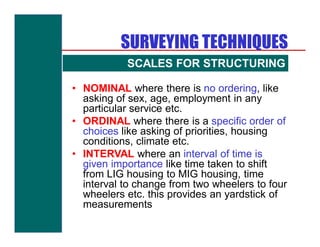
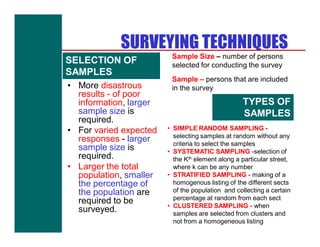
- Types of surveys including regional, town, land use, density, and traffic surveys
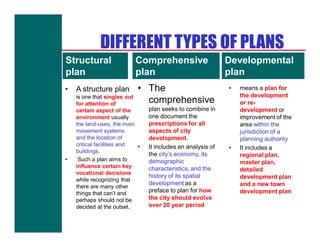
- Different types of plans including structural, comprehensive, and developmental plans