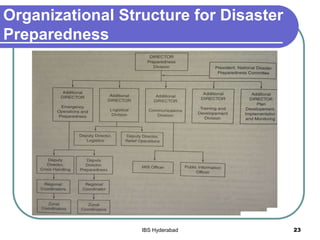
The document discusses key aspects of disaster preparedness including the three A's of aim, action and accountability. It outlines the principles, steps, and organizational structure for effective preparedness. Contingency planning and building team relations are identified as important. Training needs analysis and emergency operational plans with defined contents are also covered as critical preparedness elements. Examples from past cyclones in Orissa, India are reviewed to highlight lessons learned.