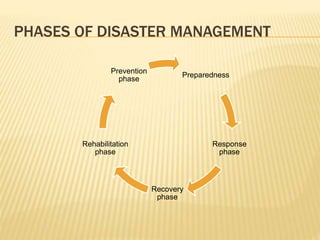
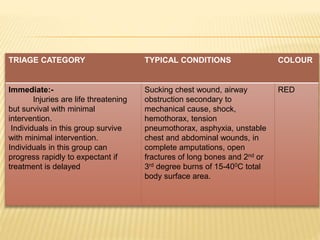
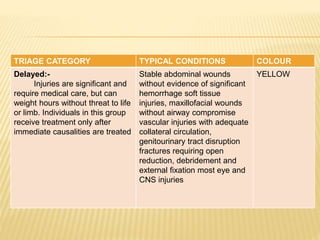
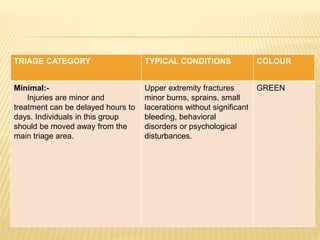
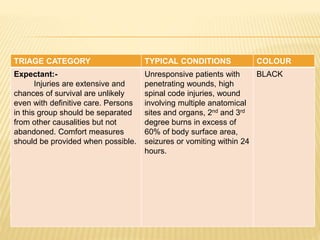
Disasters can be natural, man-made, or hybrid. They cause disruption and harm to communities. Disaster management involves preparing for, responding to, and recovering from disasters. Key aspects include defining disaster levels; triaging casualties into red, yellow, green, and black categories; and having disaster plans, committees, and rapid response teams in place at the community level. The nurse's role includes assessing disaster risks and threats, planning and practicing disaster response, and evaluating effectiveness. International agencies provide humanitarian assistance during disasters.