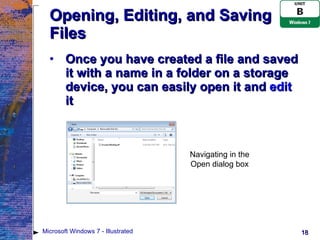
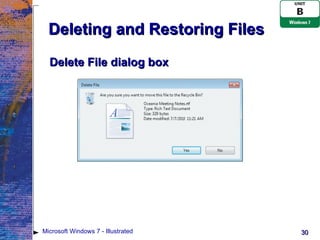
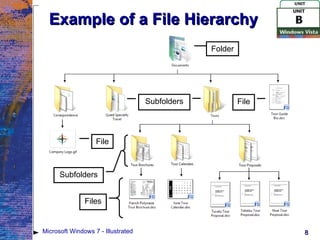
The document provides an overview of file management tasks in Microsoft Windows 7 such as understanding folders and files, creating and saving files, exploring files and folders, opening and editing files, copying and moving files, searching for files, and deleting and restoring files. It explains concepts like file hierarchies, libraries, drives, file extensions, and gives instructions for common file operations like saving, copying, searching, and deleting.









![Drive Names and Drive Icons Microsoft Windows 7 - Illustrated Drive Type Drive Icon Friendly Name Drive Name Called Hard Disk Drive Local Disk C: Drive C CD Drive CD-RW Drive, CD-R Drive, or CD-ROM Drive Next available drive letter, for example, D: Drive D DVD Drive DVD-RW Drive, DVD-R Drive, or DVD-ROM Drive Next available drive letter, for example, E: Drive E USB Flash Drive [varies] Next available drive letter, for example, F: Drive F](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitb-100813024758-phpapp01/85/Unit-B-Windows-7-16-320.jpg)