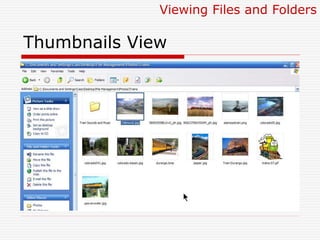
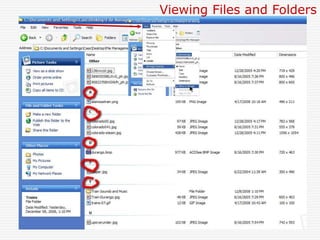
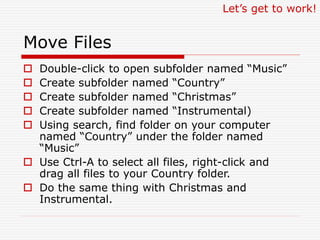
This document provides an overview of file management and how to organize files on a computer. It defines key concepts like files, folders, subfolders and file extensions. It explains the basics of file management including why it's important to organize files and how to do so using Windows Explorer. It also covers viewing files and folders in different modes like icons, list and details. The document teaches how to copy, move and delete files as well as create new folders using drag and drop or the file menu options.