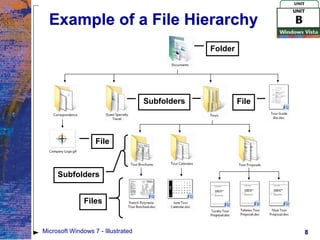
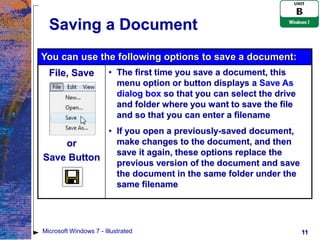
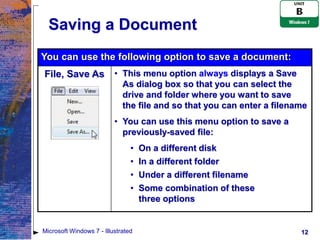
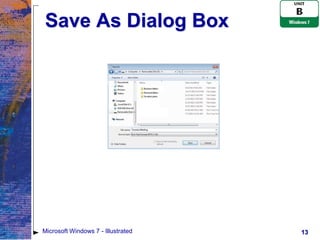
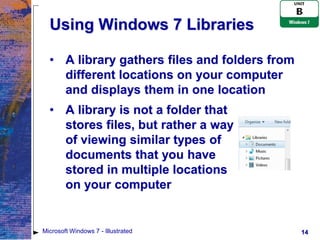
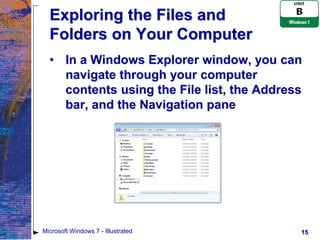
The document provides an overview of file management tasks in Microsoft Windows 7, including understanding folders and files, creating and saving files, exploring files and folders, opening and editing files, copying and moving files, searching for files, and deleting and restoring files. Key points covered include using folders to organize files, saving files for the first time or overwriting existing files, navigating drives and libraries to find files, and using the Recycle Bin to restore accidentally deleted files.









![Drive Names and Drive Icons
Drive
Drive Icon Friendly Name Drive Name Called
Type
Hard Local Disk C: Drive C
Disk
Drive
CD Drive CD-RW Drive, Next available Drive D
CD-R Drive, or drive letter,
CD-ROM Drive for example, D:
DVD DVD-RW Drive, Next available Drive E
Drive DVD-R Drive, or drive letter,
DVD-ROM Drive for example, E:
USB [varies] Next available Drive F
Flash drive letter,
Drive for example, F:
Microsoft Windows 7 - Illustrated 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/windows7unitb-121212105342-phpapp02/85/Windows-7-Unit-B-PPT-16-320.jpg)