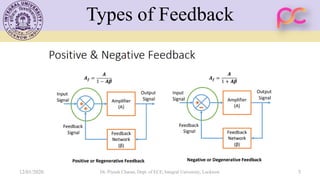
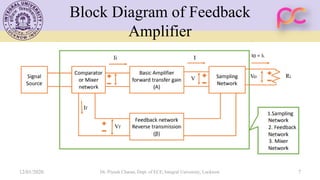
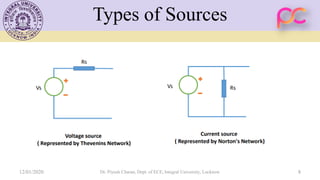
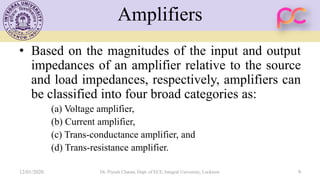
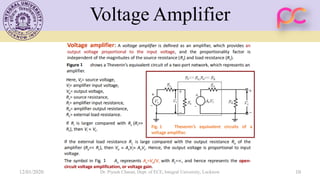
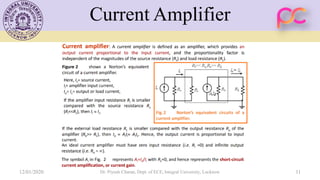
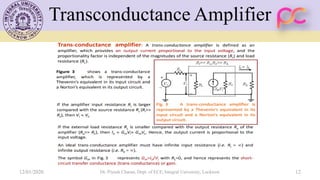
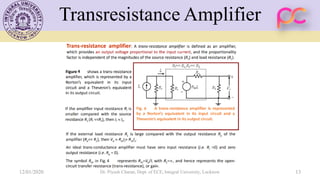
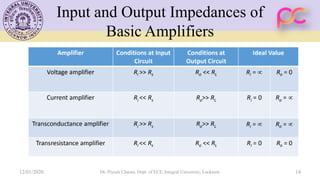
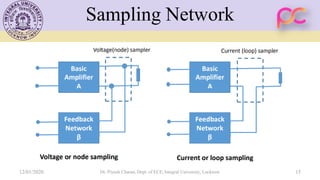
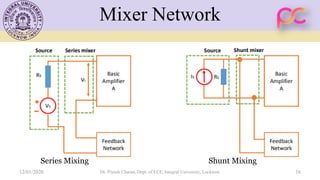
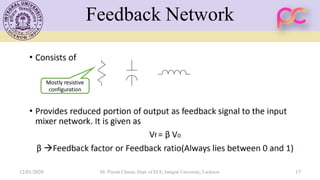
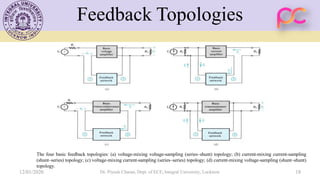
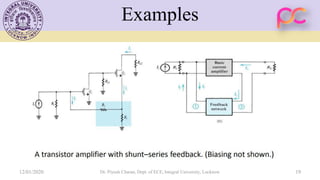
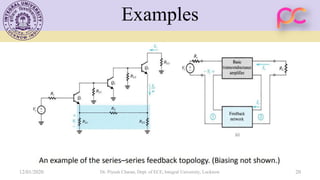
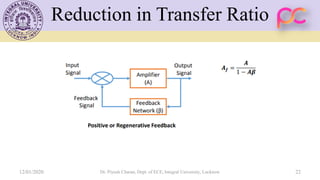
This document provides lecture notes on feedback amplifiers and their types. It discusses the basic concept of feedback, classification of feedback, voltage/current shunt and series feedback, and stability of feedback amplifiers. The document describes how negative feedback affects amplifier characteristics by reducing gain, increasing input resistance and bandwidth, and decreasing noise and distortion. It also defines different types of amplifiers including voltage, current, transconductance, and transresistance amplifiers, and discusses various feedback topologies.