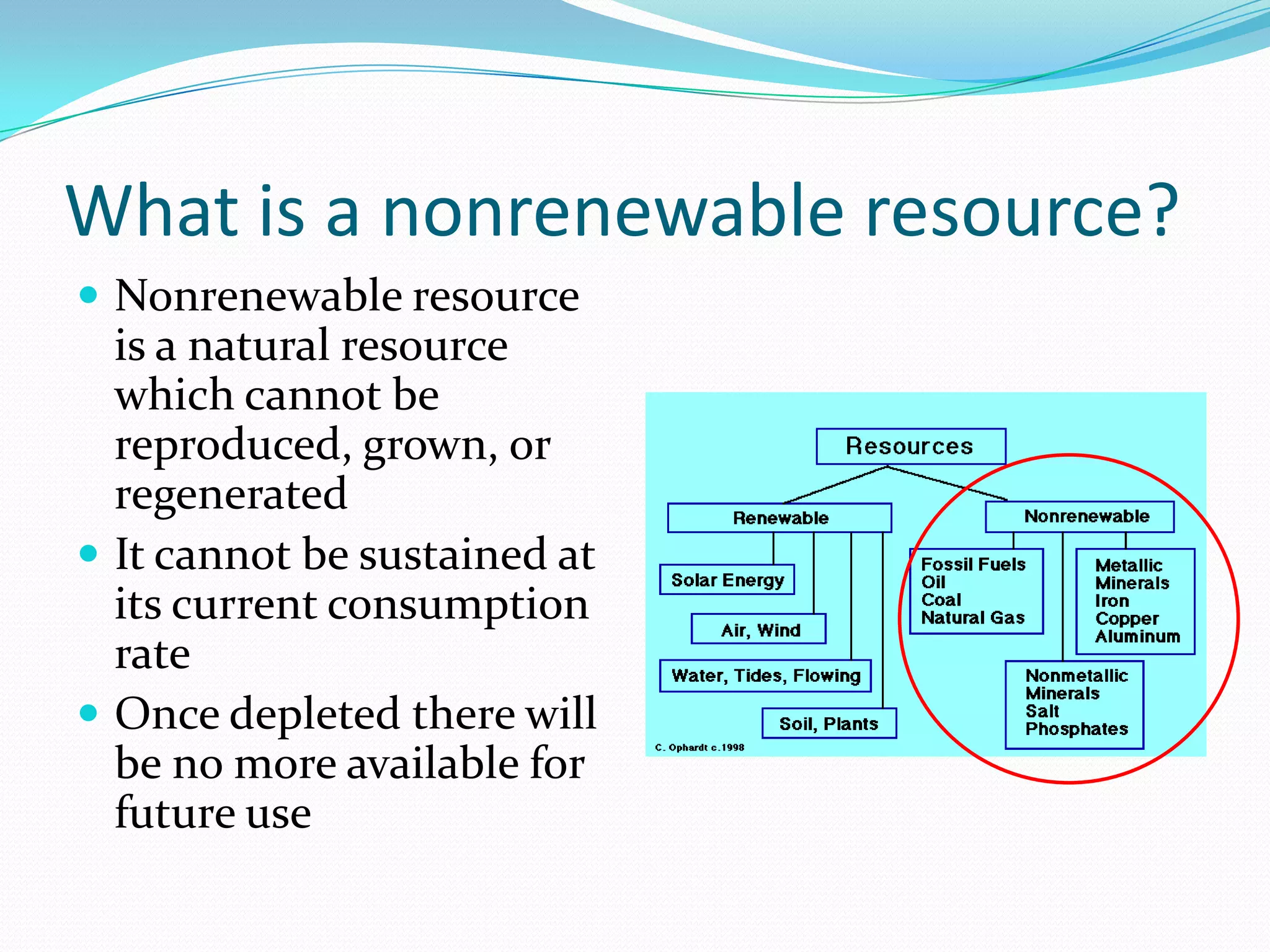
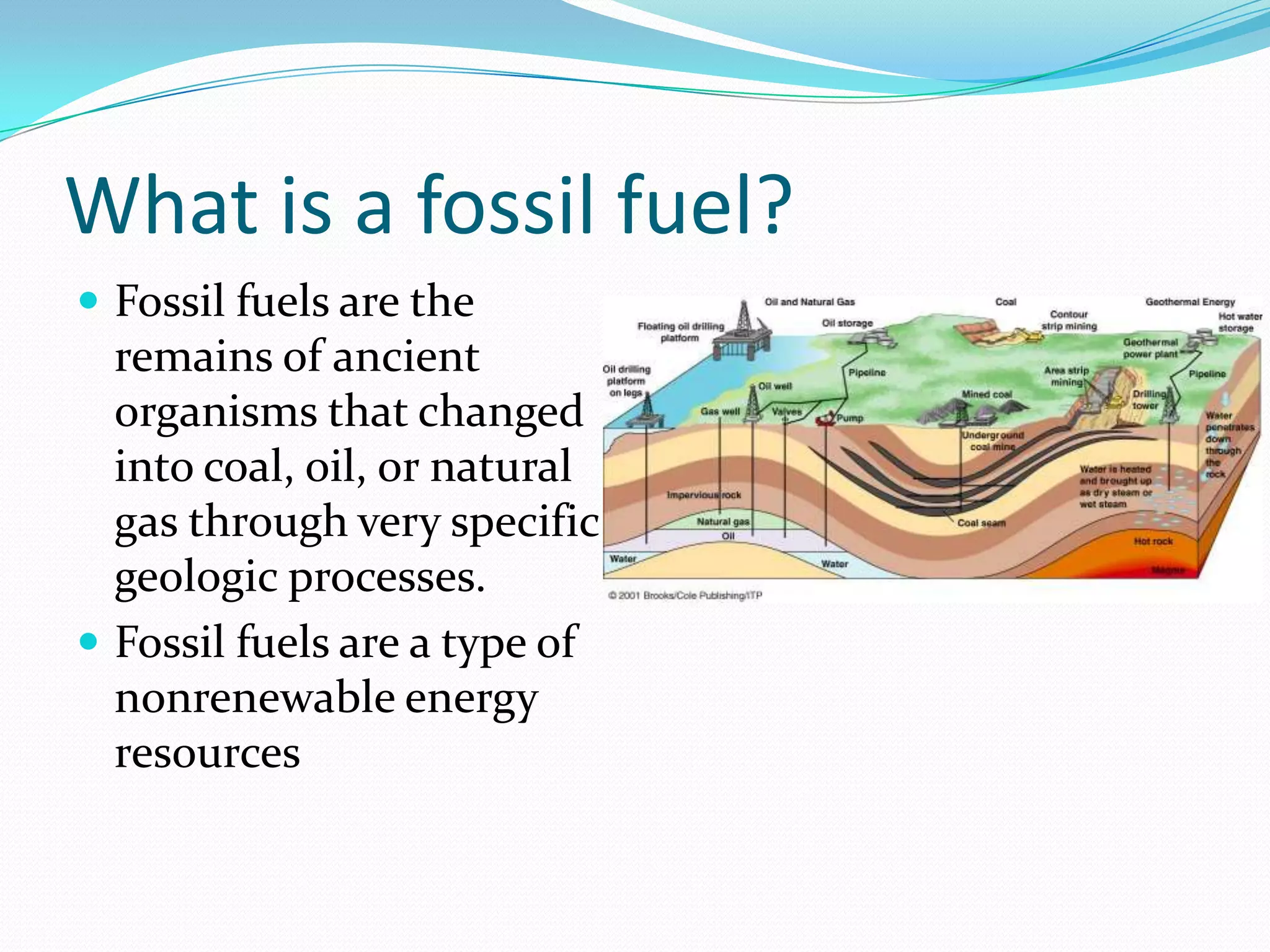
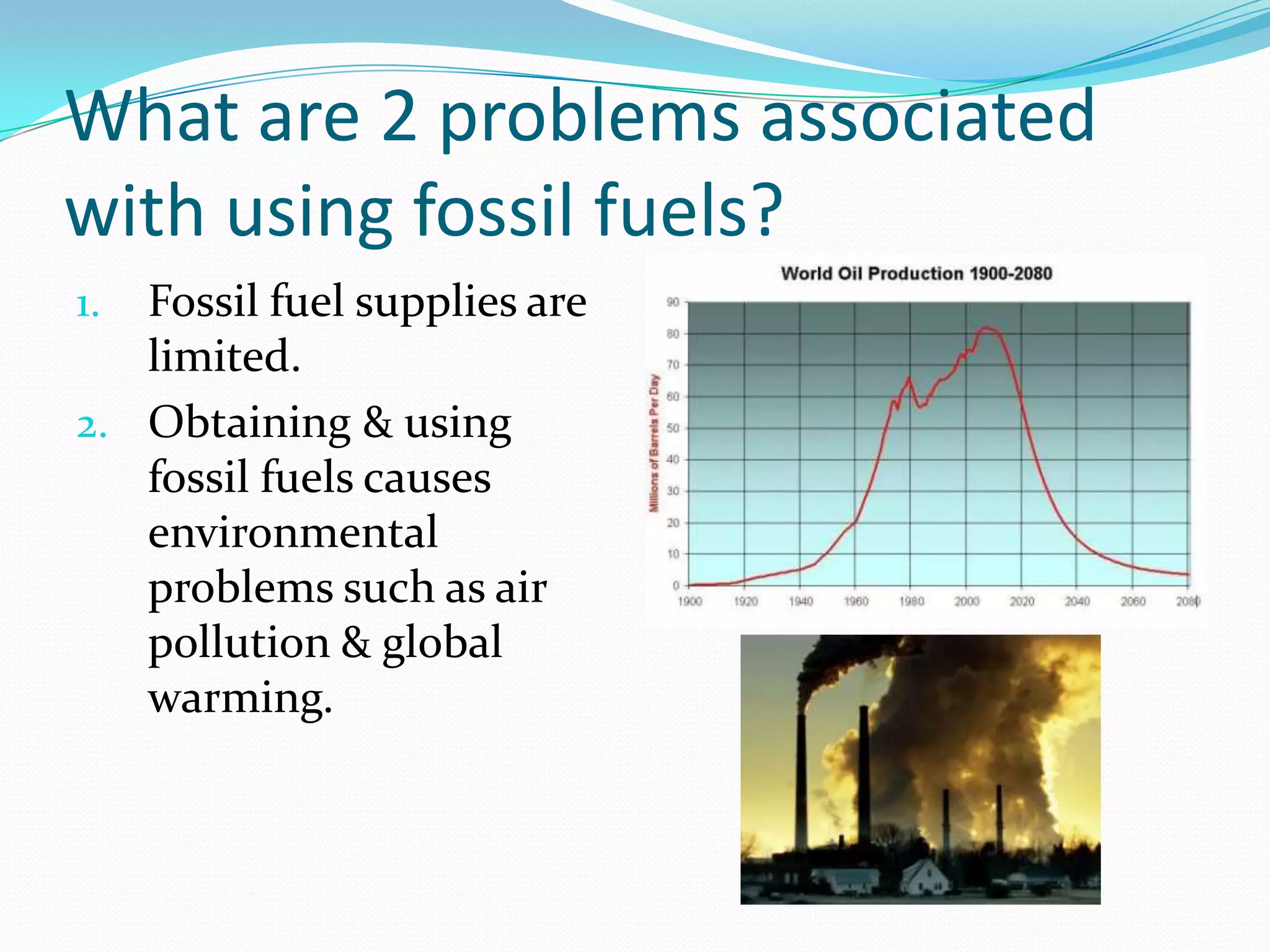
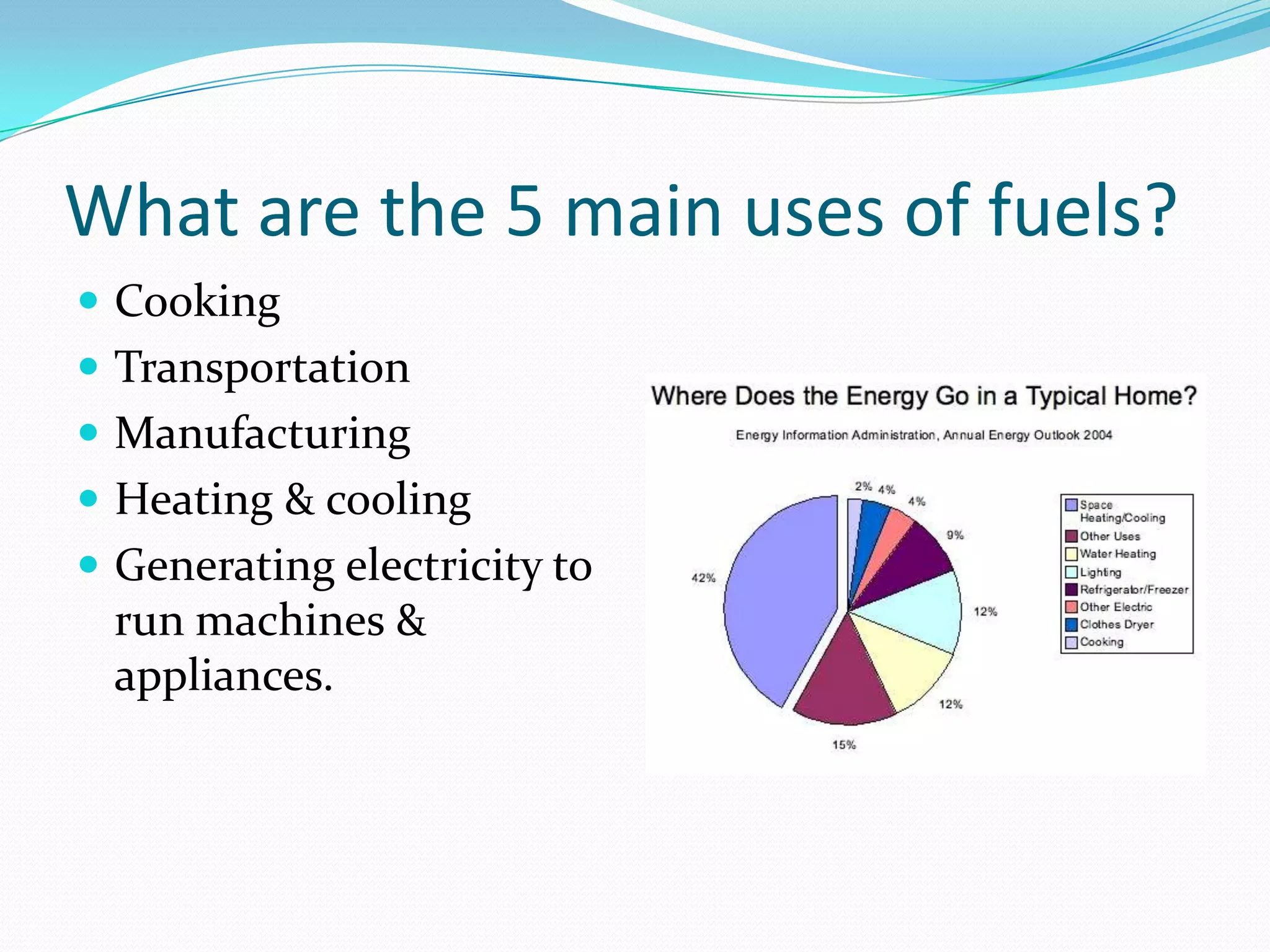
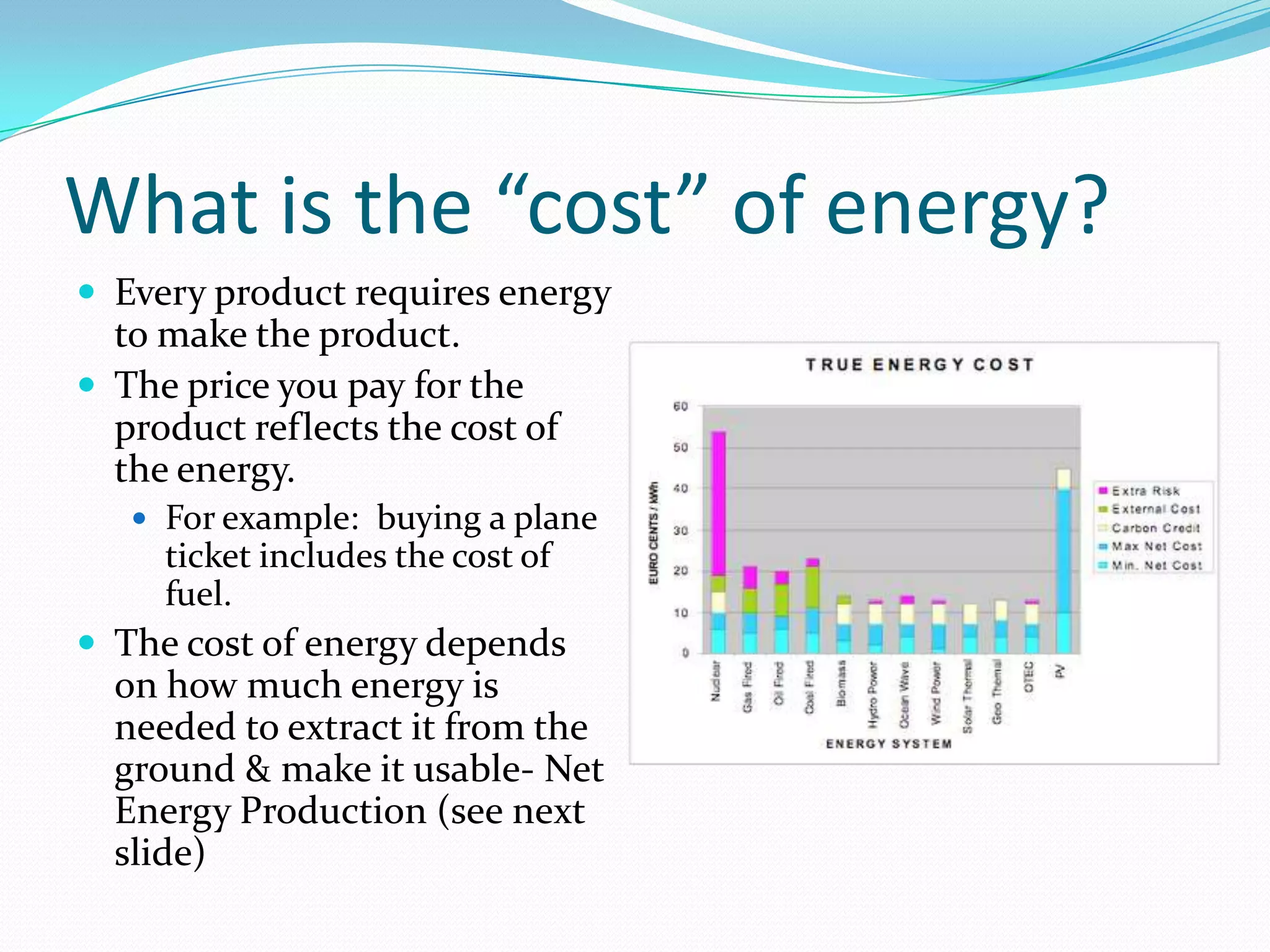
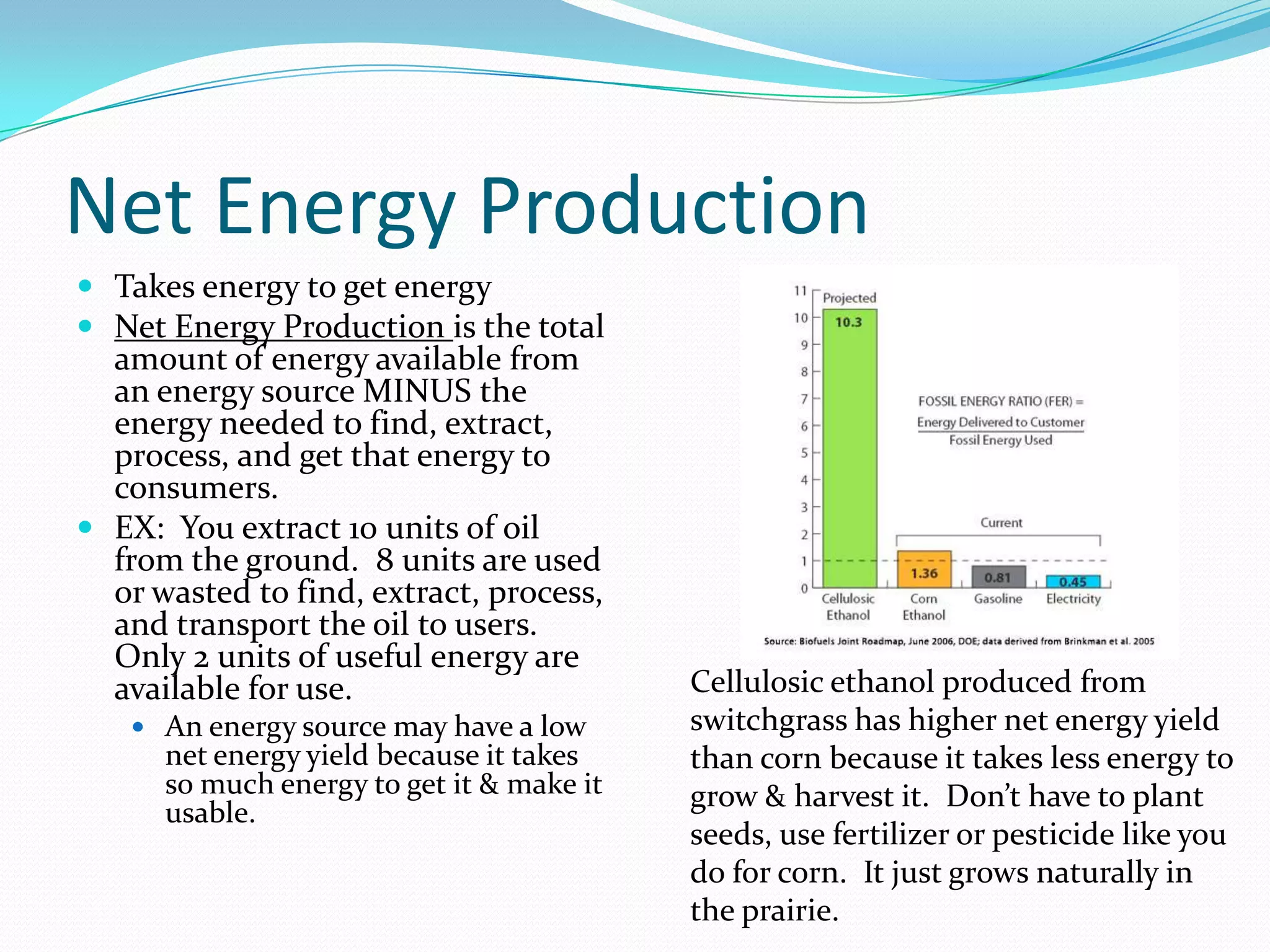
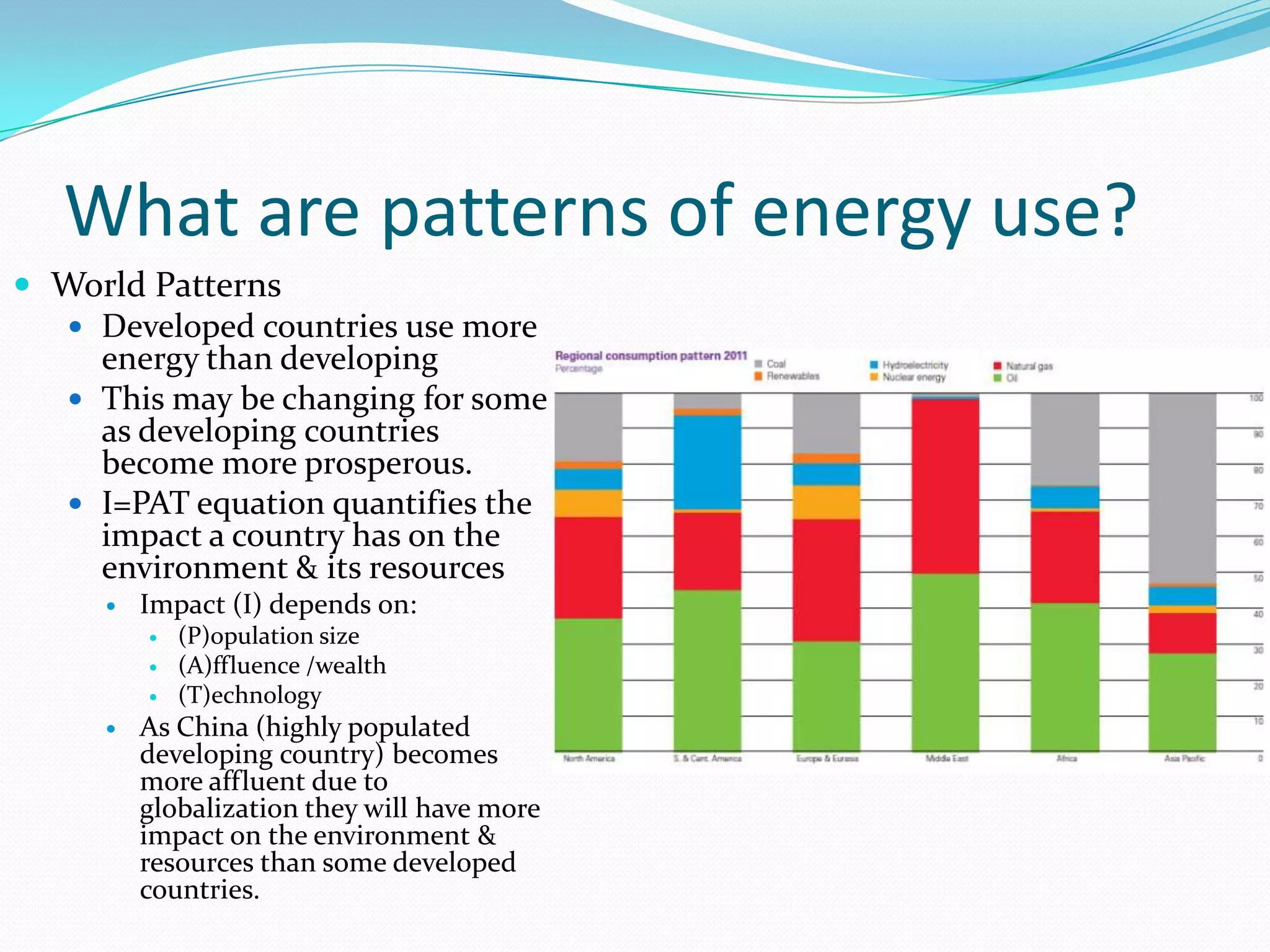
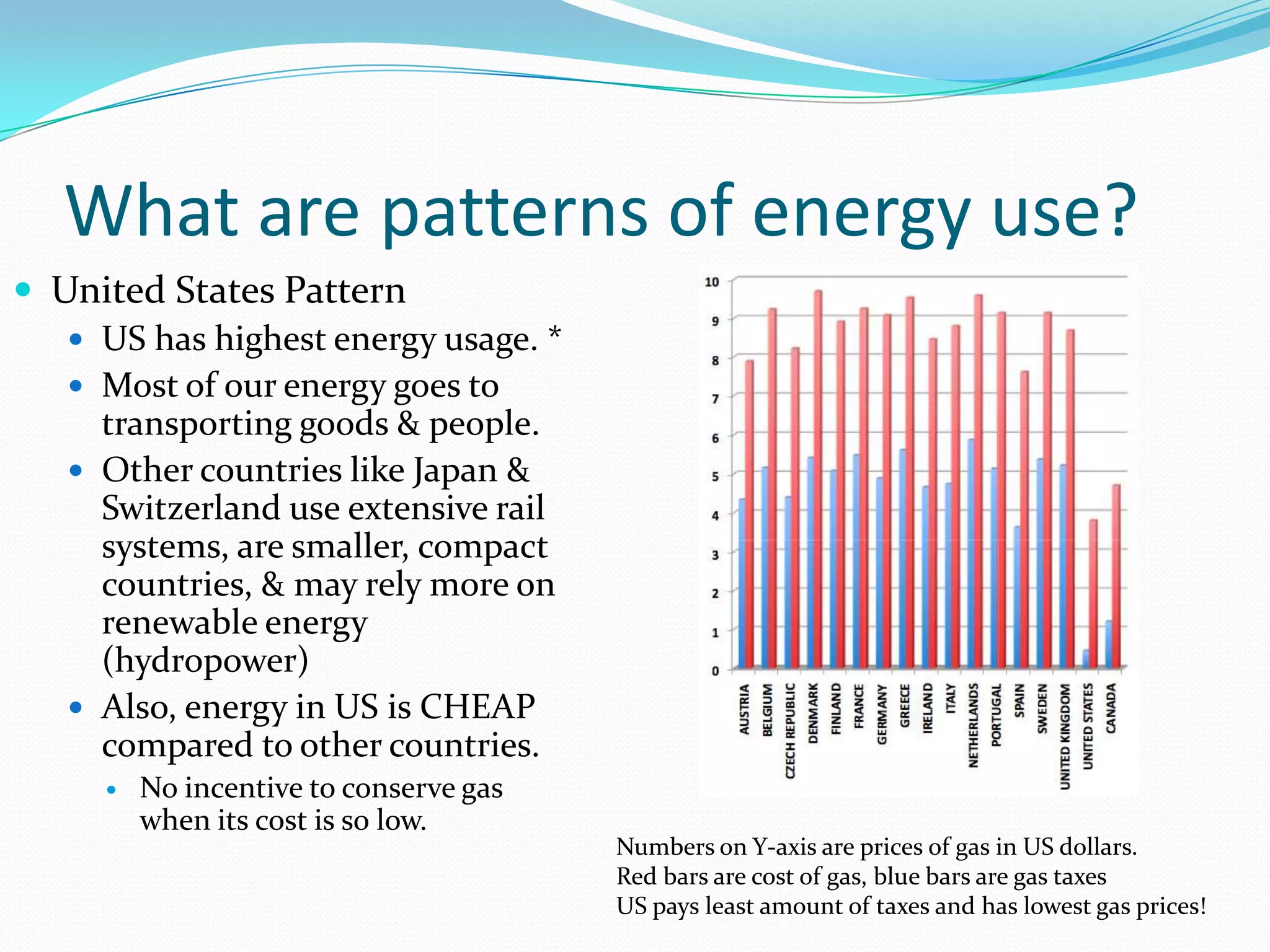
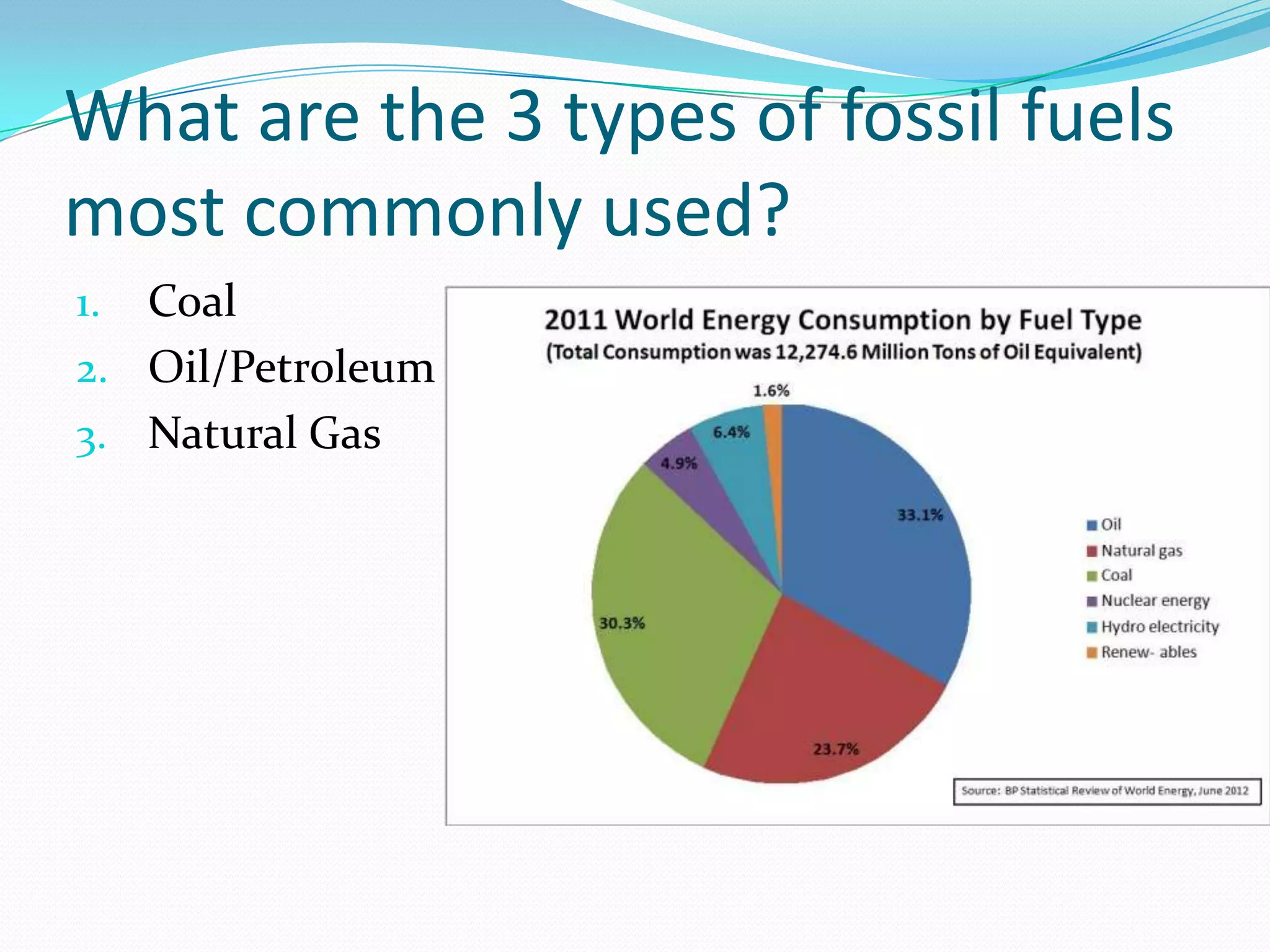
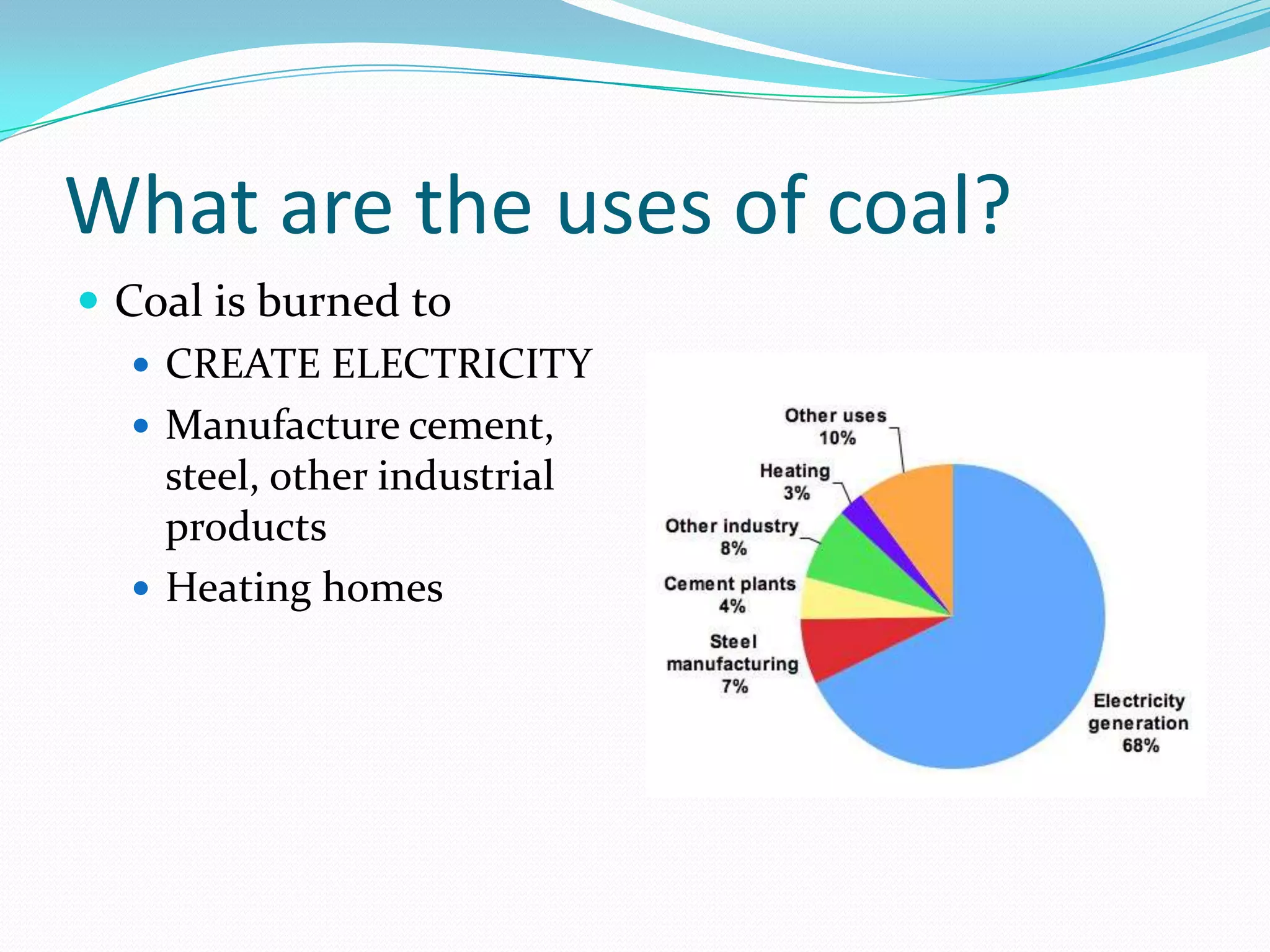
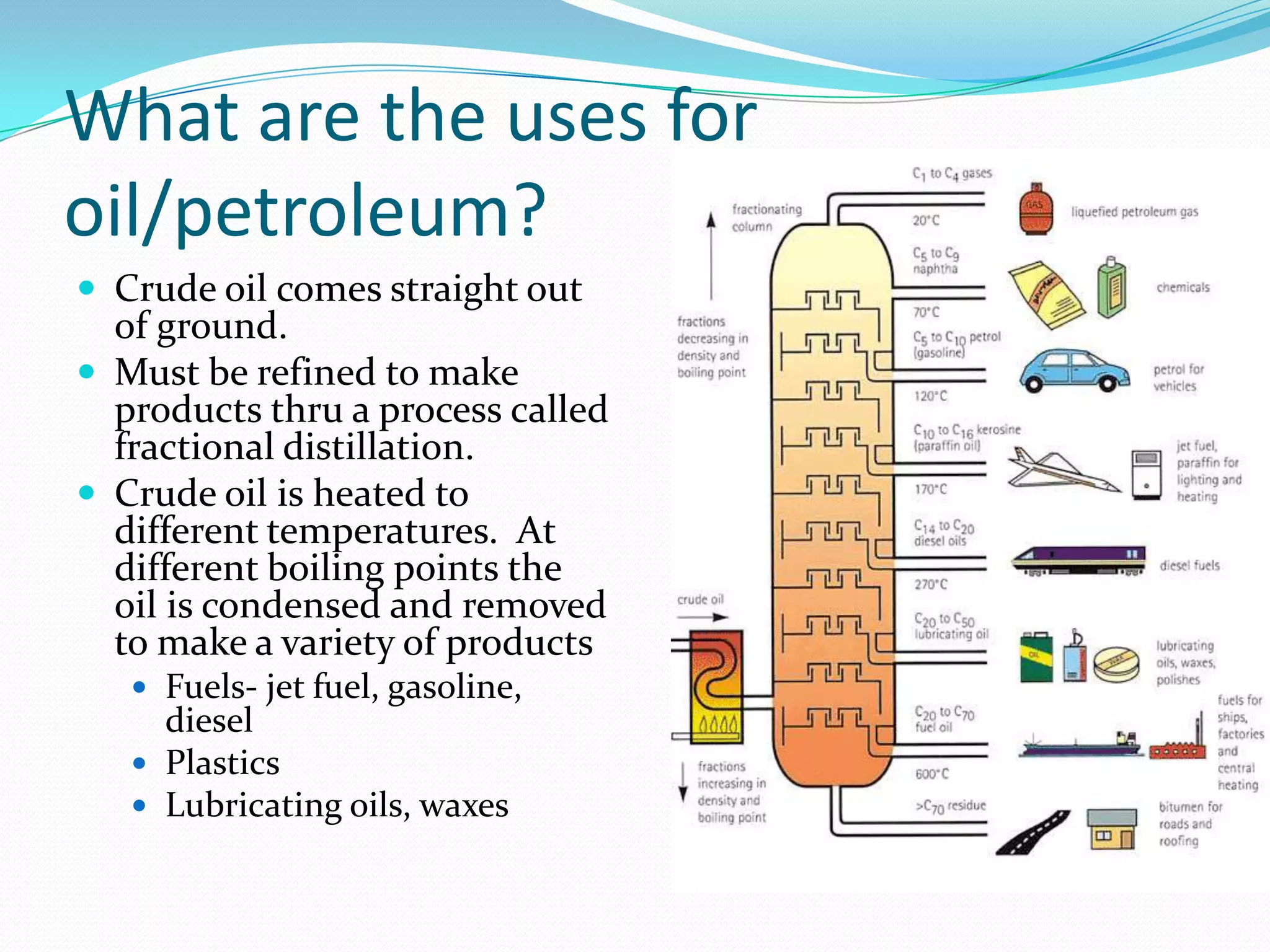
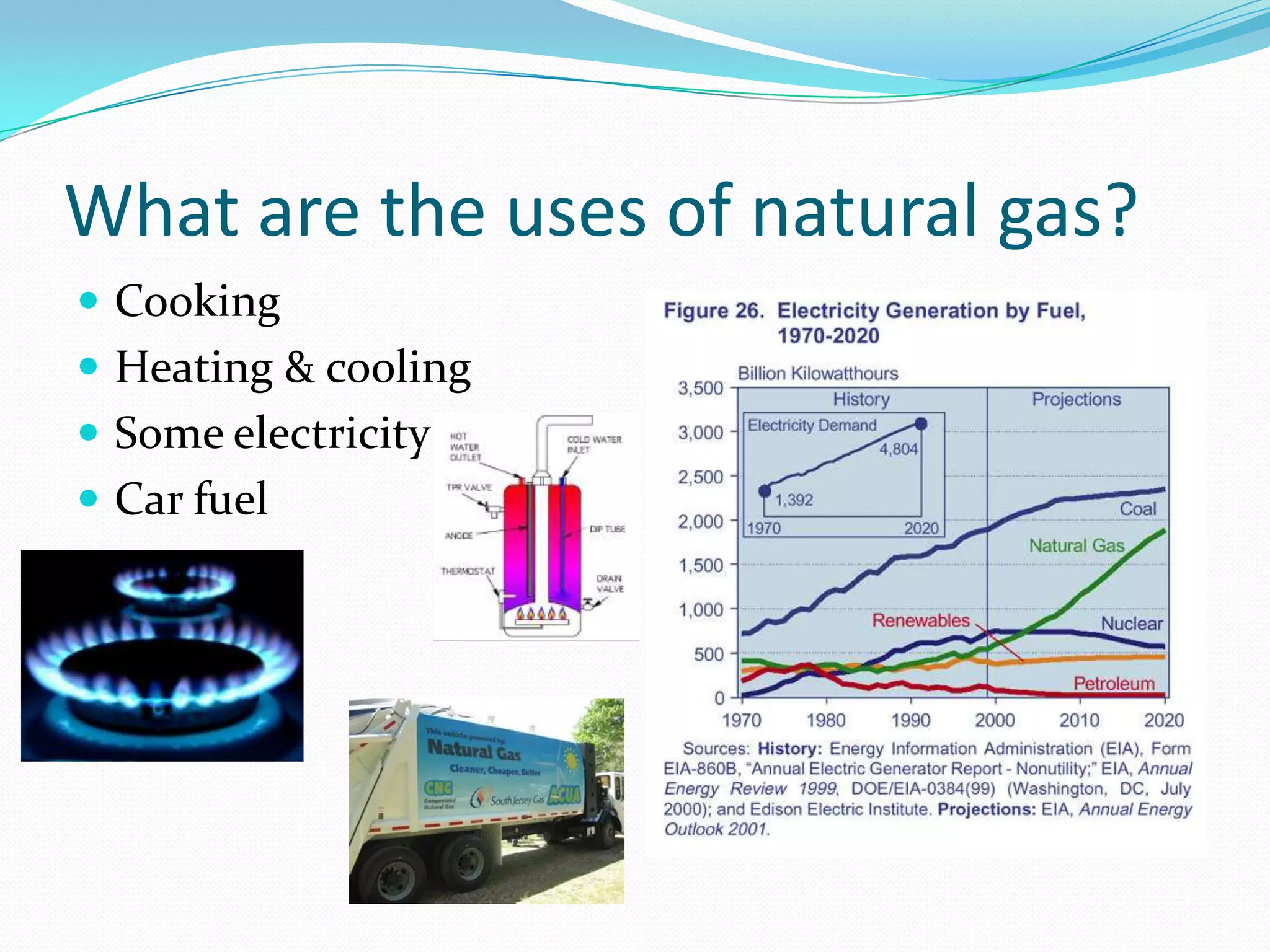
This document discusses energy resources and fossil fuels. It defines nonrenewable resources and fossil fuels, noting that fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas formed from the remains of ancient organisms over millions of years. The two main problems with fossil fuel use are limited supplies and environmental impacts like pollution and climate change. The document outlines how the three primary fossil fuels formed naturally and their various uses and advantages and disadvantages. Methods to reduce pollution from fossil fuel extraction and use are also summarized.