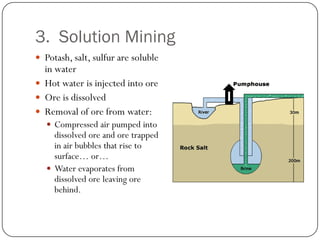
The document describes the process of mineral exploration and mining. There are several key steps: (1) prospecting to find mineral deposits, (2) exploration to determine if extraction is economically viable, (3) mining to extract the ore, (4) extraction to separate the minerals from waste rock, and (5) smelting and refining to purify the extracted minerals. Mining occurs either through subsurface techniques like room and pillar mining or longwall mining, or surface techniques including open pit mining and quarrying. The document also discusses how minerals are located and tested before mining begins.