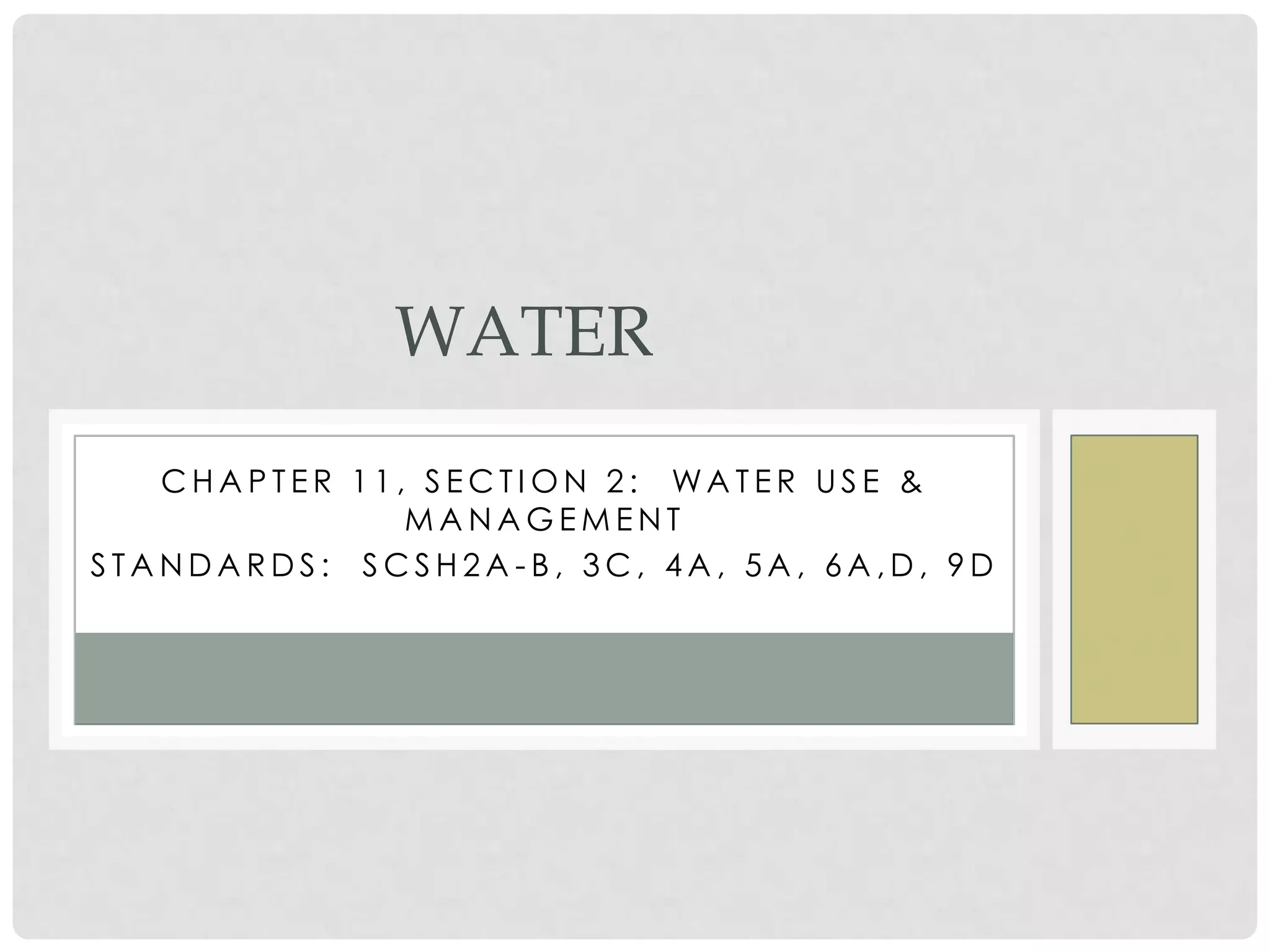
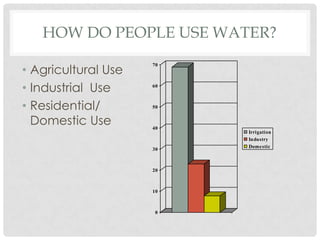
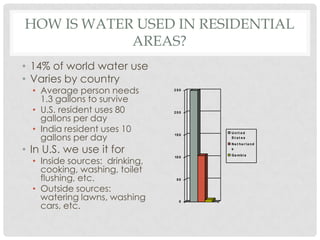
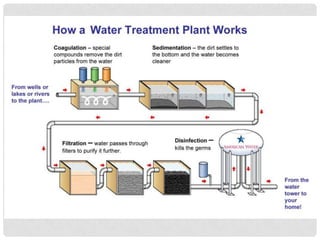
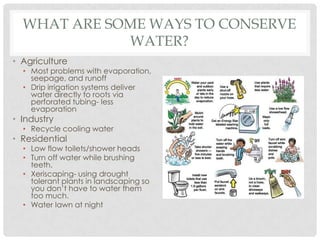
This document discusses water use and management. It explains that the majority of water usage globally is for agriculture at 67%, while residential use accounts for 14% and industry 19%. It then describes how water is treated to become potable through various filtration, disinfection, and treatment steps. Finally, it discusses various water management projects including dams, which provide benefits like water storage and hydropower but also costs like habitat destruction and downstream impacts.