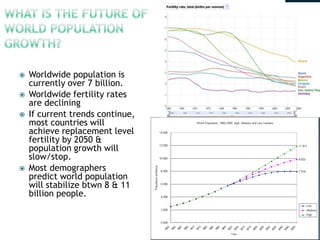
The document discusses global population trends, noting that China and India currently have the largest populations but India is projected to surpass China by 2030. Developing countries are experiencing rapid population growth during a time when resources are already stressed. Rapid population growth can overwhelm infrastructure and resources, affecting access to necessities like fuel, water, arable land, and adequate housing. Some governments try to address overpopulation through incentives for smaller families and increased access to family planning.