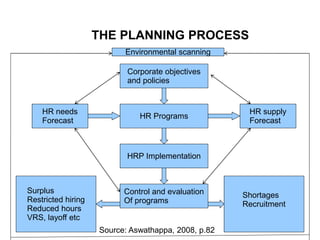
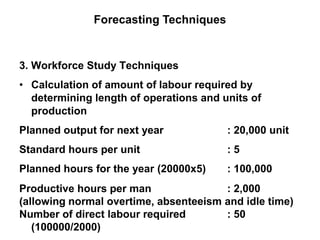
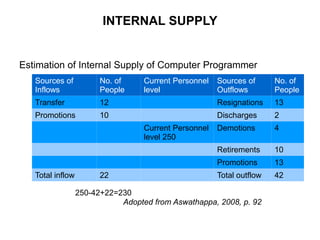
Human resource planning is a process that involves forecasting future human resource needs and the availability of qualified candidates to meet organizational goals. It includes determining future personnel needs through forecasting techniques, developing HR programs to address surpluses or shortages, implementing plans through actions like recruitment and training, and evaluating outcomes. Key factors that influence planning are organizational strategy, growth stage, environmental uncertainties, and quality of forecasting data. Barriers can include weak linkage to corporate strategy and lack of management support. Requisites for success are integrating HRP with strategic planning, centralized responsibility, and ongoing improvement of planning processes.