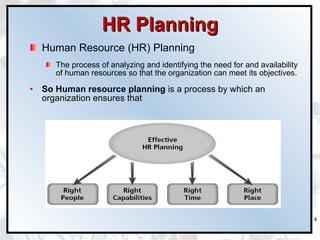
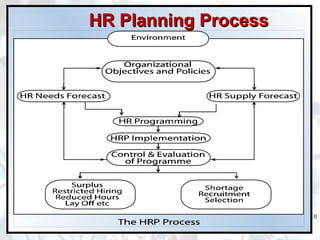
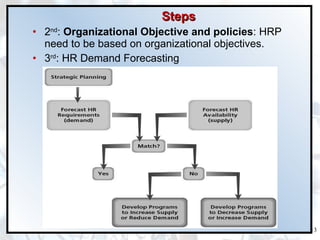
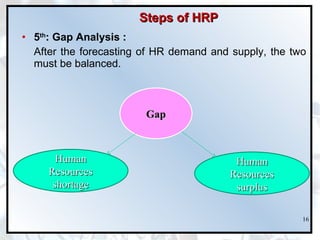
The document discusses the importance of human resource planning (HRP) for organizations. It outlines the key steps in the HRP process as: 1) environmental scanning, 2) defining organizational objectives and policies, 3) forecasting HR demand, 4) forecasting HR supply, 5) analyzing gaps between demand and supply, and 6) developing solutions to address gaps. An effective HRP ensures the right people are available at the right time through recruitment, training, succession planning and other retention activities.