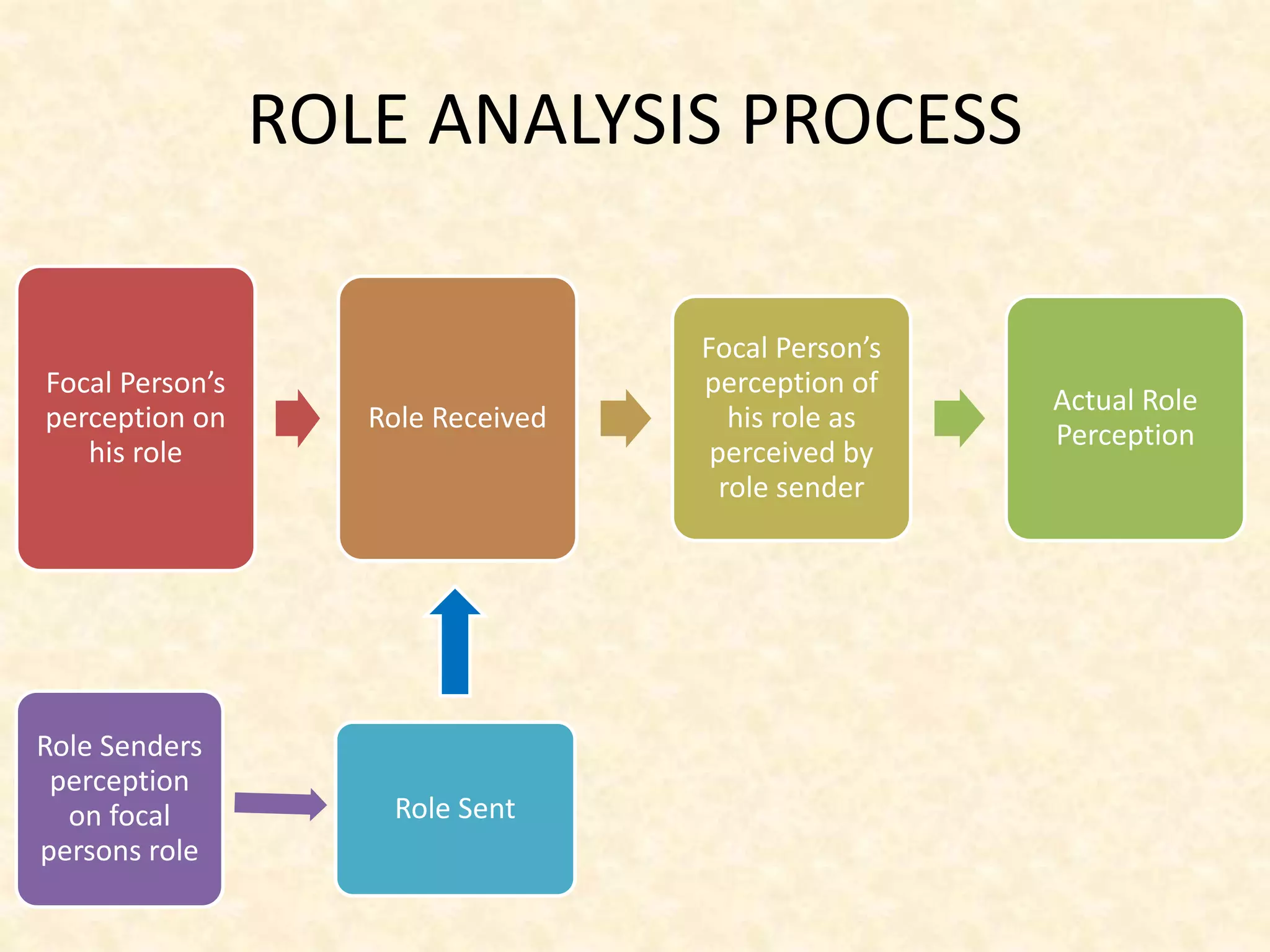
Performance planning, role analysis, and evaluation are important performance management processes. Performance planning involves managers and employees setting goals and expectations for the upcoming period. It aims to align employee goals with organizational objectives. Role analysis defines an individual's role and responsibilities based on expectations from others in the organization. Performance evaluation assesses an employee's progress on goals and provides feedback. It is done annually by supervisors, managers, and sometimes peers or customers to recognize excellence, identify training needs, and inform compensation decisions. The goal is to improve performance and services through objective setting, progress assessments, and comprehensive evaluations.