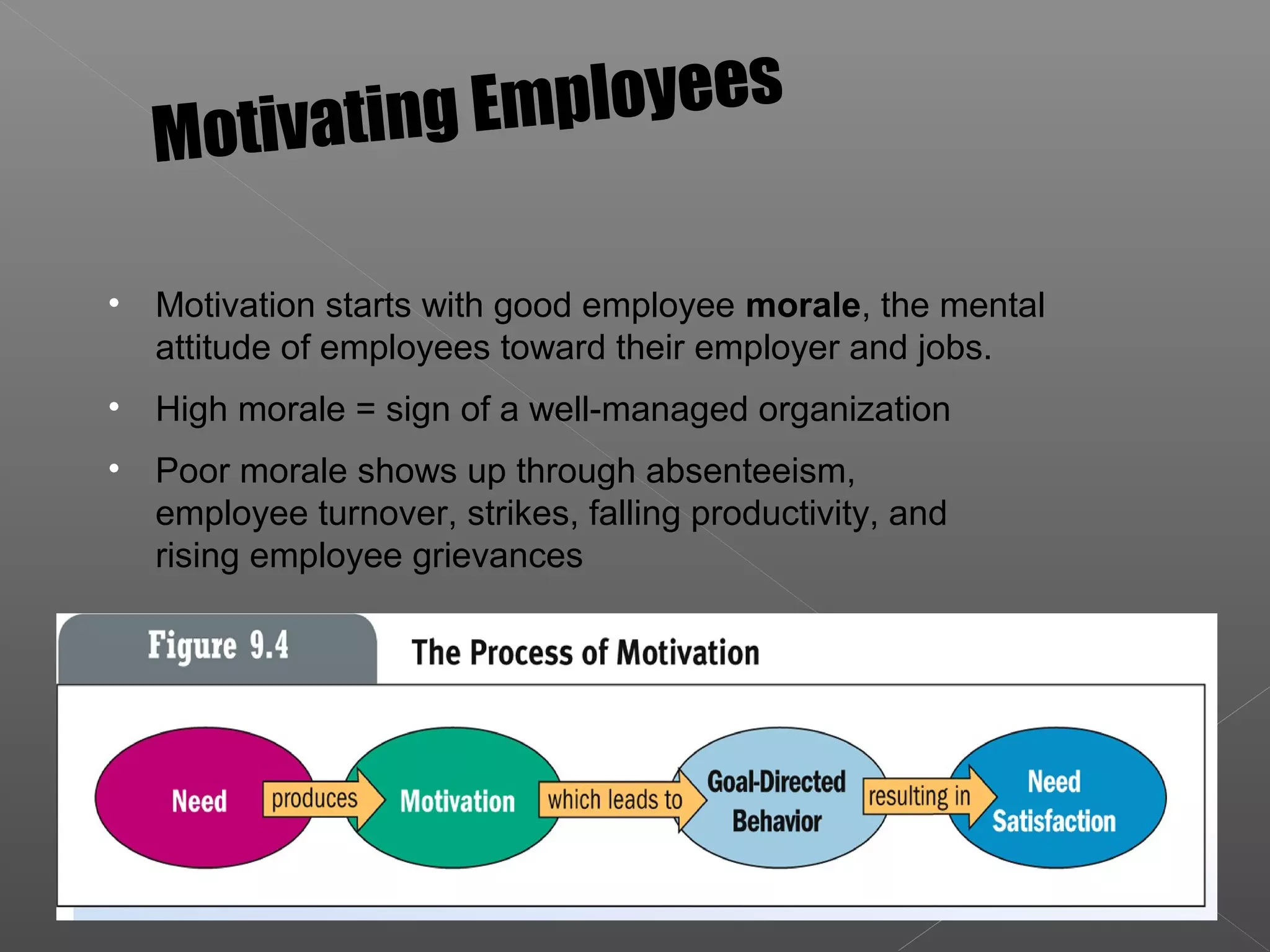
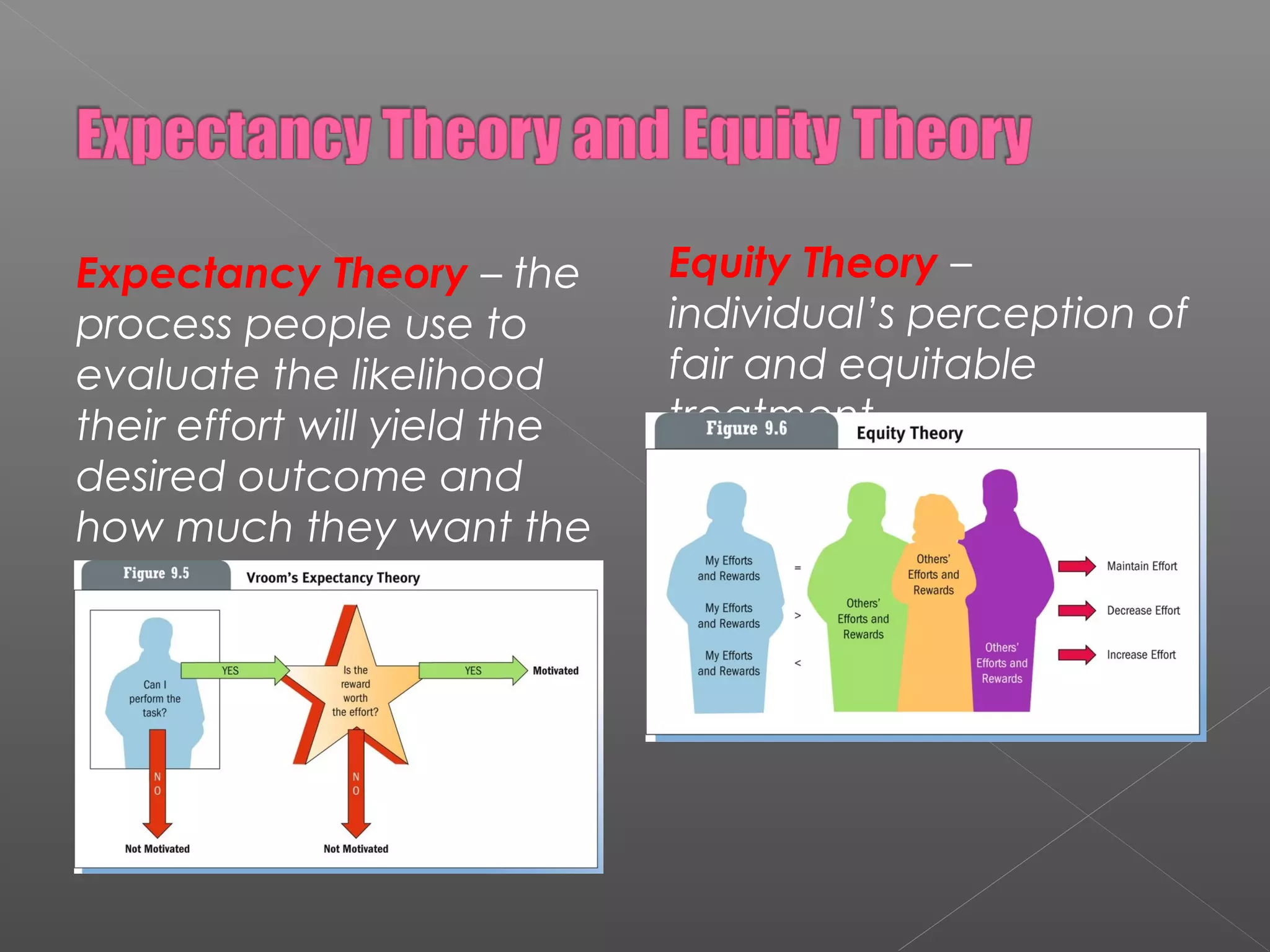
This document discusses key aspects of human resource management including recruitment and selection, training programs, performance appraisals, compensation, and employee separation. It addresses how these human resource responsibilities help organizations attract, develop, and retain qualified employees. Additionally, it examines theories related to motivating employees, such as Maslow's hierarchy of needs, goal setting, job design, and managers' attitudes.