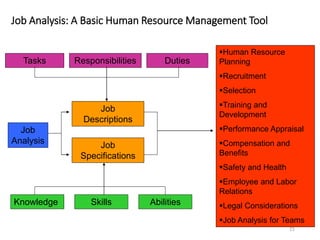
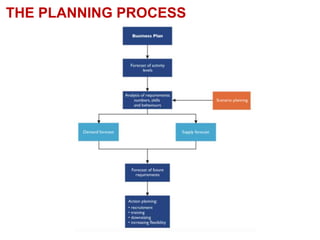
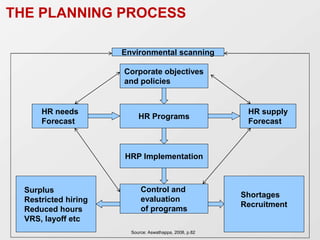
Human resource planning is a process that forecasts an organization's future demand and supply of employees. It involves determining HR needs based on factors like the organization's strategy, growth, and environment. The planning process includes forecasting demand and supply of employees, identifying surpluses or shortages, and developing programs to address them. Forecasting techniques help estimate demand and include managerial judgments, ratio trend analysis, and regression analysis. The HR plan is then implemented through actions like recruitment, training, retention programs, and downsizing if needed. Regular evaluation ensures the plan adapts to changes in the organization or environment.