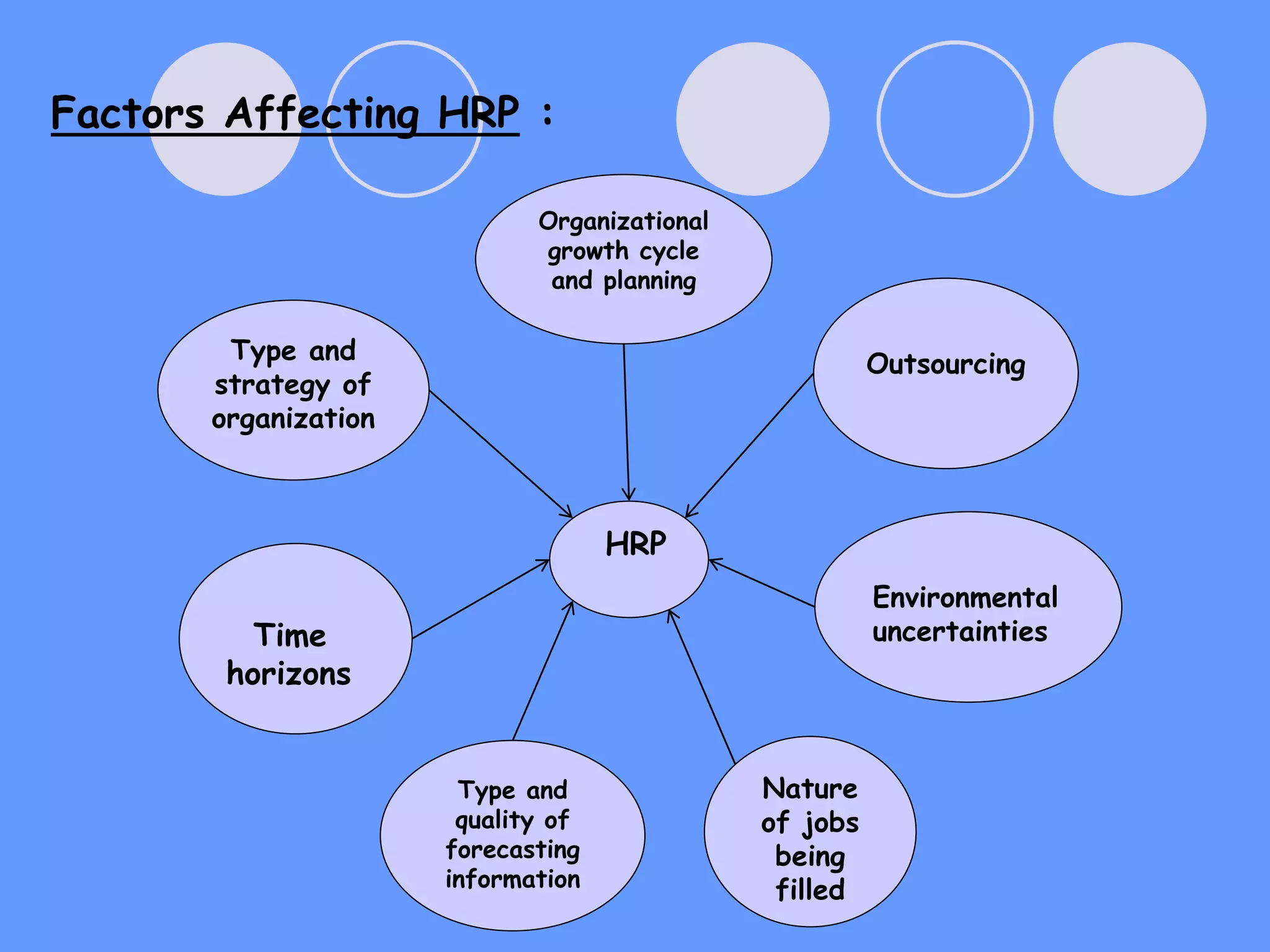
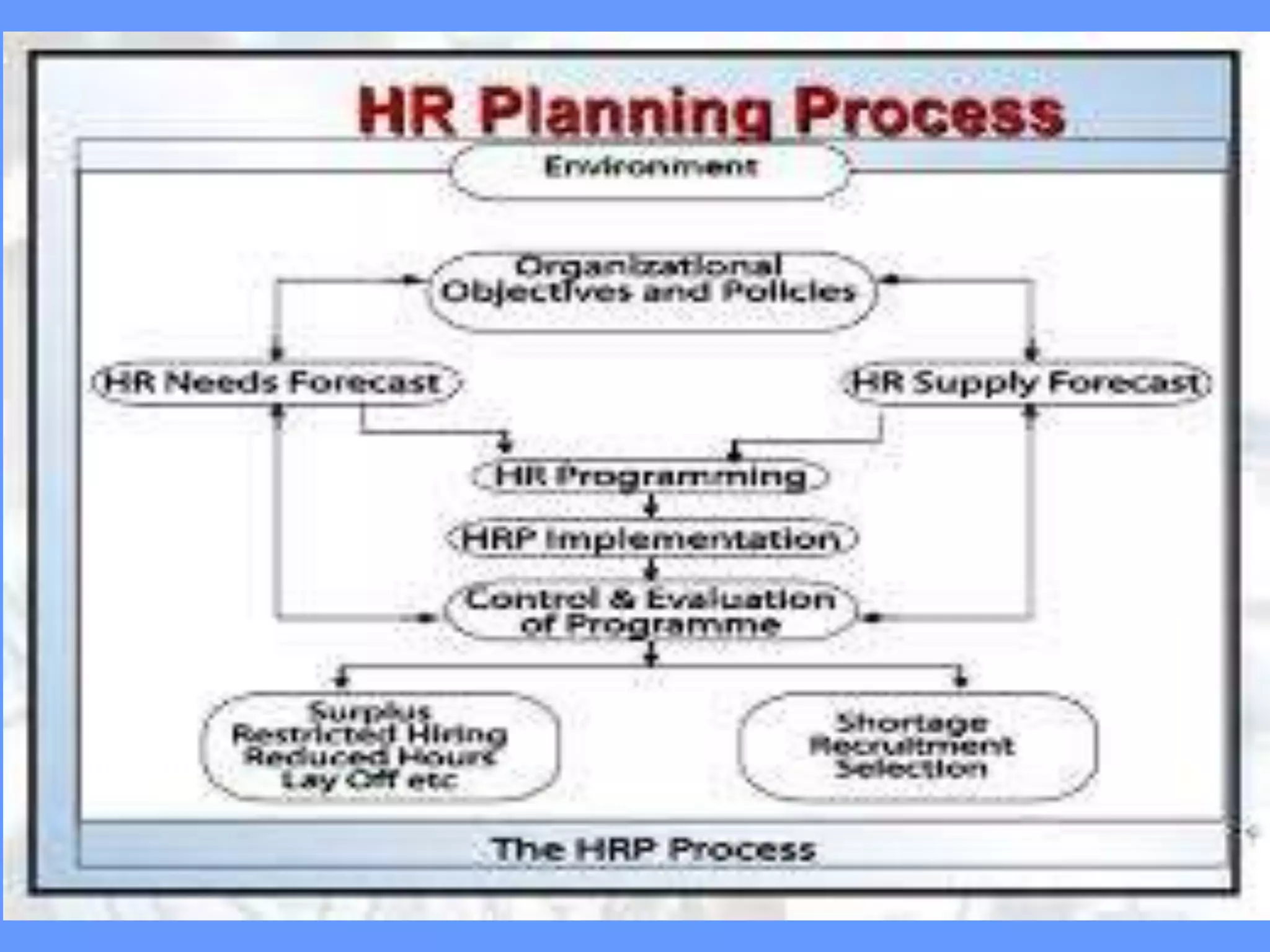
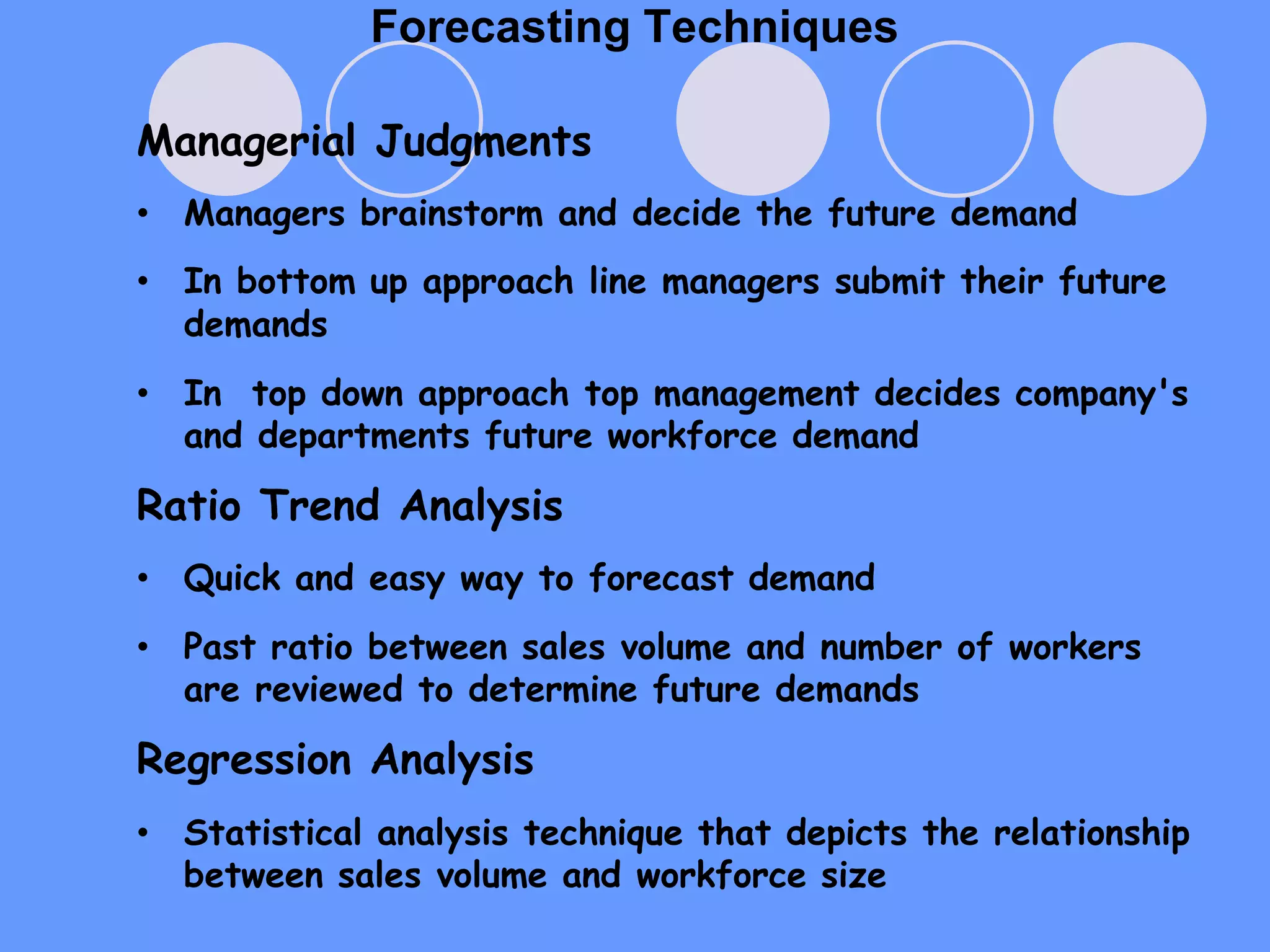
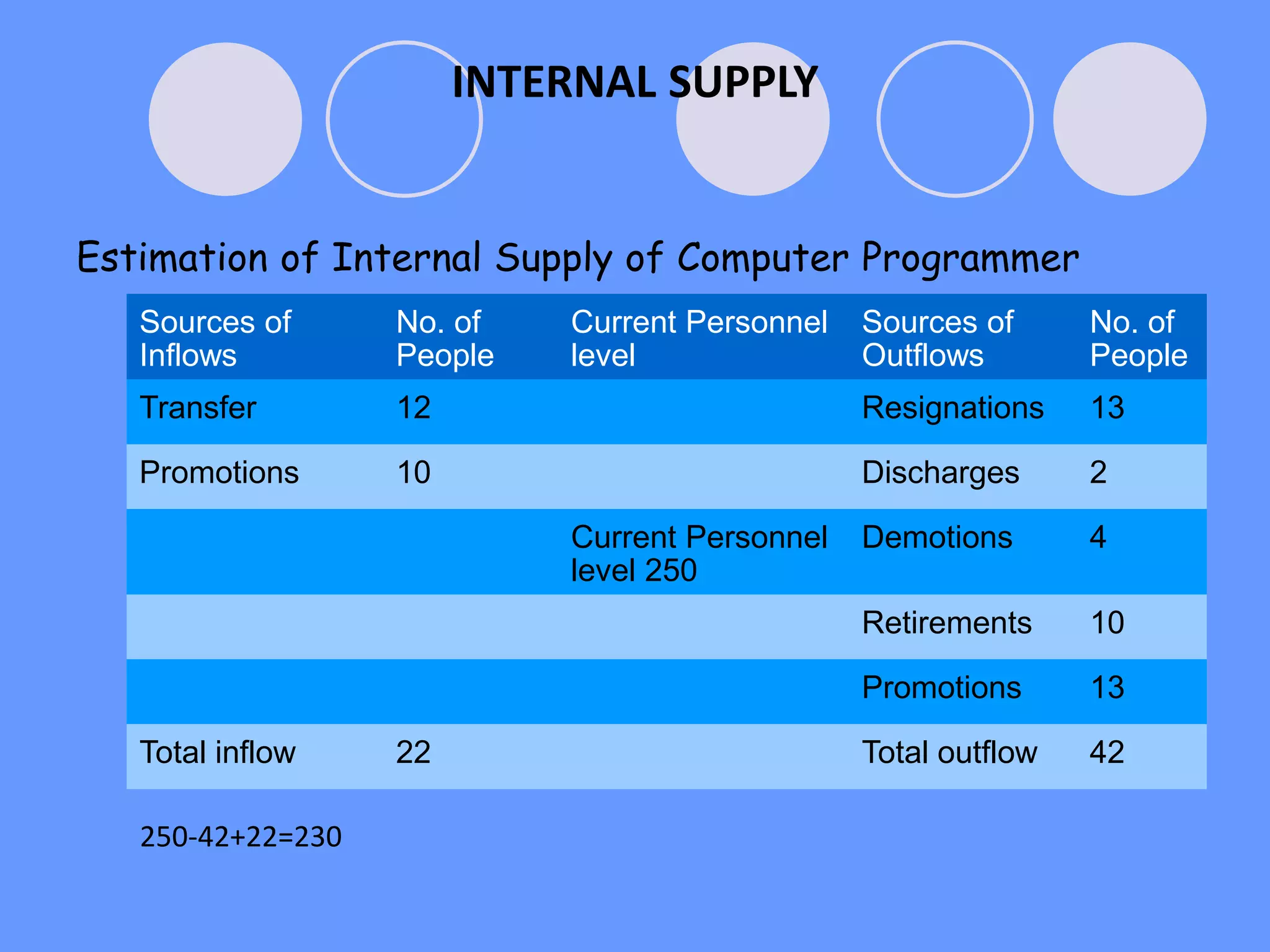
This document provides an overview of human resource planning (HRP). It defines HRP as forecasting an organization's future demand for and supply of employees. The importance of HRP is that it ensures the organization has the right number and types of qualified employees. The HRP process involves environmental scanning, demand forecasting using techniques like ratios and regression analysis, supply forecasting using internal sources like current employees and external sources like new hiring, and implementing plans through recruitment, training, and retention strategies. Barriers to effective HRP include lack of managerial expertise, incompatible information, lack of manager involvement, time consumption, and unions. Requirements for effective HRP are alignment with corporate objectives, complete personnel records, long-term time