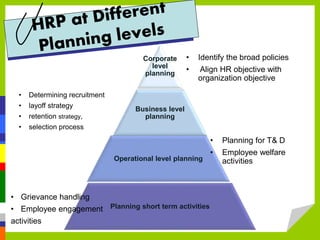
The document discusses human resource planning (HRP), including its definition, importance, process, and challenges. It provides details on:
- HRP involves determining future human resource needs and how to utilize current staff effectively.
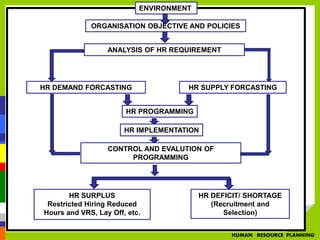
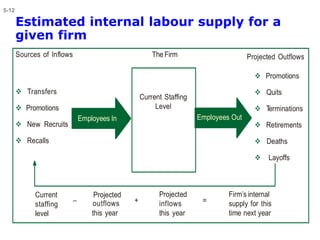
- The HRP process includes forecasting future HR demand and supply, developing HR programs, implementation, and evaluation.
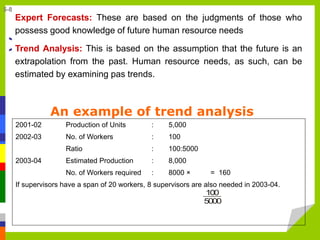
- Forecasting techniques include managerial judgment, trend analysis, and the Delphi method.
- HRP helps ensure the right people are in the right jobs at the right time to achieve organizational goals. It also facilitates succession planning and allows organizations to expand or contract as needed.
- Challenges include the time and costs involved, uncertainties in forecasting