The document discusses the process of conducting a human resources (HR) audit within an organization. It describes the purpose of an HR audit as reviewing HR policies, procedures, and practices to evaluate their effectiveness and compliance. The summary includes:
1) An HR audit evaluates the strengths and weaknesses of an organization's HR systems and identifies issues to improve the HR function.
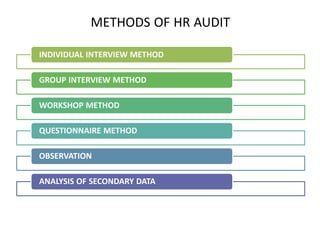
2) The audit process typically involves assessing HR strategies, functions, managerial compliance, and employee satisfaction through methods like interviews, questionnaires, and analyzing records.
3) The results of an audit are documented in a report that identifies risks, prioritizes solutions, and develops an HR improvement plan to address issues.