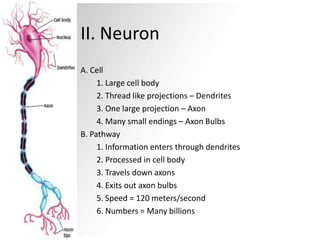
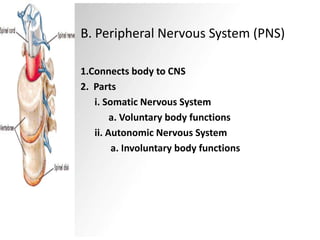
The nervous system functions to receive information through the senses, store information in the brain and spinal cord, make decisions, and send responses through the body. It is composed of neurons, which are cells that transmit electrochemical signals. Information enters neurons through dendrites, is processed in the cell body, and travels down the axon through axon bulbs. At synapses, neurotransmitters are released by the axon bulb to signal the next neuron. The central nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord, while the peripheral nervous system connects the body to the CNS and controls voluntary and involuntary functions. Reflexes are rapid, unconscious responses to stimuli. Nervous system injuries like concussions and spinal cord damage can impair functions or