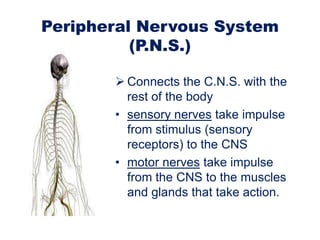
The nervous system is made up of neurons that transmit signals between the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS contains the brain and spinal cord, which coordinate sensation, movement, and homeostasis. The PNS connects the CNS to sensory receptors and effector organs. Neurons communicate via synapses using neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine. The CNS controls voluntary and involuntary functions while the PNS connects to sensory organs and muscles.