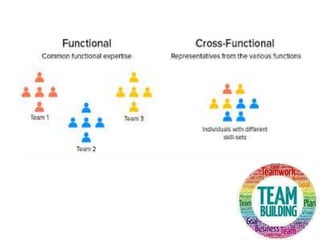
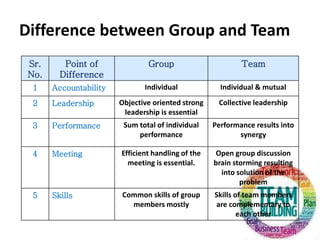
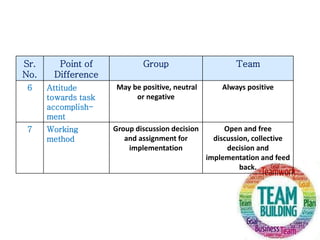
The document outlines the essential elements of building effective teams, emphasizing the importance of complementary skills, commitment to common goals, and the differences between groups and teams. It discusses internal and external networks that enhance team effectiveness, as well as the internal and external dynamics that influence team performance. Additionally, it provides a structured process for team building, highlighting guiding principles such as clear objectives, effective communication, and the importance of collaboration across departments.