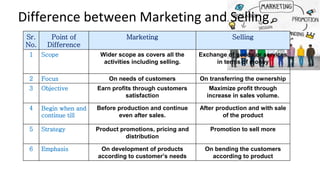
The document discusses various aspects of marketing and sales management, defining key concepts such as sales, marketing, and marketing management. It distinguishes between marketing and selling, outlines marketing concepts, and summarizes the importance of marketing in industrial development and consumer satisfaction. Additionally, it explores retail marketing and types of retailers, including store and non-store retailing, while detailing their characteristics and functions.