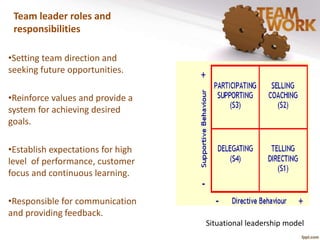
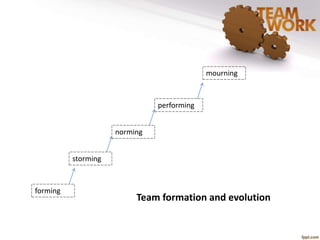
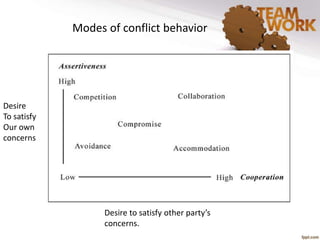
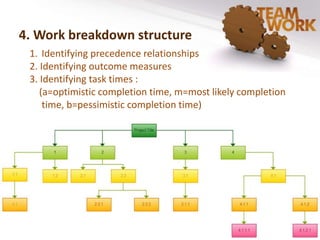
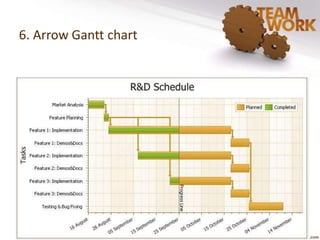
The document discusses the management of quality improvement teams and emphasizes the importance of teamwork and employee empowerment in handling complex work environments. It outlines various types of teams, such as process improvement teams, cross-functional teams, and virtual teams, and their roles and responsibilities in organizational improvement. Additionally, it touches upon conflict resolution in teams and tools for project management, including project charters and Gantt charts.