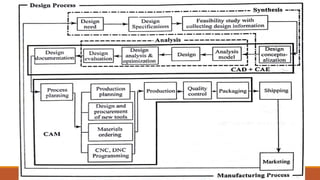
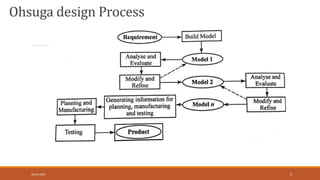
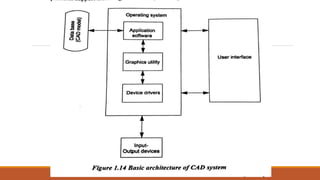
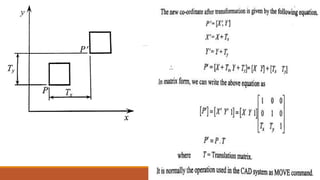
This document provides an introduction and syllabus for a course on computer aided design and manufacturing (CAD/CAM). It discusses the product design and manufacturing processes, including sequential and concurrent engineering models. It also describes CAD systems and computer graphics technologies used to design products digitally. This includes topics like 2D and 3D coordinate systems, geometric transformations, line drawing algorithms, and viewing transformations. The goal of the course is to introduce students to how computer technologies are used in the product design and manufacturing fields.