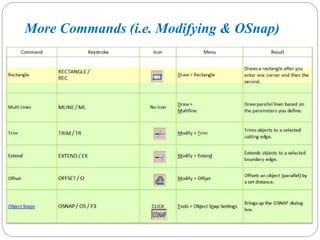
This document provides an overview of Computer-Aided Design (CAD), including its evolution from traditional engineering drawing methods to modern techniques that utilize software for design and manufacturing. It outlines the capabilities of CAD, including solid modeling, flexibility in editing, and project reporting, while also discussing the benefits and drawbacks of CAD systems. The document emphasizes the importance of CAD in streamlining the design process and integrates aspects of Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) and Computer-Aided Analysis (CAE).