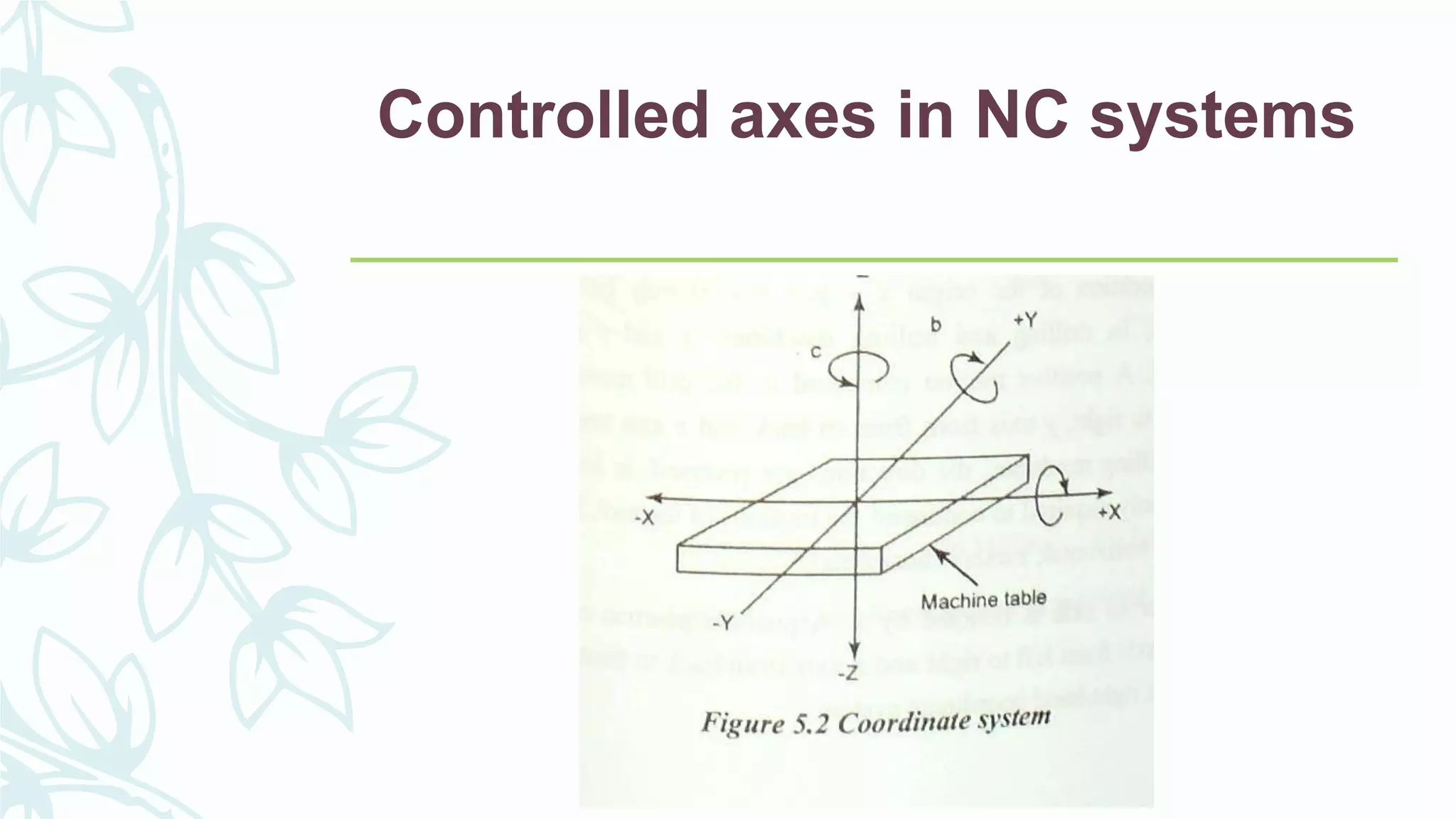
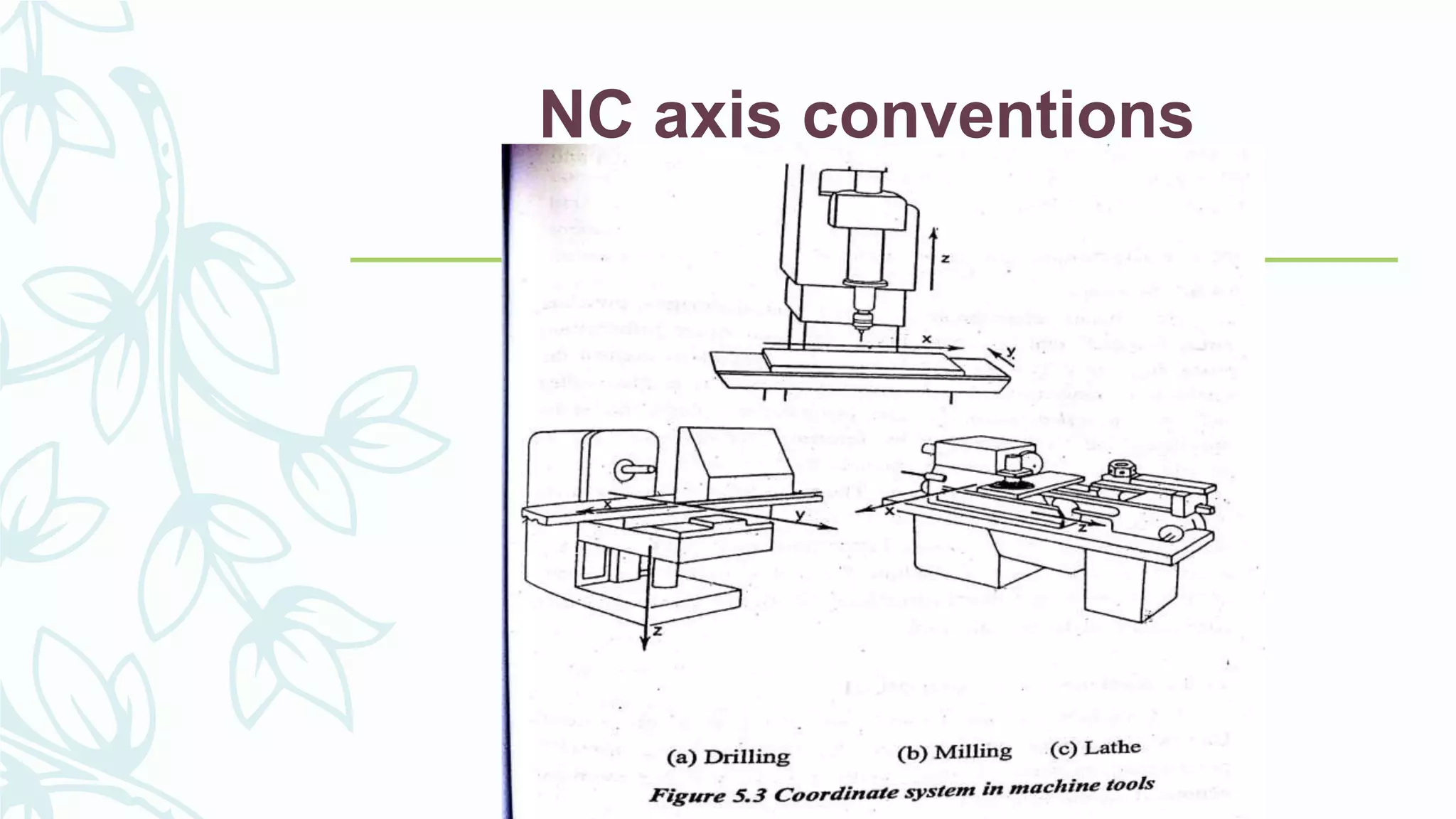
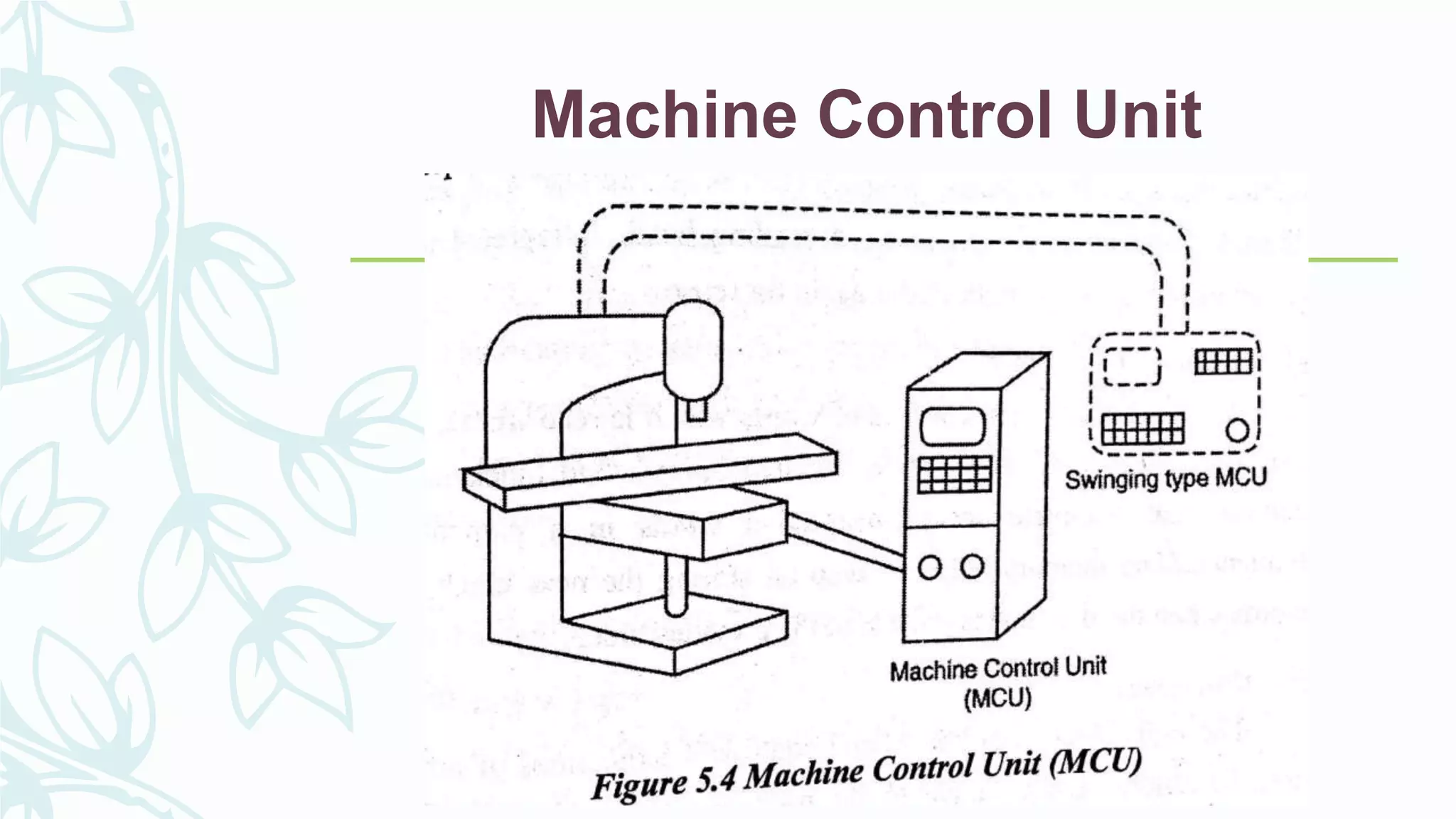
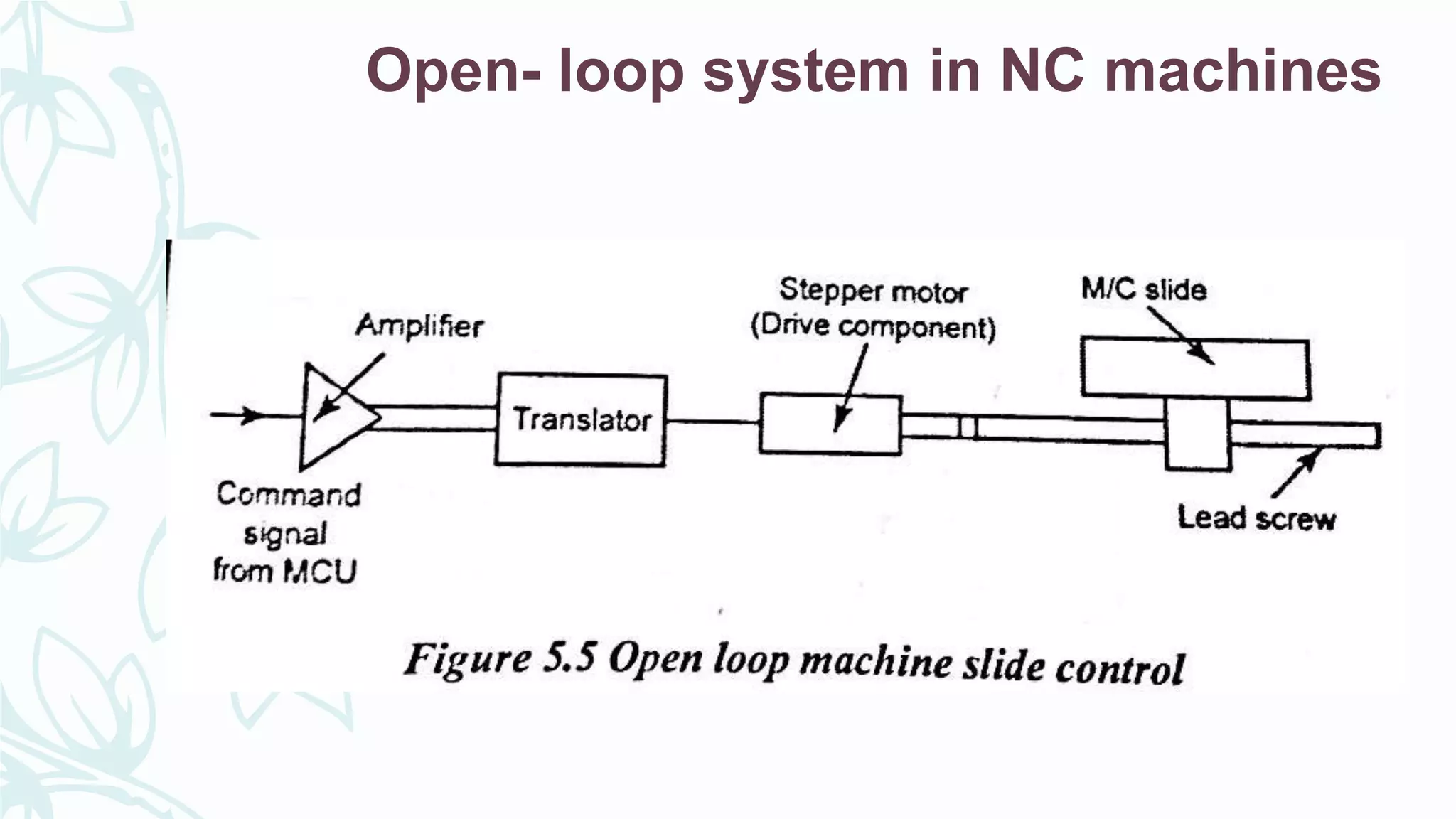
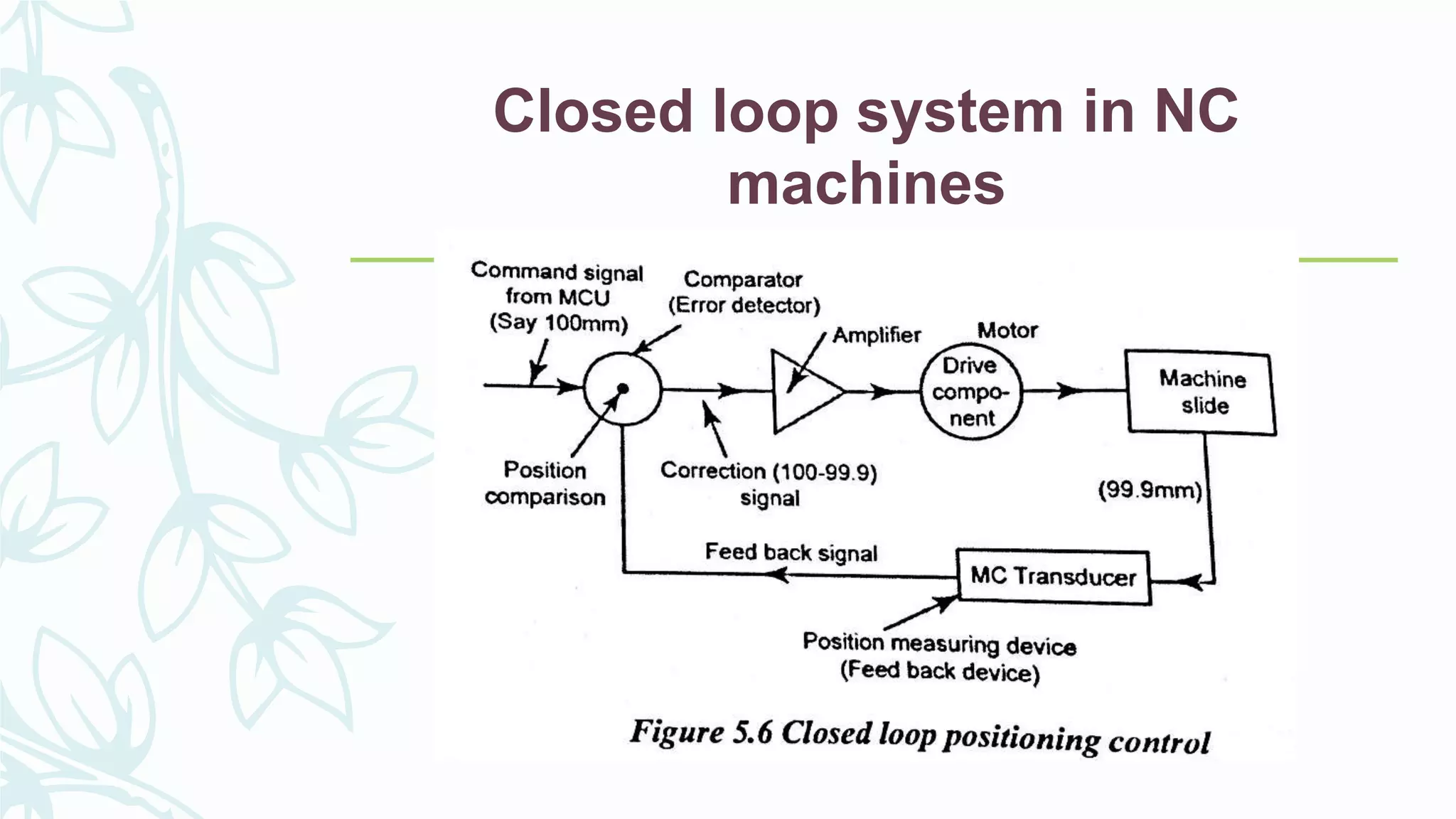
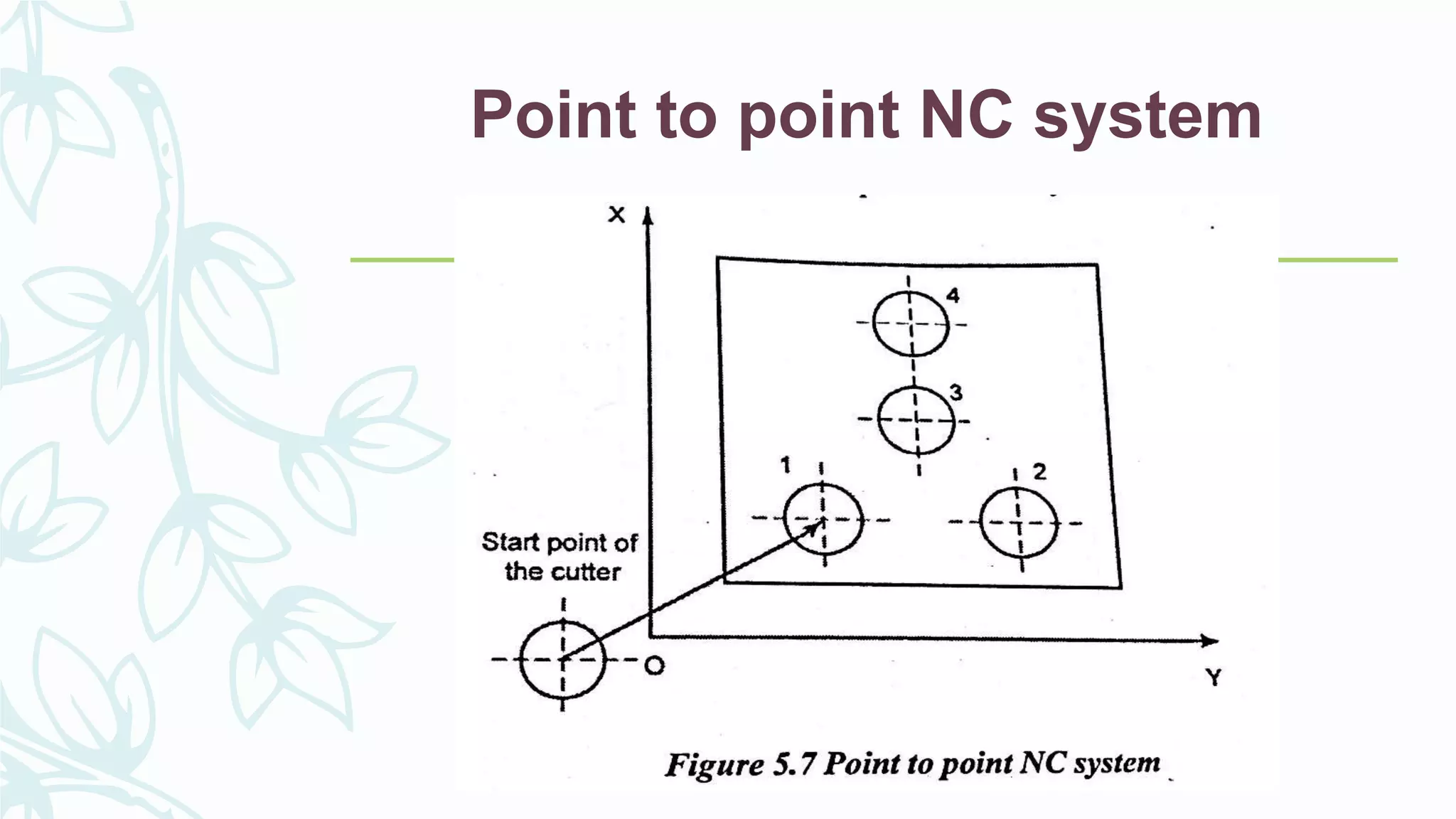
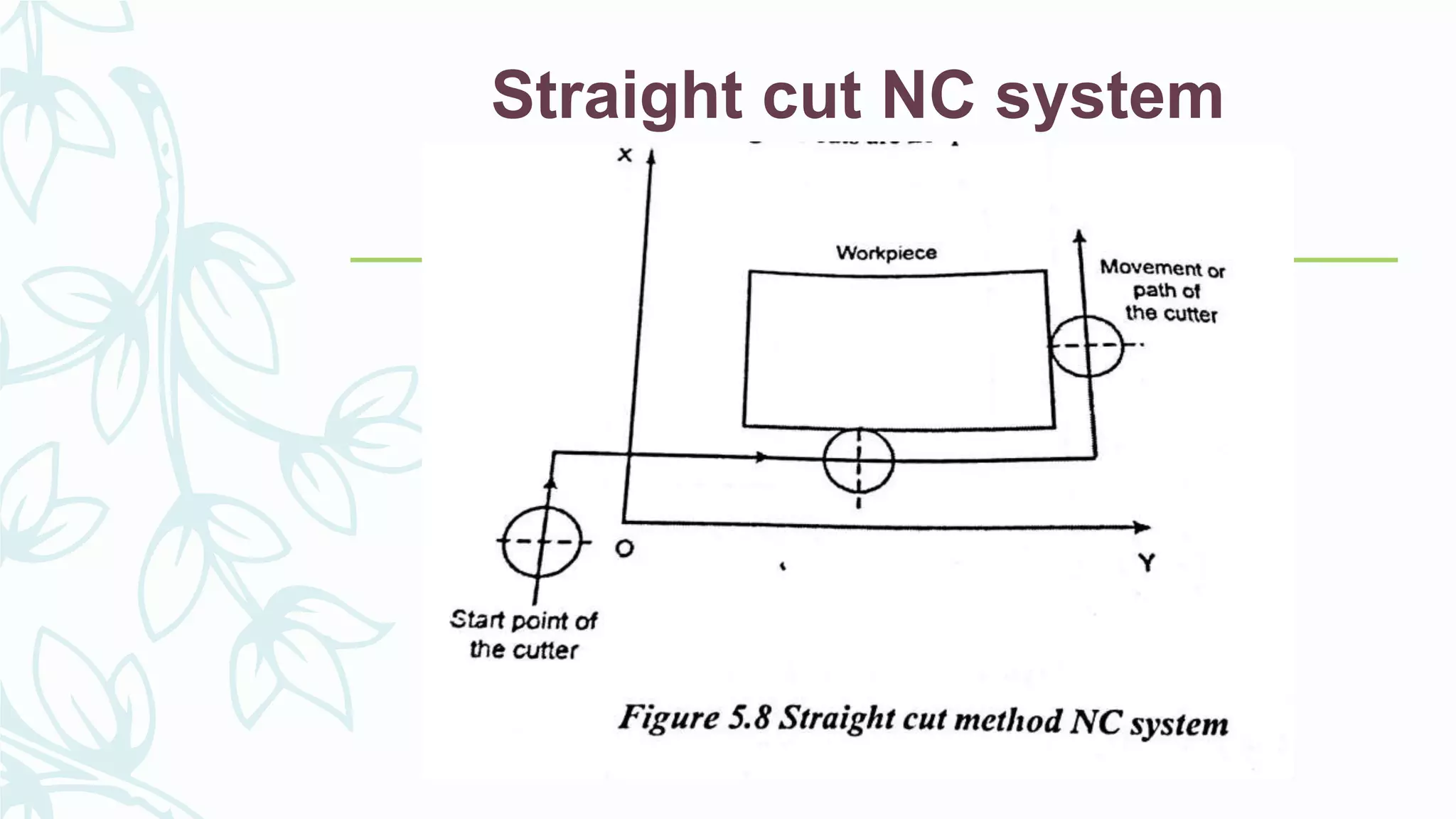
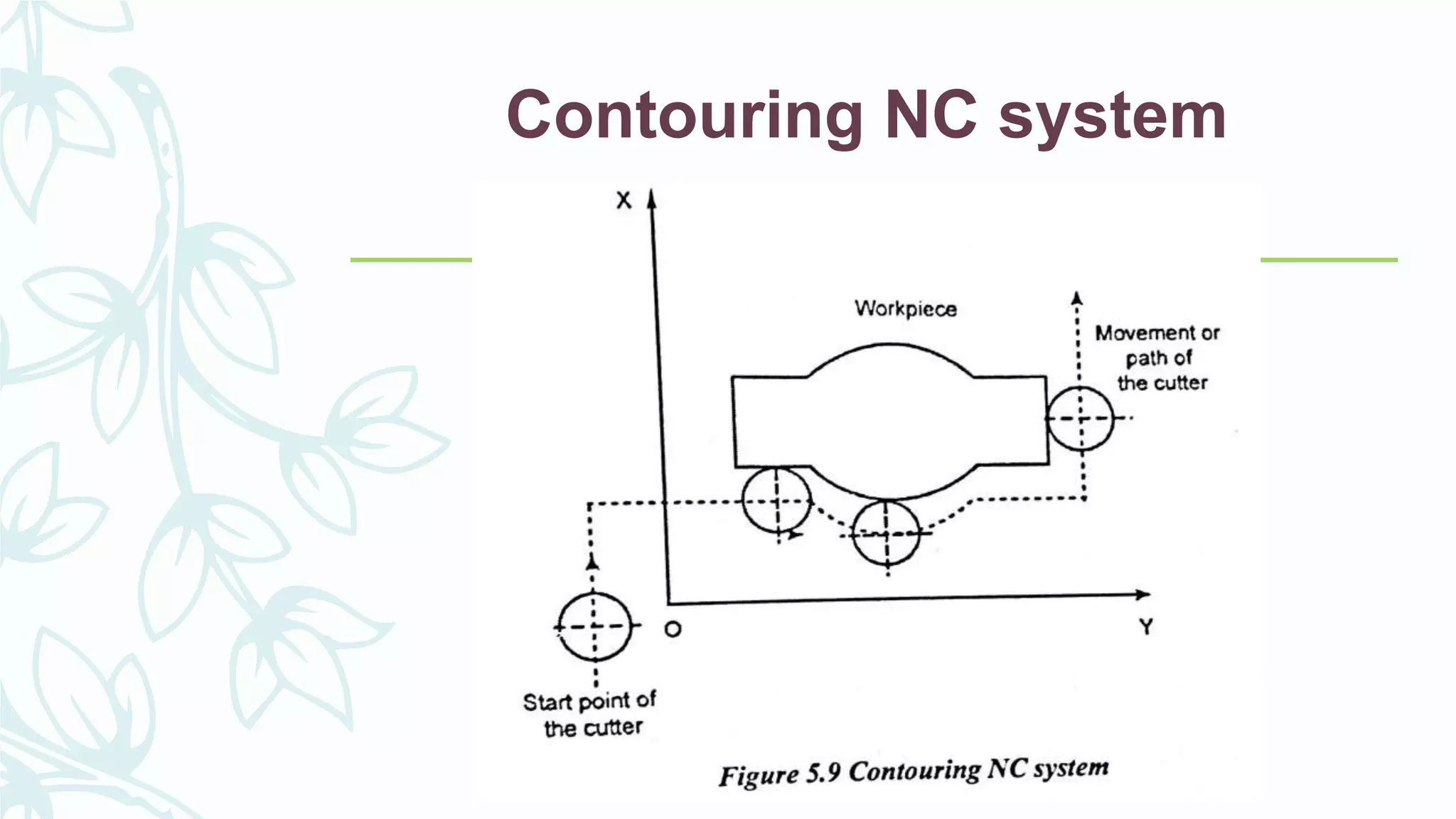
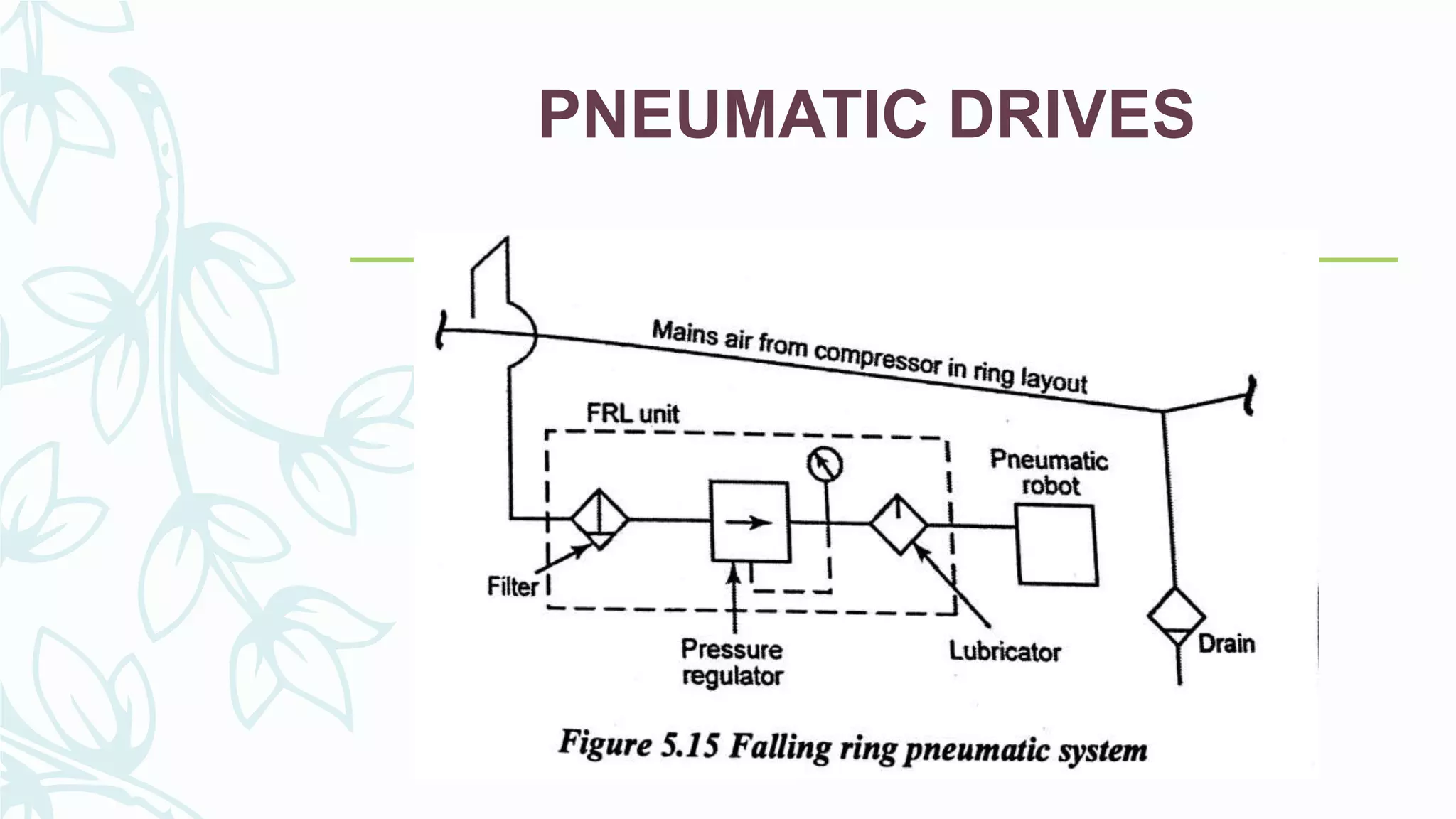
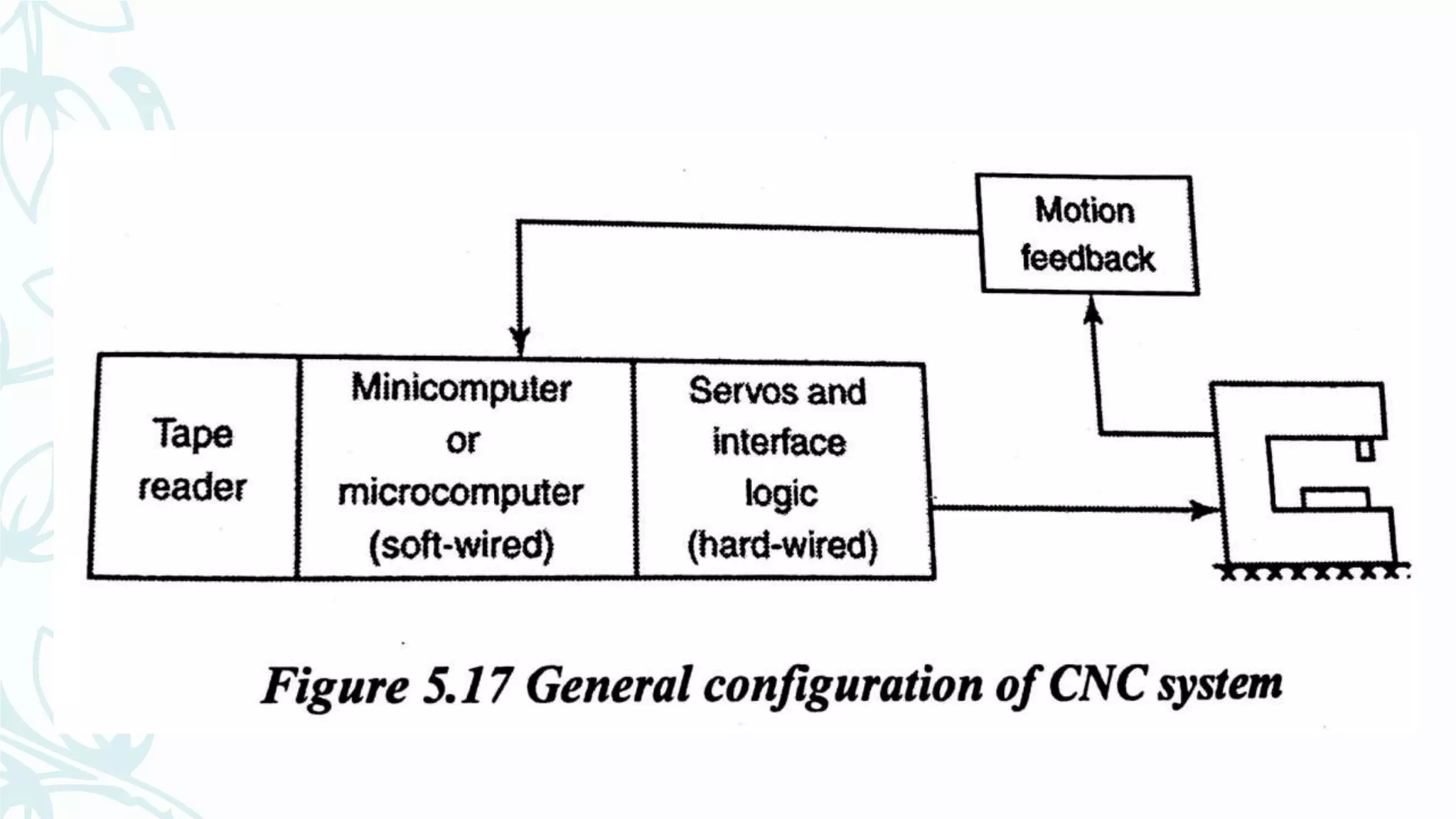
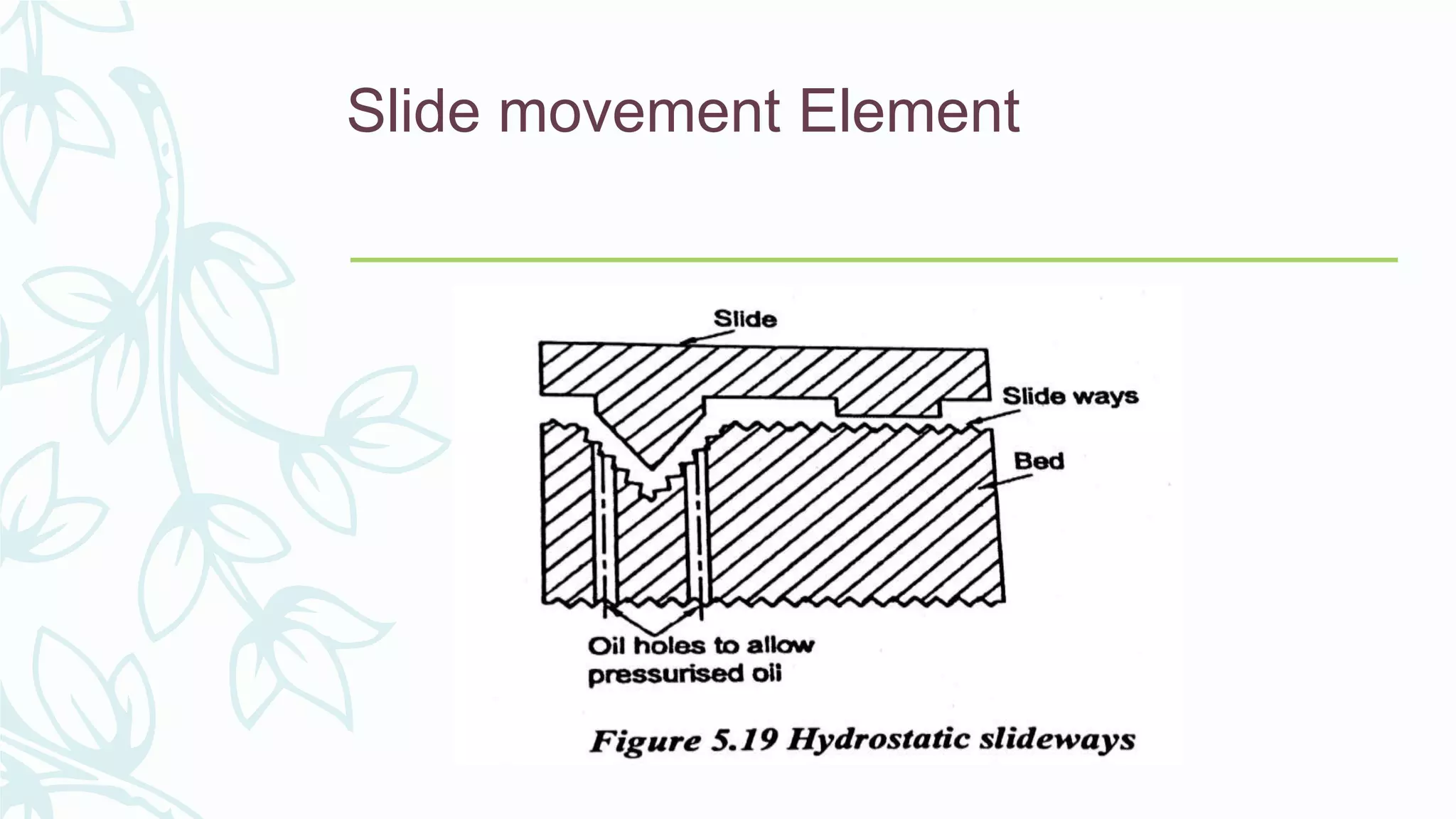
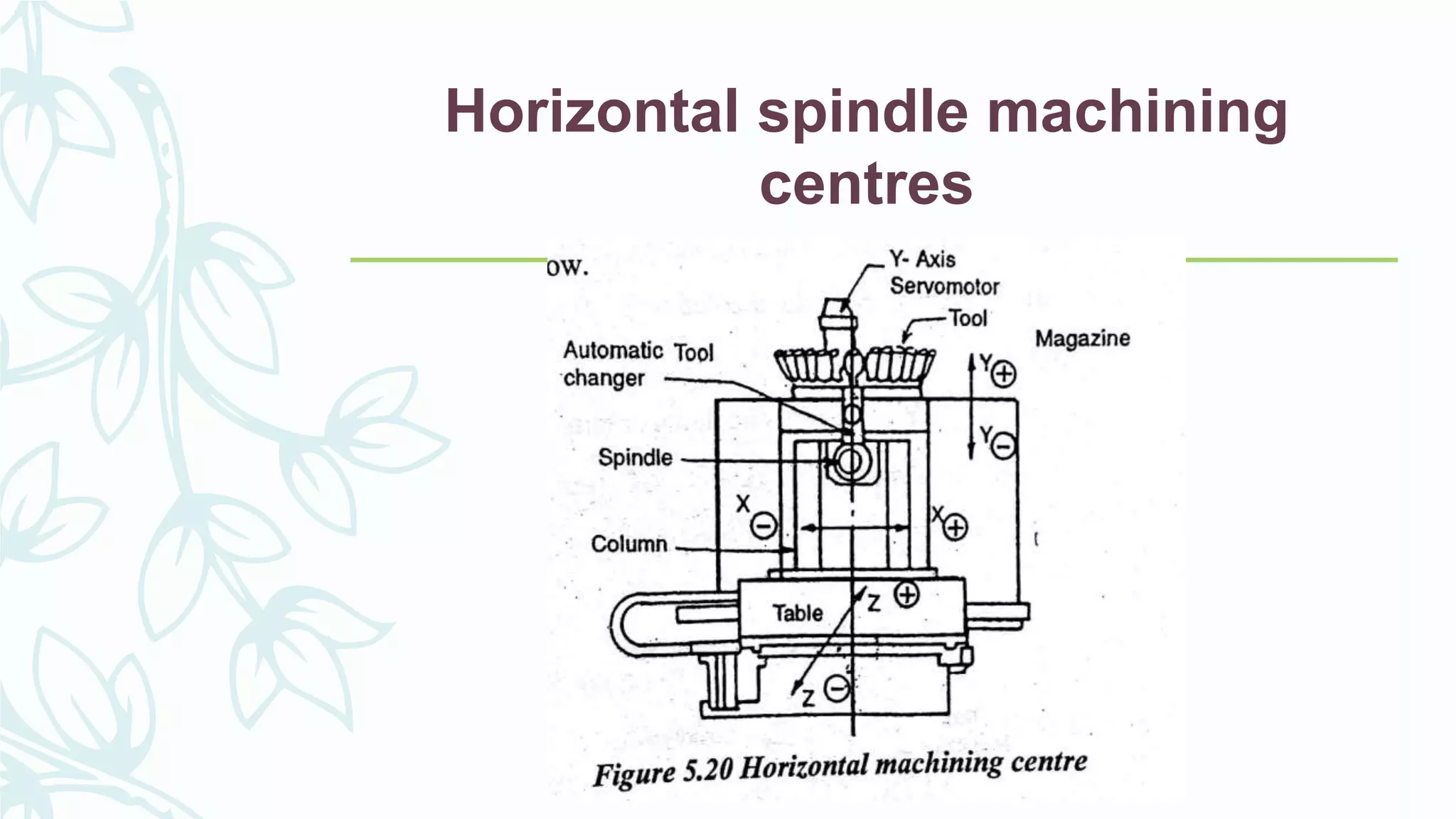
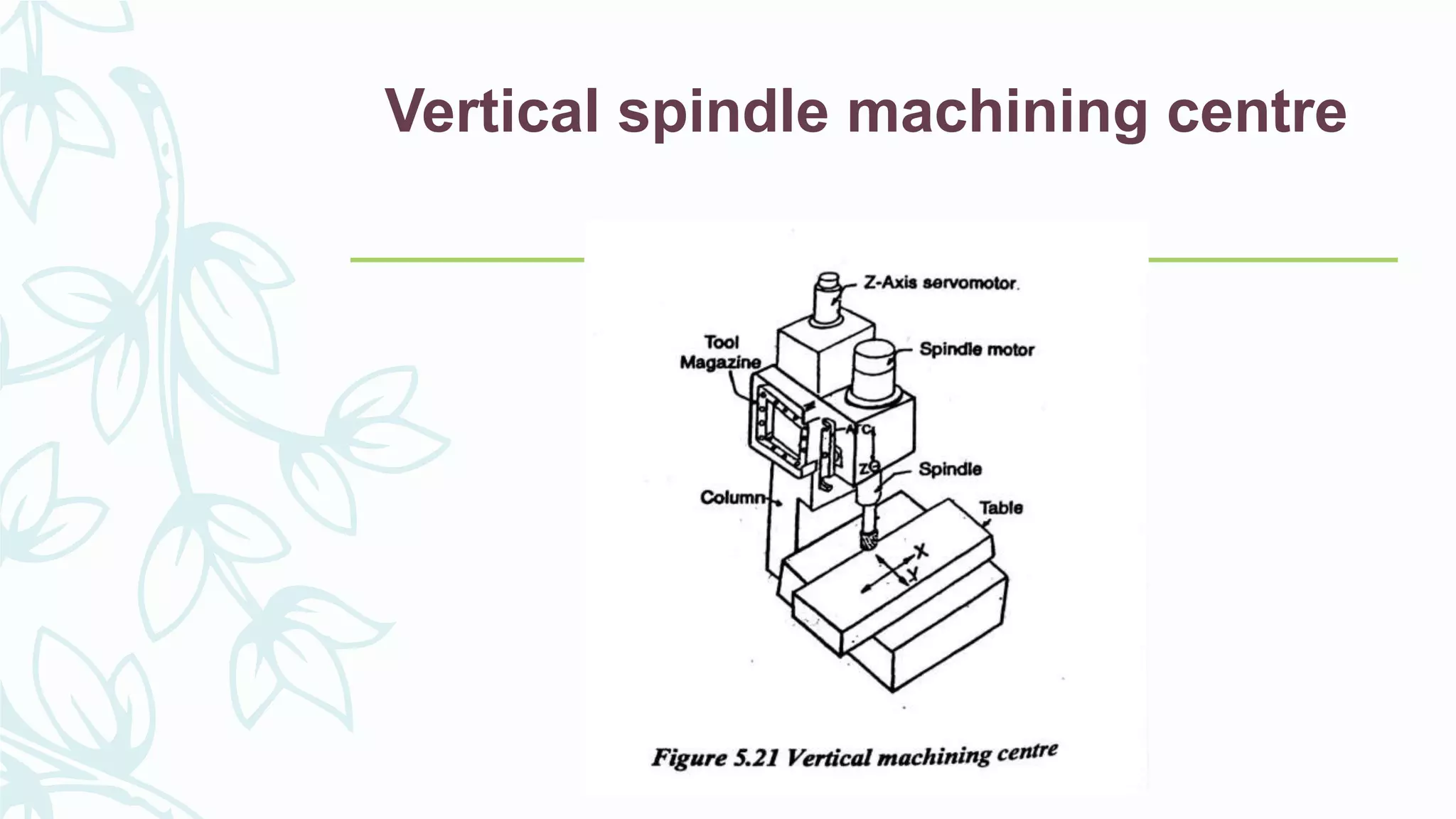
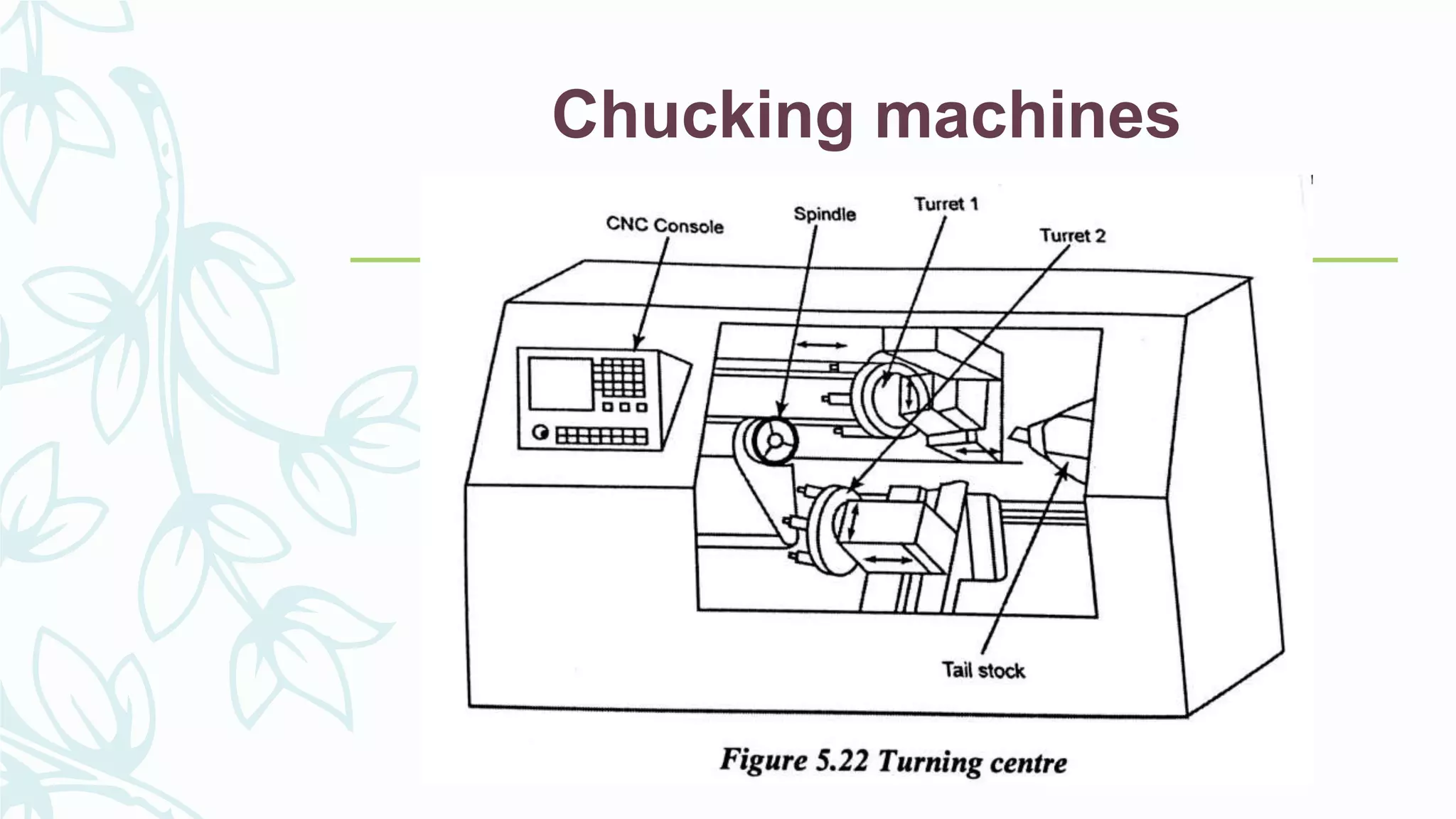
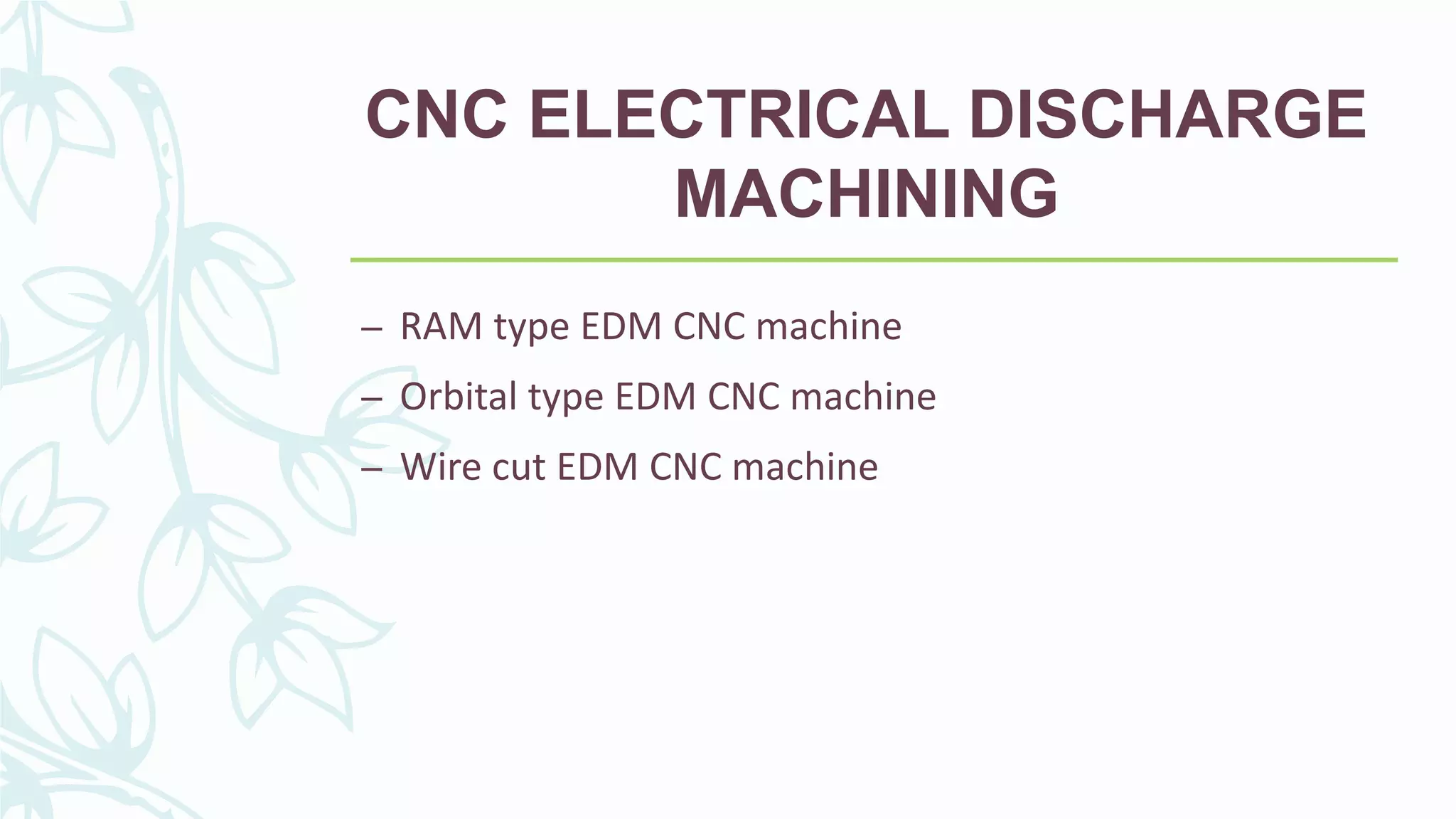
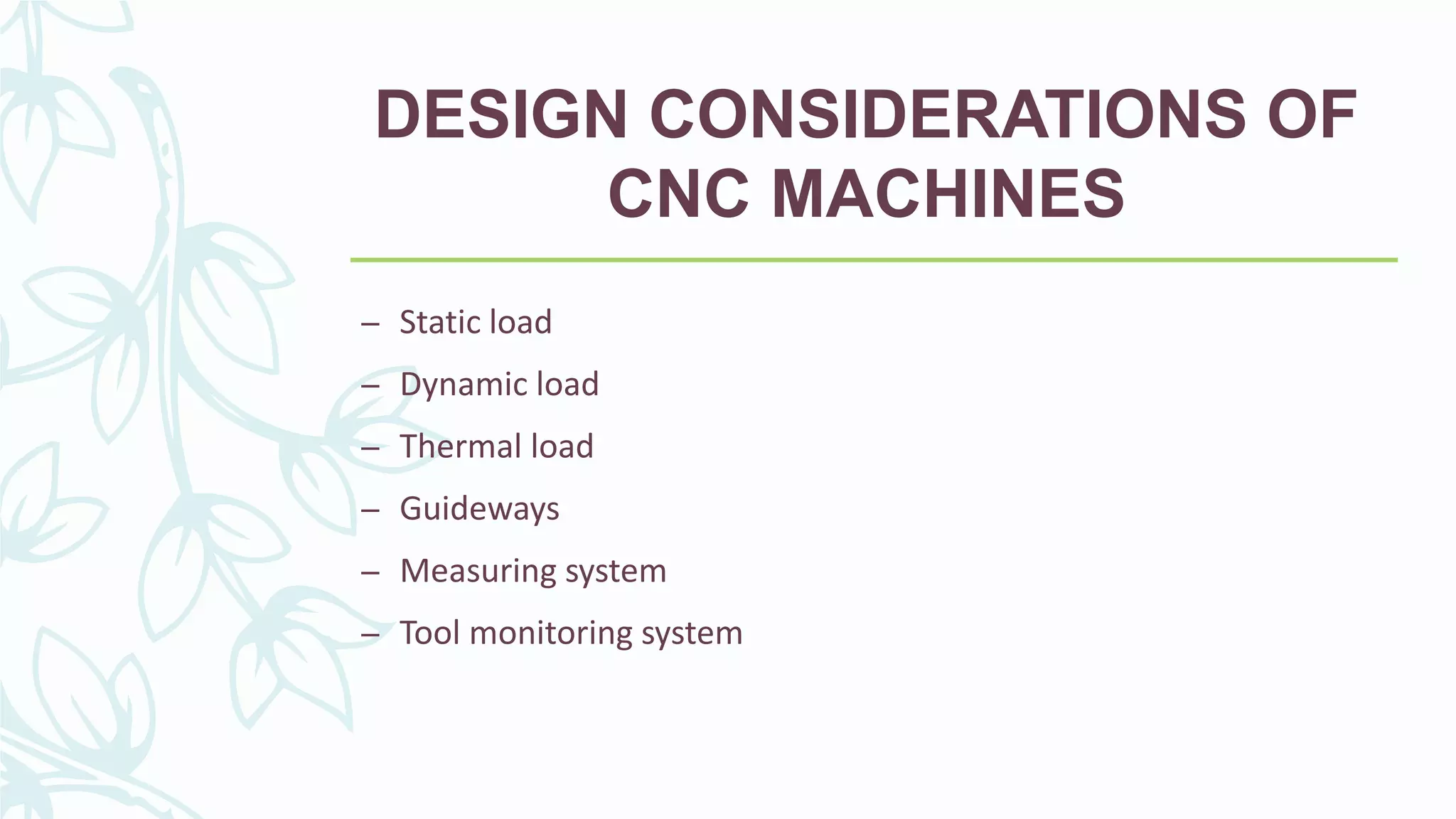
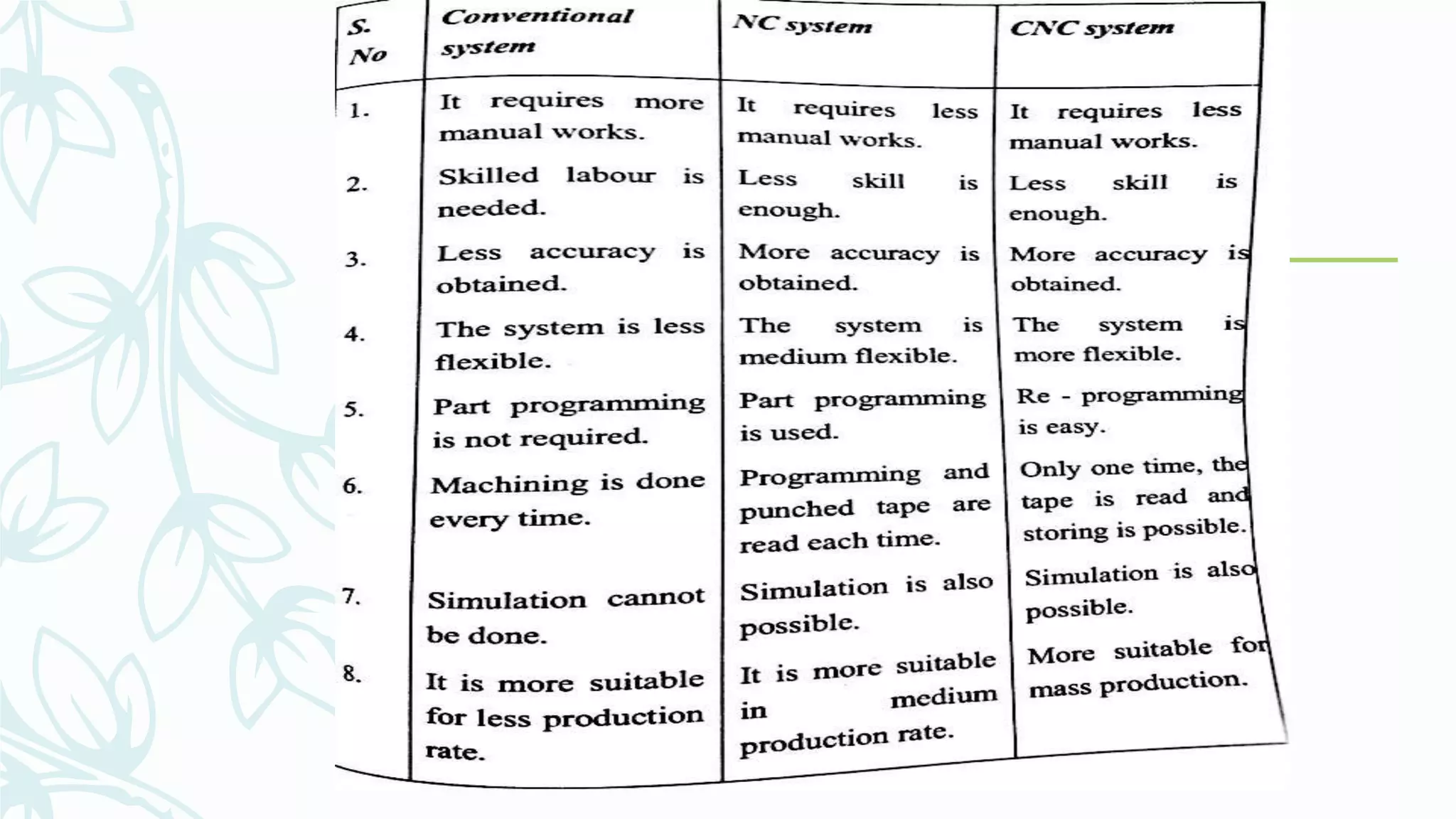
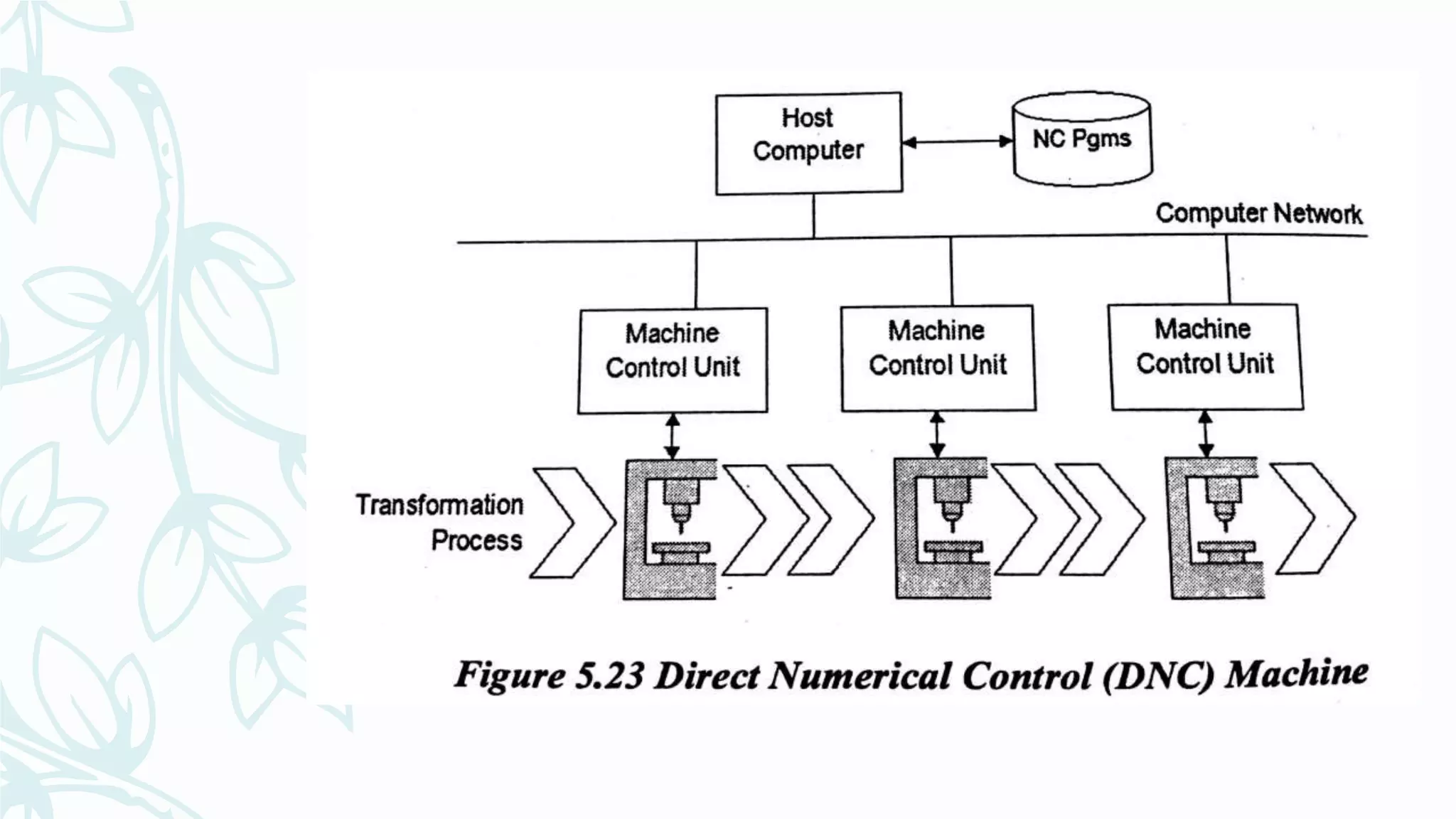
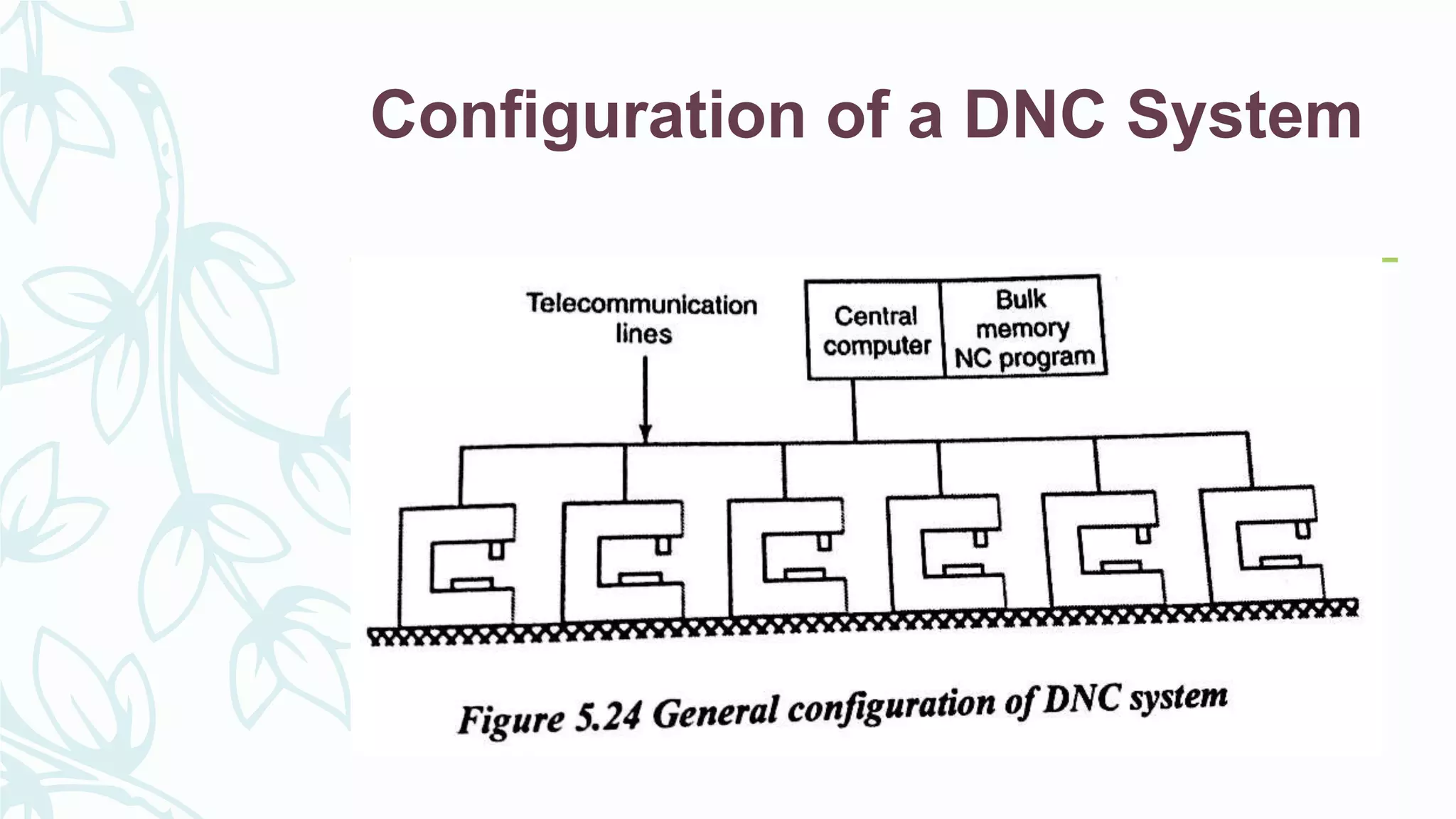
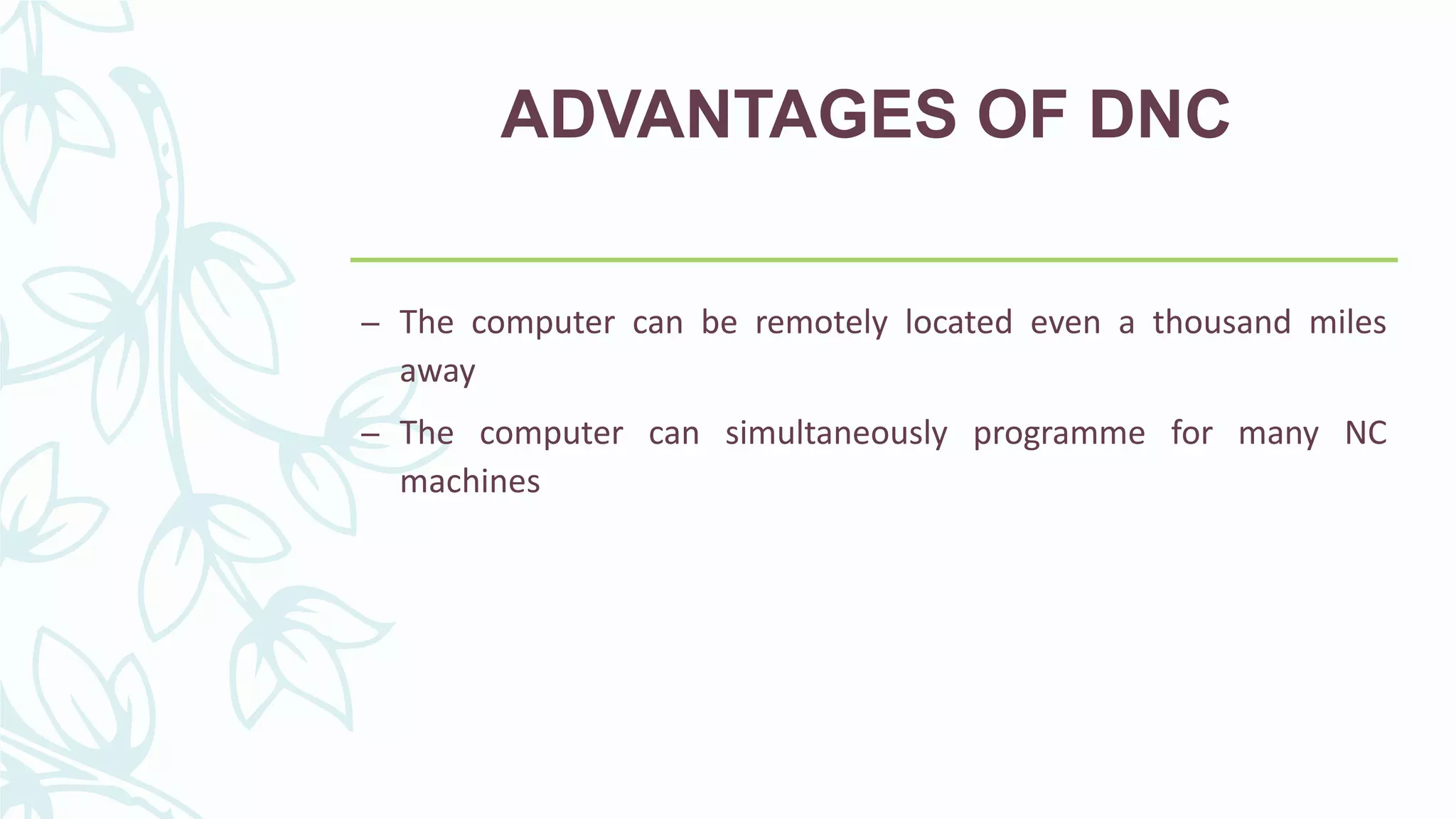
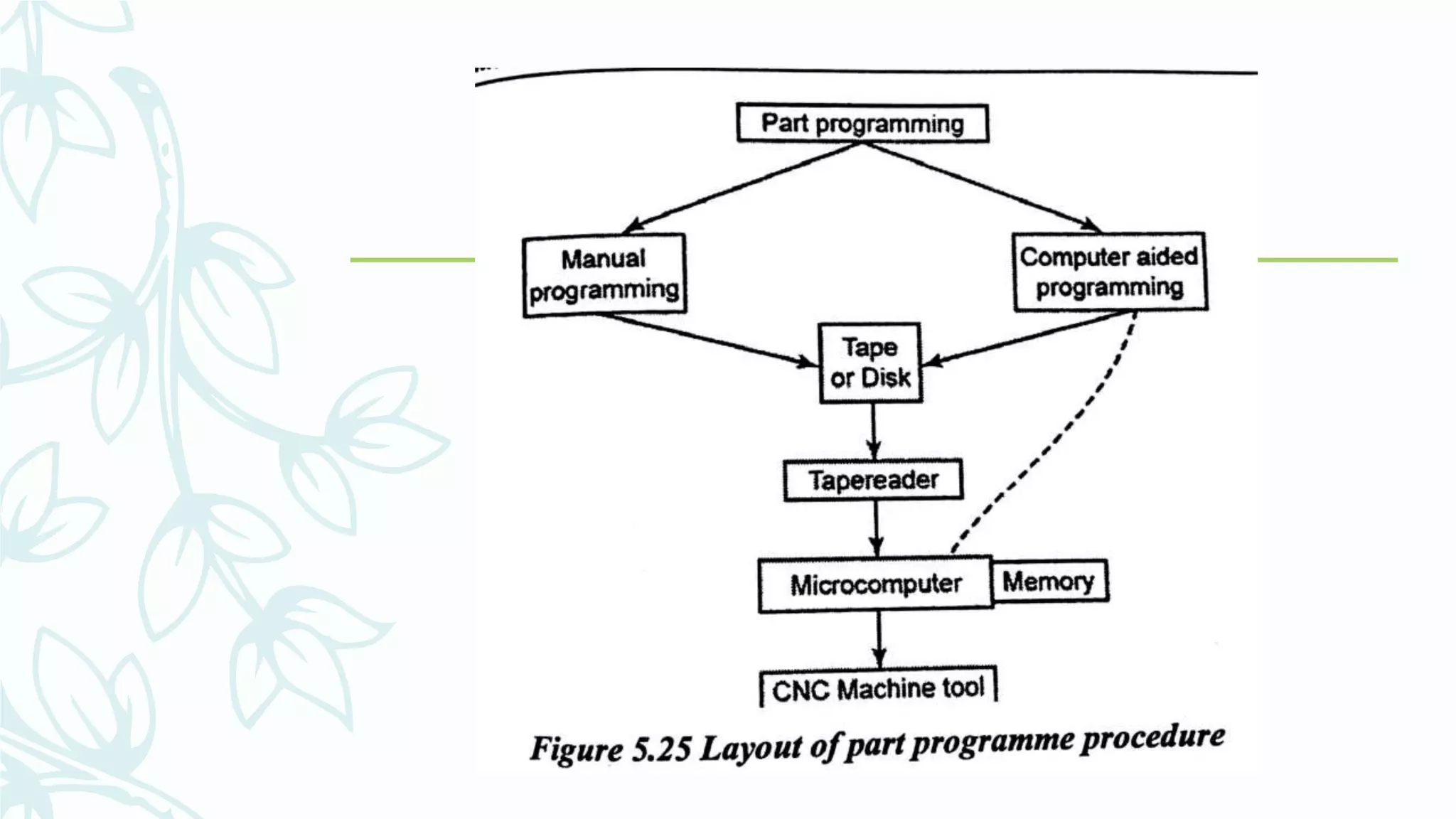
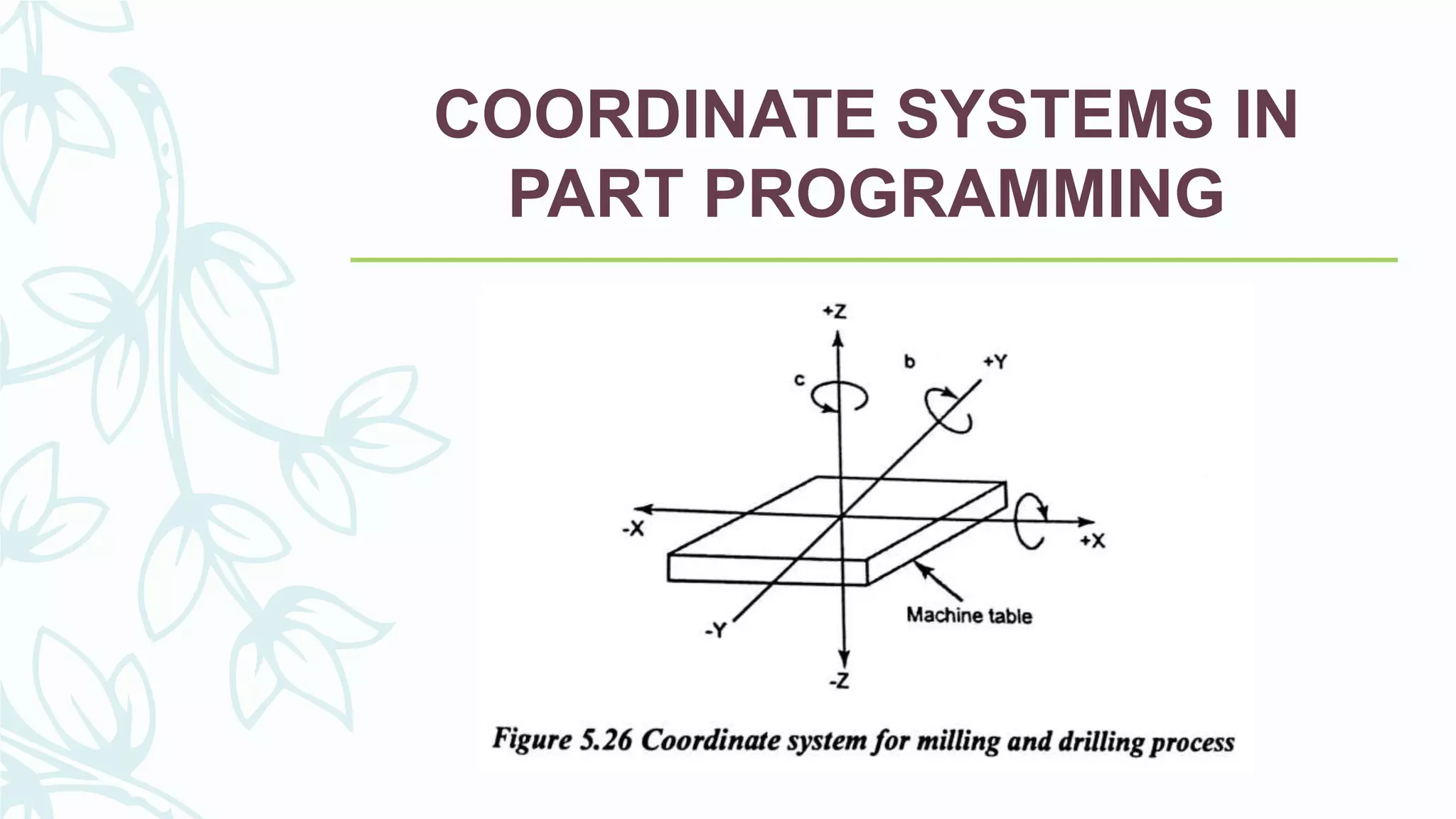
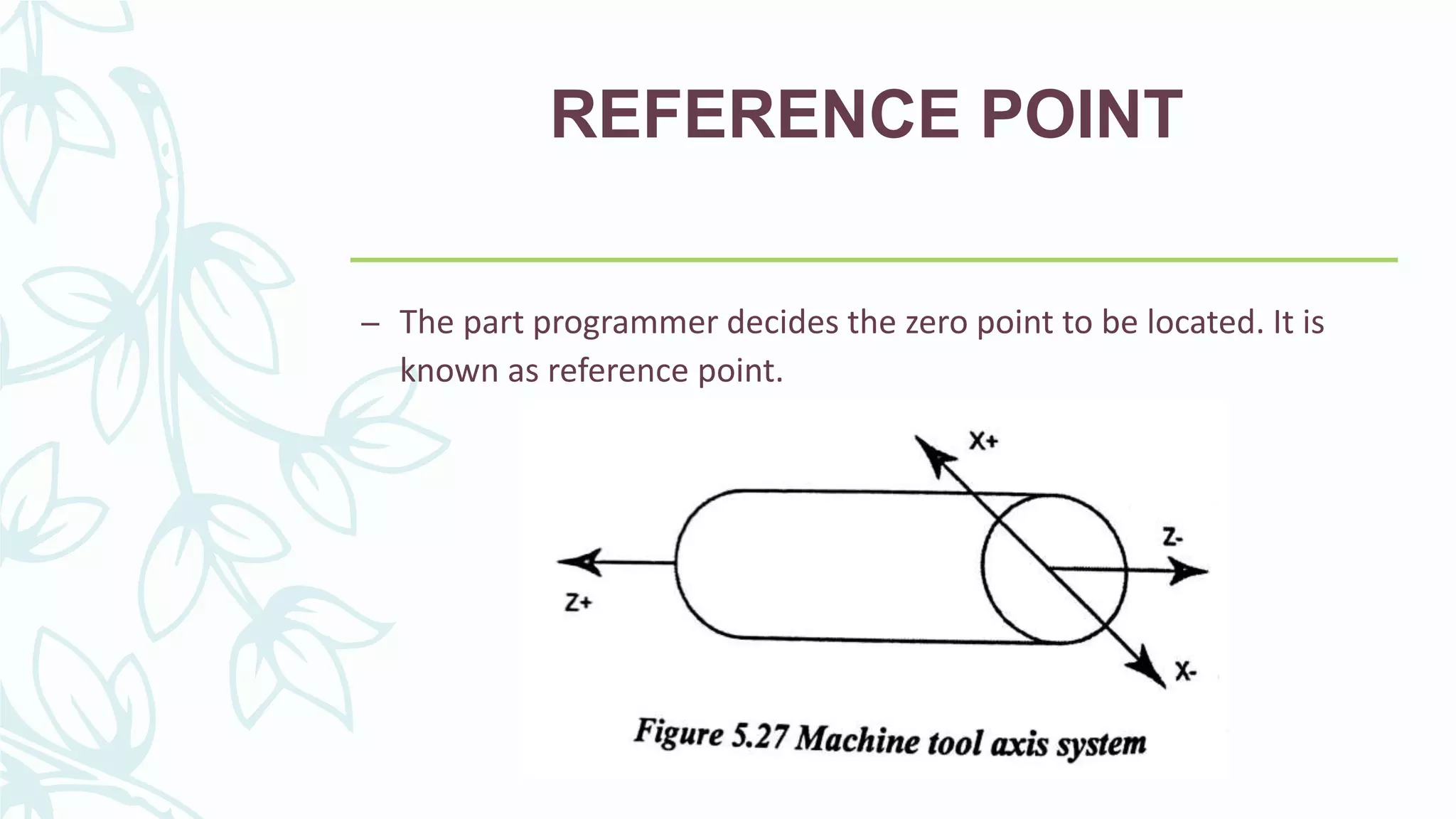
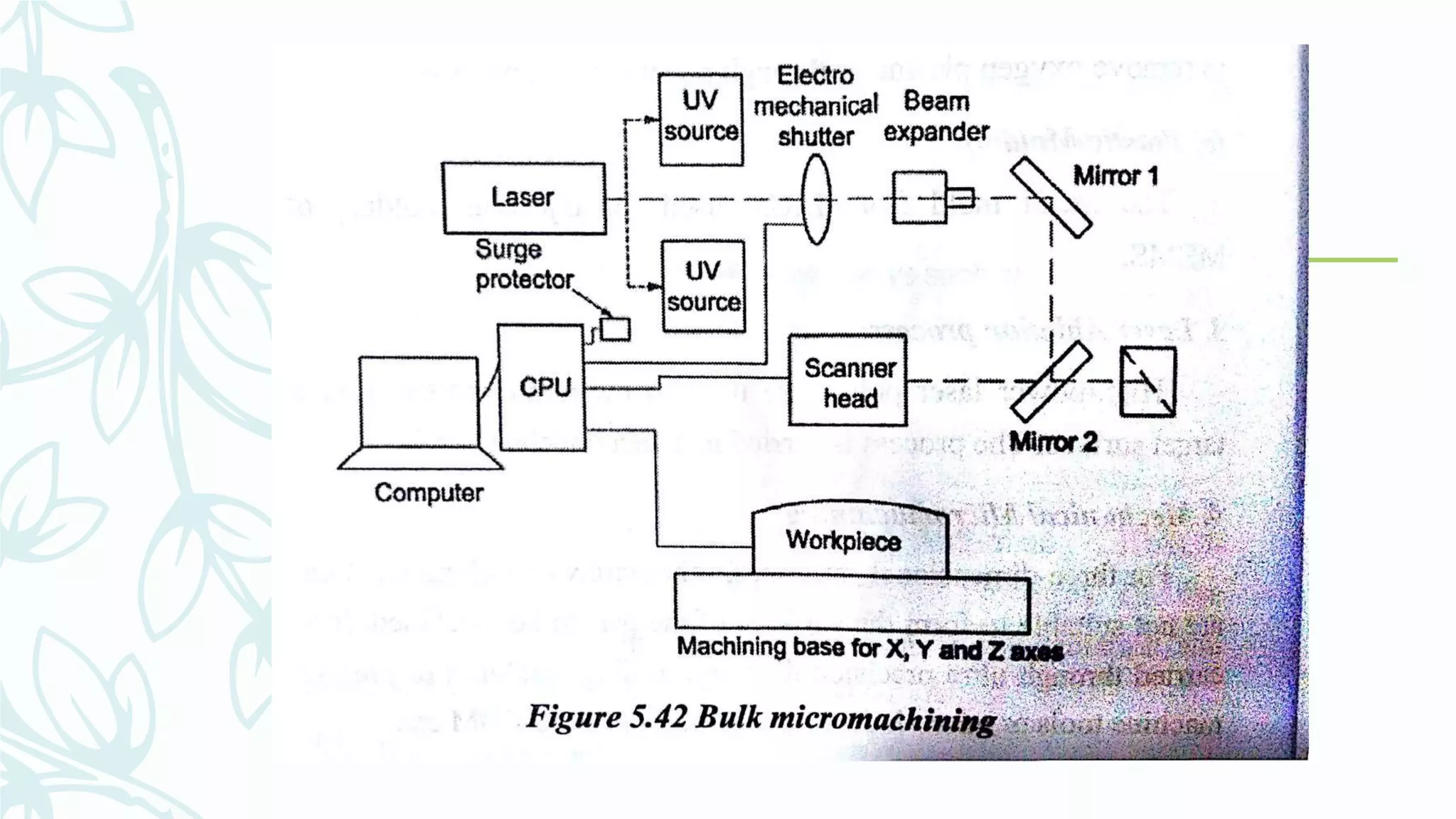
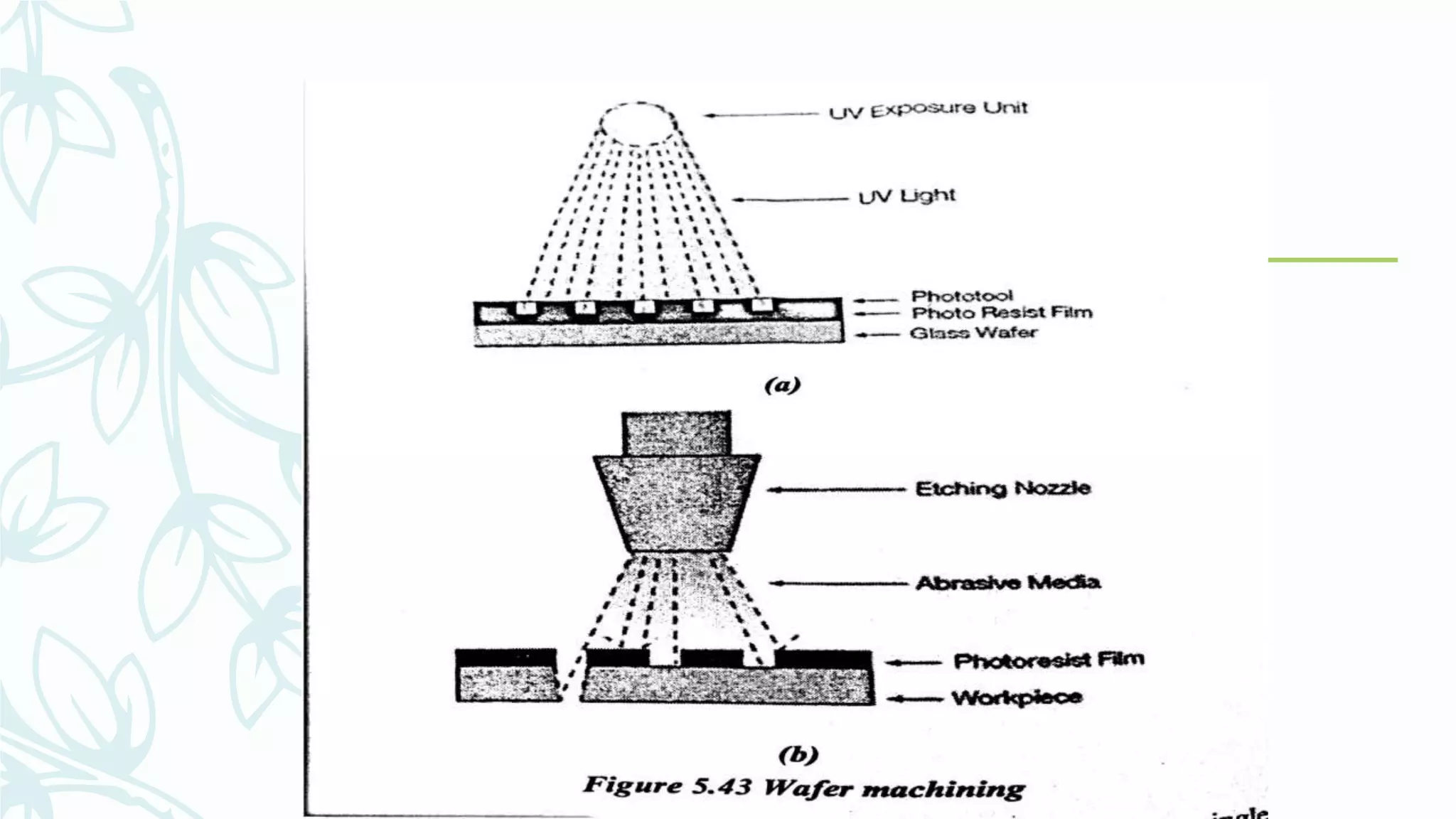
This document provides information on numerical control systems and computer numerical control (CNC) systems. It defines numerical control and describes traditional NC, CNC, and DNC systems. It discusses the basic components of NC systems including software, machine control units, and machine tools. It also covers CNC machine construction, driving systems, tooling systems, applications, advantages, and disadvantages of NC and CNC machines. Finally, it discusses topics like part programming fundamentals, coordinate systems, canned cycles, and micromachining.