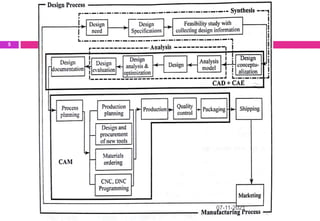
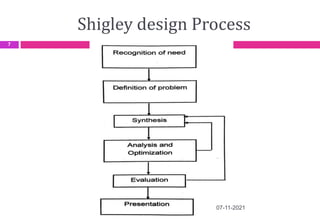
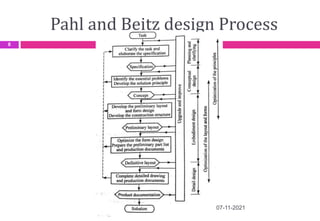
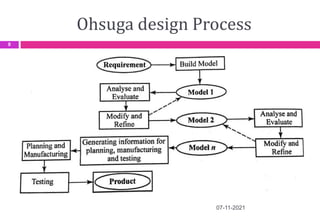
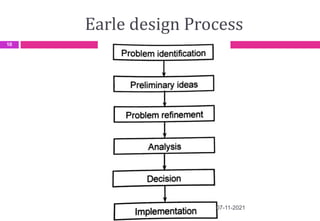
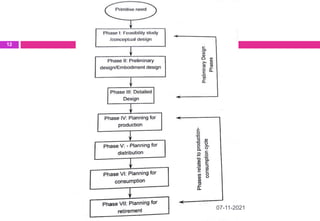
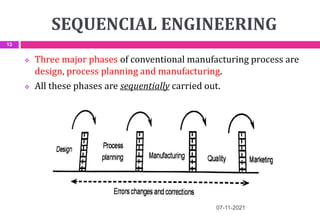
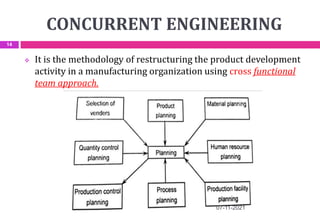
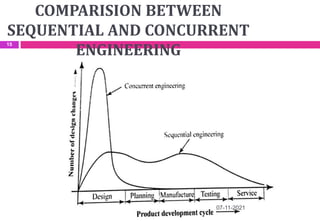
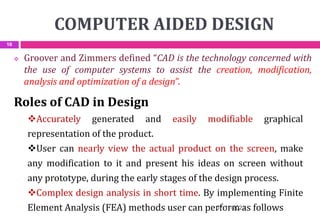
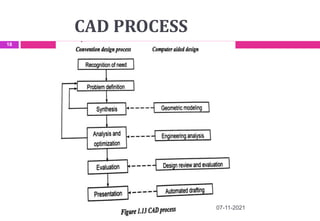
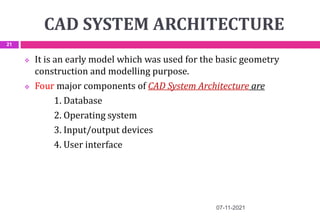
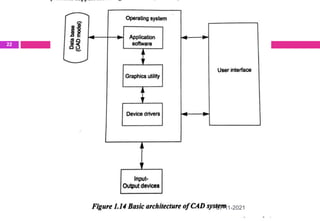
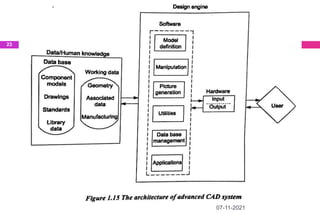
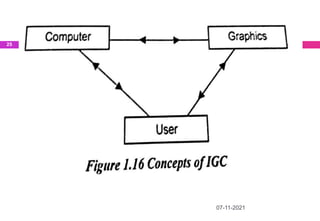
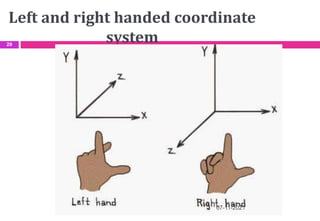
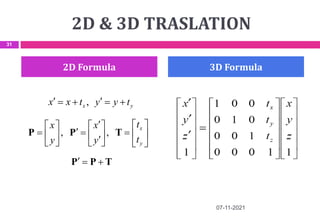
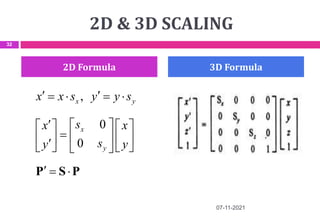
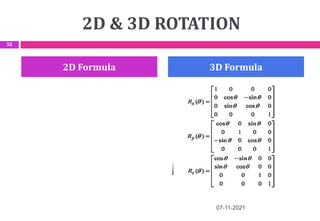
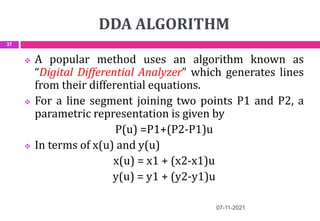
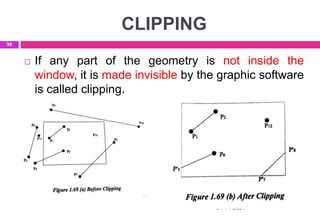
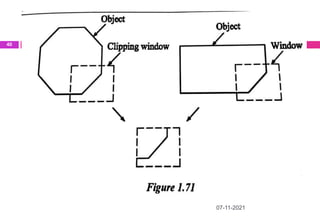
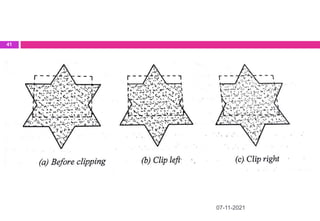
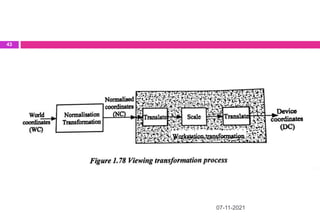
This document provides an overview of computer aided design (CAD) and computer graphics. It discusses the CAD design process, including sequential and concurrent engineering. CAD systems use computer graphics to represent geometric models in 2D and 3D coordinate systems. Transformations like translation, scaling, and rotation can manipulate these models. The document also describes techniques for line drawing, clipping, and viewing transformations in CAD and computer graphics.