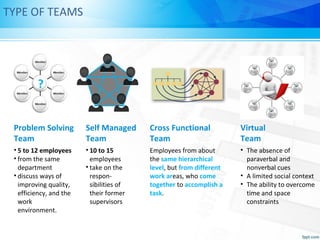
This document discusses what makes an effective work team. It defines a team as a small group of people with complementary skills committed to a common purpose and shared goals. The key points made about effective teams are:
1) Teams typically outperform individuals because they are able to utilize each member's talents better and are more flexible and responsive to changes.
2) Teams facilitate employee involvement and are an effective way to democratize an organization and increase motivation.
3) For a team to be effective it needs the right context, composition, and processes. The context includes adequate resources, leadership, trust, and rewards. The composition considers the abilities, personalities, roles, and diversity of members. Effective processes include a