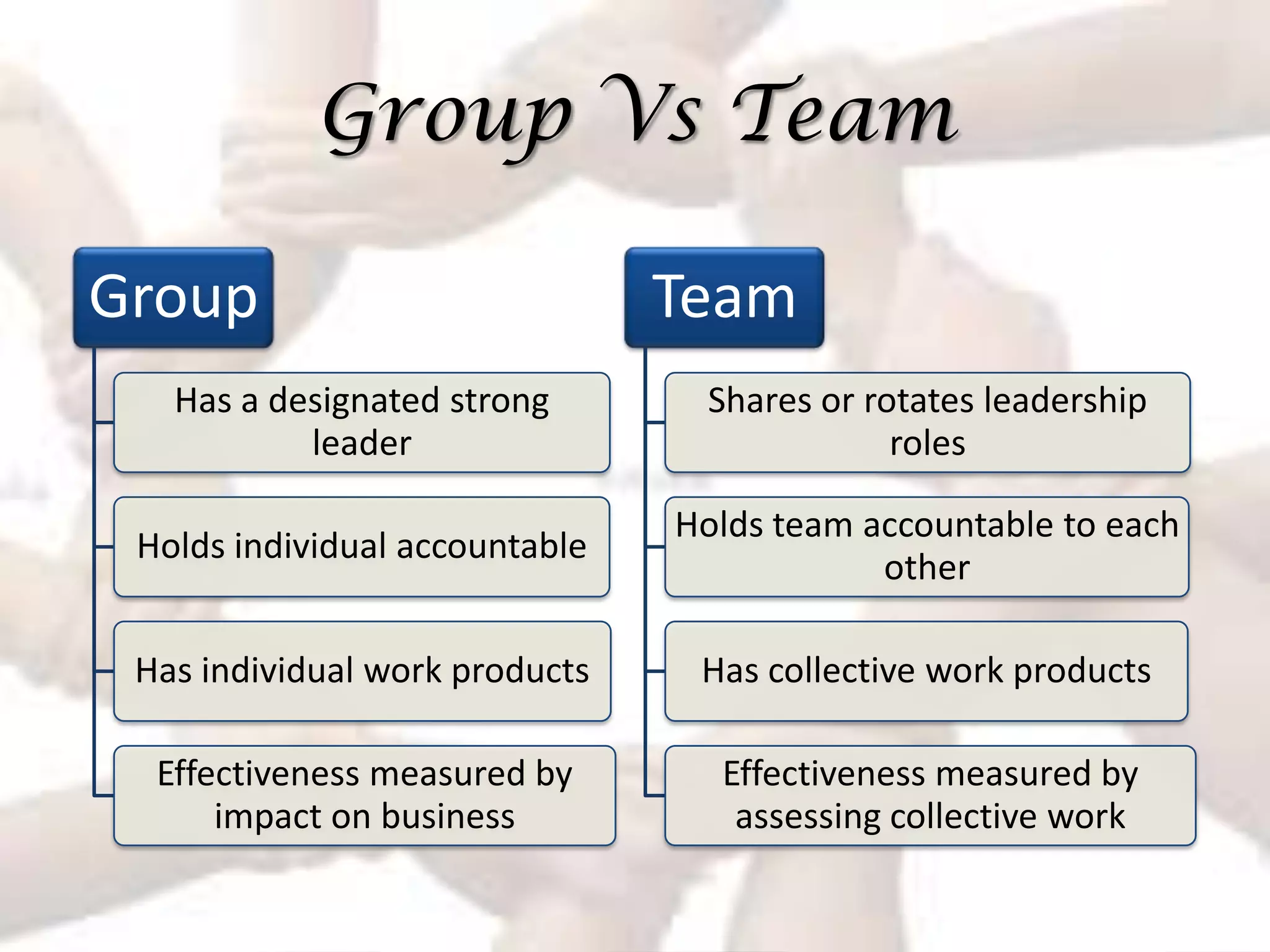
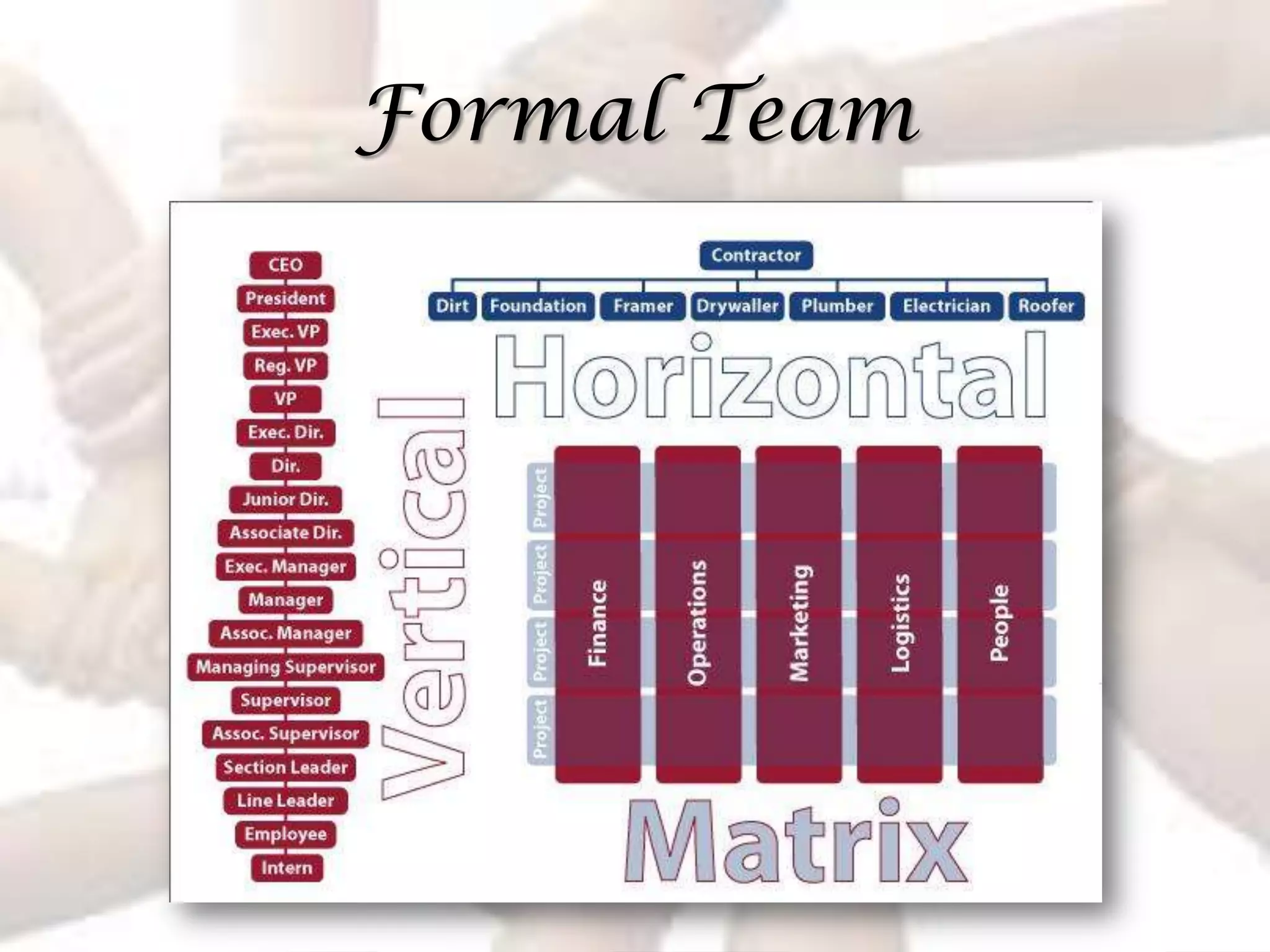
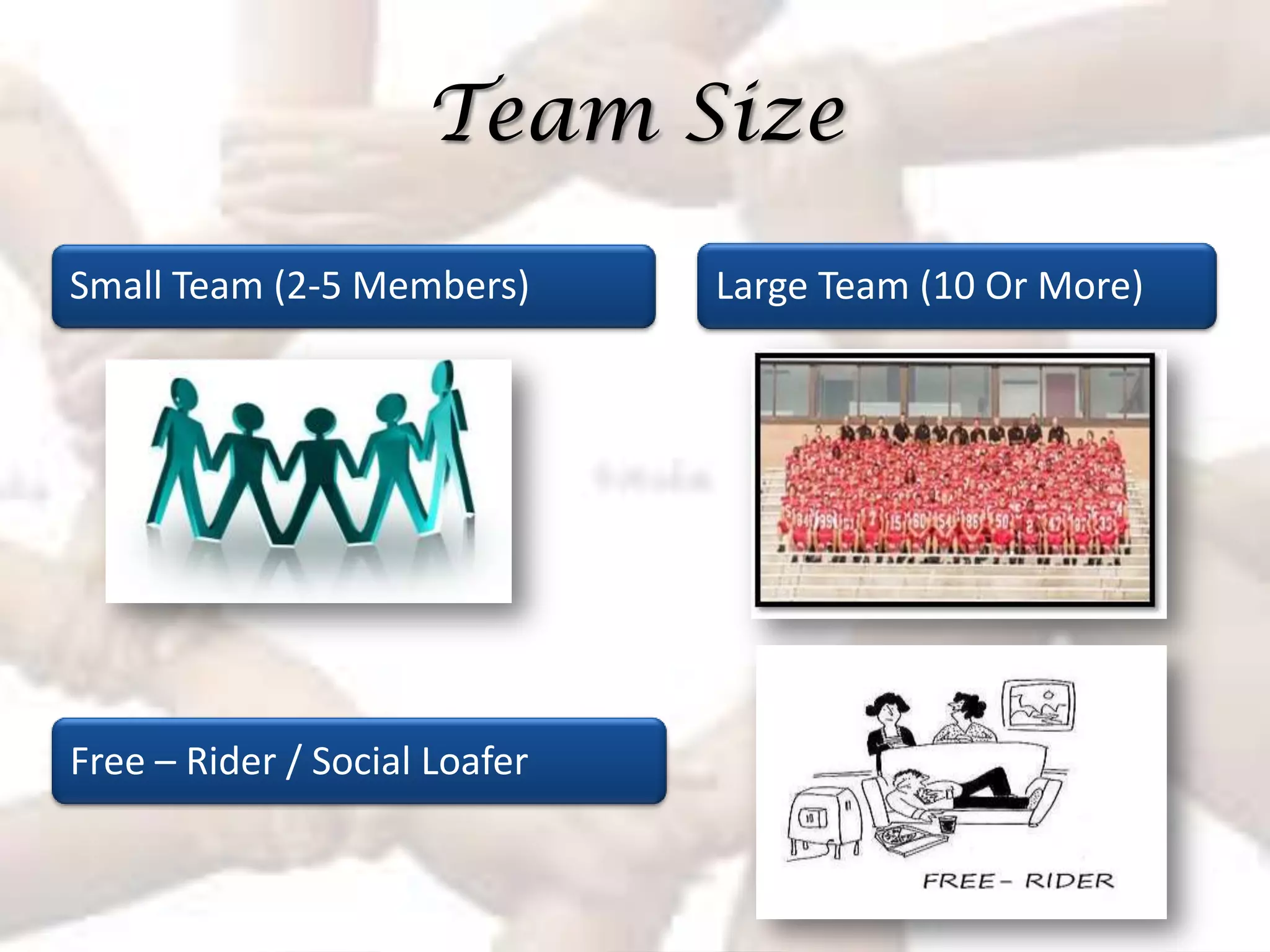
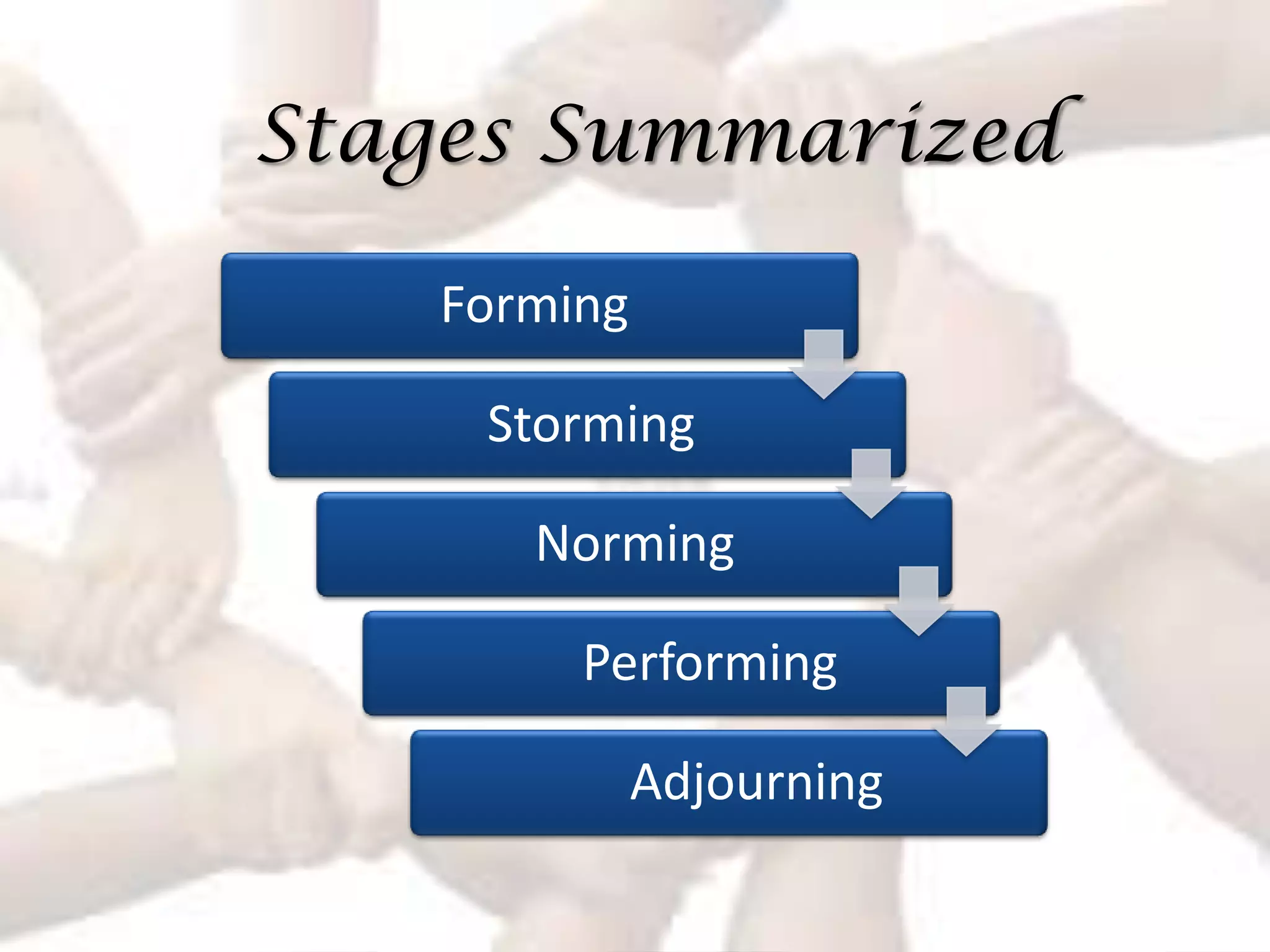
The document summarizes key aspects of effective teamwork, including defining what a team is, different types of teams, team characteristics, processes, and factors that influence effectiveness. It discusses formal vs informal teams, characteristics like size and diversity, stages of team development, cohesiveness, managing conflicts, and elements that determine a team's productivity, member satisfaction, and ability to adapt.