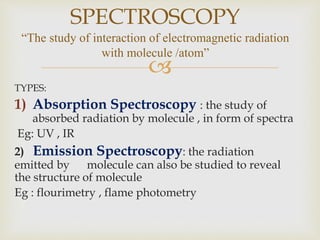
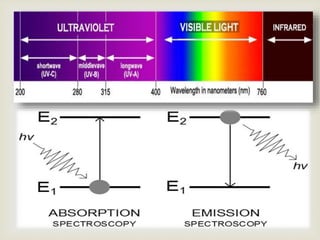
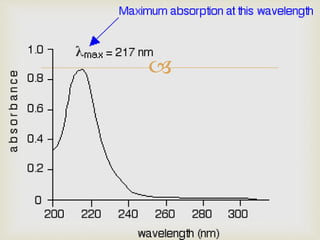
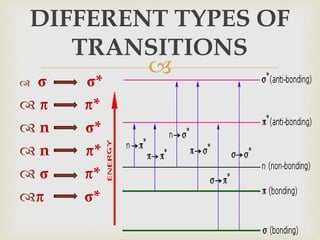
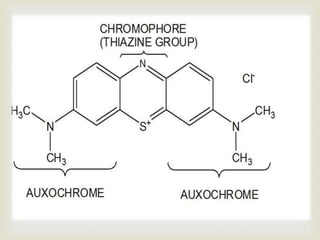
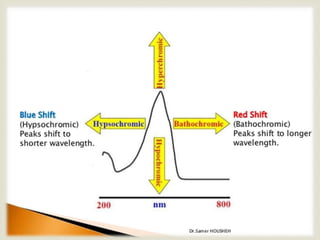
UV spectroscopy involves promoting electrons from the ground state to excited states of molecules using ultraviolet radiation between 200-400 nm. The absorption of this radiation can be quantified using Beer's law and plotted in an absorption spectrum showing the wavelength of maximum absorption (λmax) and intensity (εmax). Chromophores are functional groups that absorb UV radiation, while auxochromes modify the absorption by inducing bathochromic, hypsochromic, hyperchromic, or hypochromic shifts.