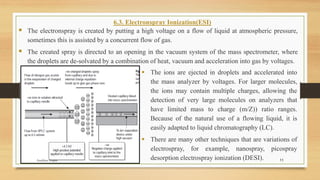
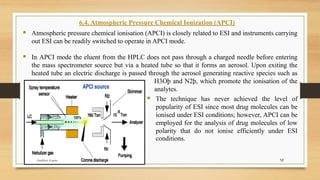
Mass spectrometry is a technique that identifies chemicals in a sample by measuring the mass-to-charge ratio and abundance of gas-phase ions. It works by ionizing a sample and separating the ions based on their mass-to-charge ratios, which are used to determine molecular structures. Key components of a mass spectrometer include an ion source that ionizes samples, a mass analyzer that separates ions, and a detector. Common ionization techniques are electron impact ionization, electrospray ionization, and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization. Popular mass analyzers include quadrupole, time-of-flight, and magnetic sector instruments. Mass spectrometry is useful for characterizing drugs, raw materials, and








![16
7.4. Analyser
▪ A mass analyser is a device that can separate atoms and molecules according to their mass.
▪ The five main characteristics for measuring the performance of a mass analyser are
1) The mass range limit or dynamic range
2) The analysis speed [u (m)S-1]
3) The transmission = No. of ion reaching the ions/No. of ions entering mass analyzer
4) The mass accuracy
5) The resolution.
▪ Mass analysers used are:
1.Magnetic sector mass analyser
2.Double focussing analyser
3.Quadrupole mass analyser
4.Time of Flight analyser (TOF)
5.Ion trap analyser
6.Ion cyclotron analyser
Anubhav Gupta](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ms-210519122452/85/mass-spectroscopy-16-320.jpg)