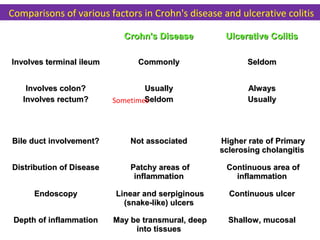
This document provides information about ulcerative colitis (UC) by discussing its epidemiology, morphology, clinical features, complications, diagnosis, comparisons to Crohn's disease, and indeterminate colitis. Key points include that UC is limited to the colon mucosa/submucosa, begins in the rectum and extends proximally, and causes bloody diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss. It has a higher risk of colon cancer than Crohn's disease. Histopathology shows crypt abscesses and a continuous area of colon inflammation. Around 10% of IBD cases are considered indeterminate colitis with overlapping UC and Crohn's features.