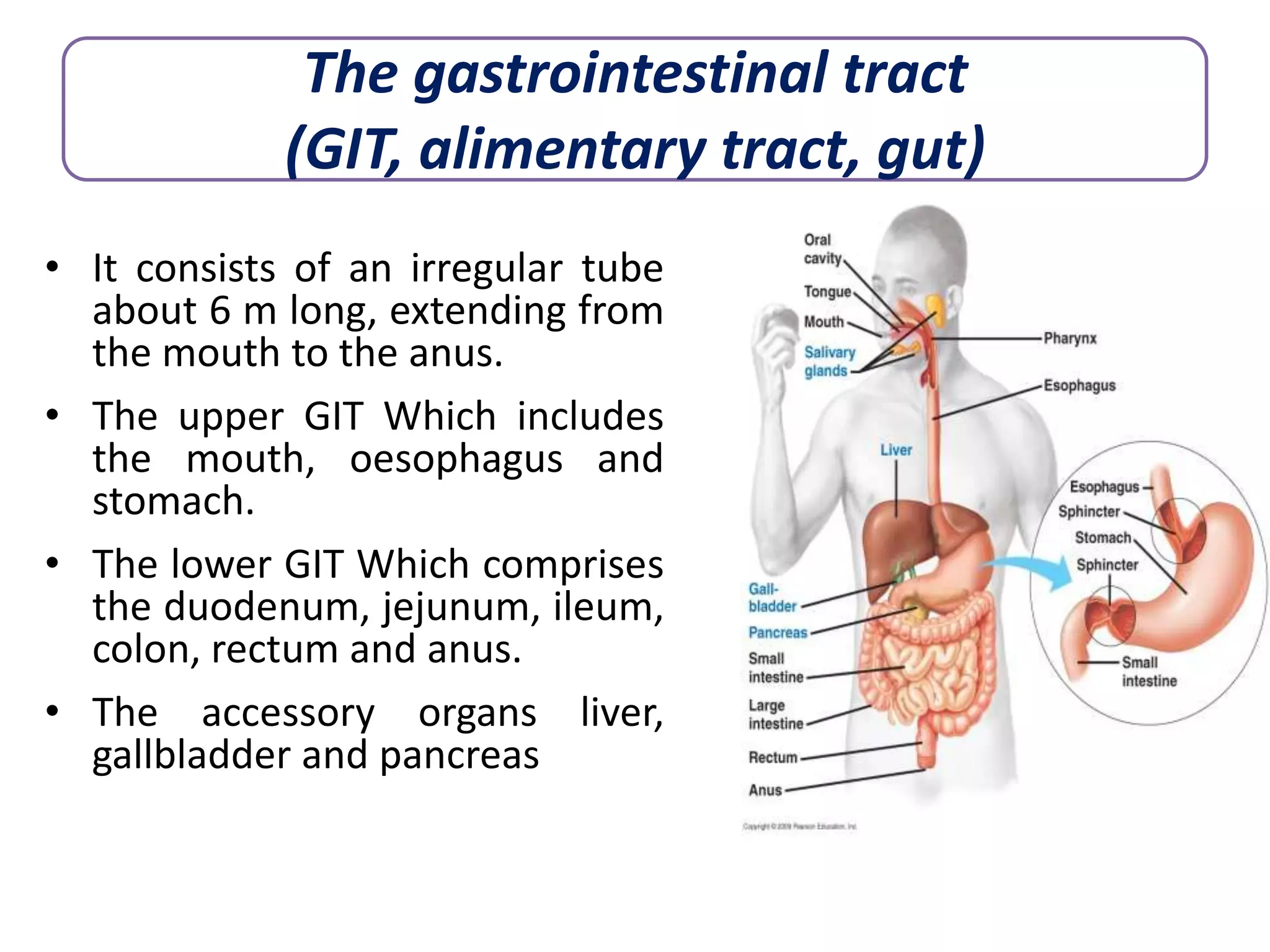
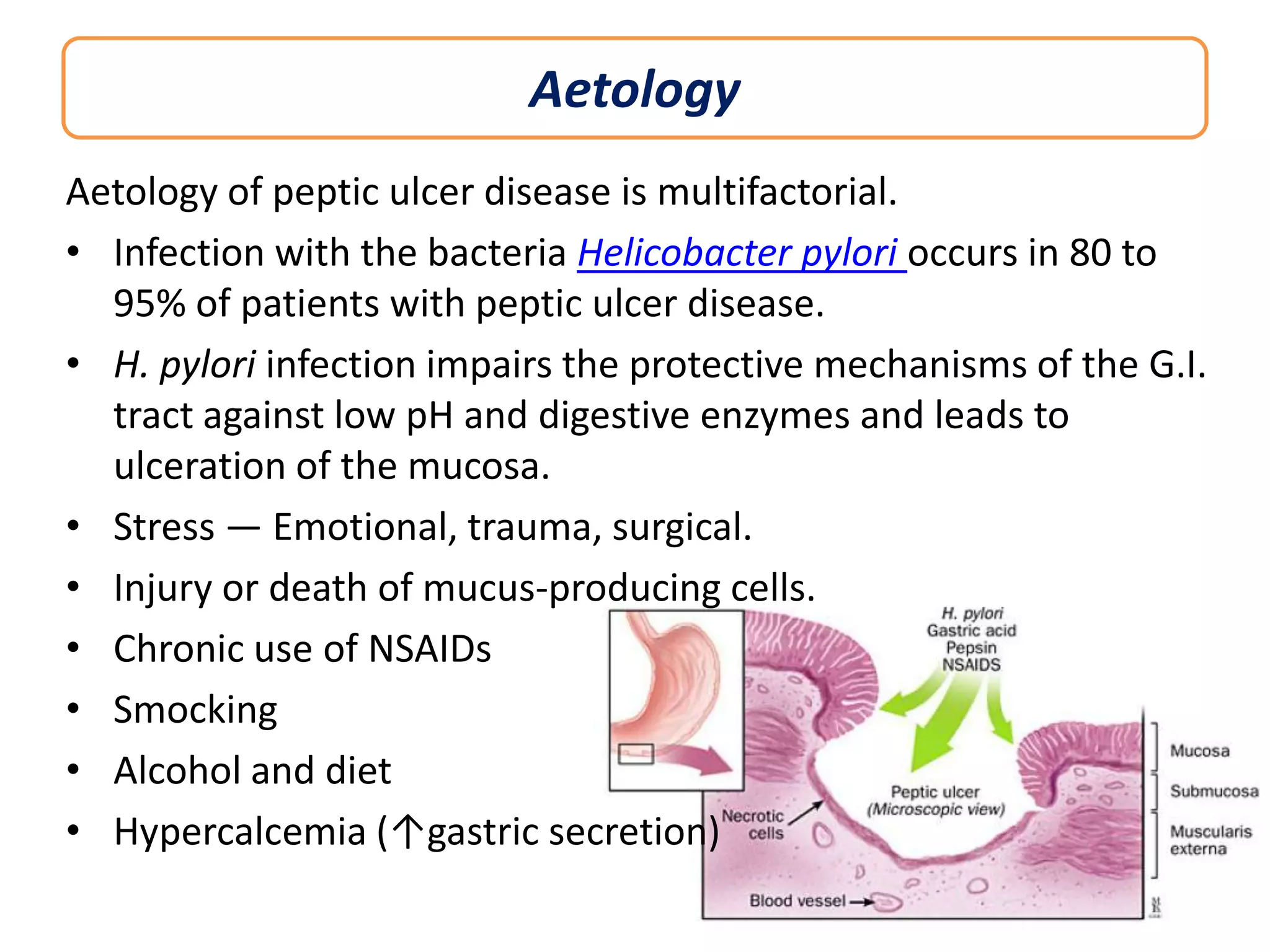
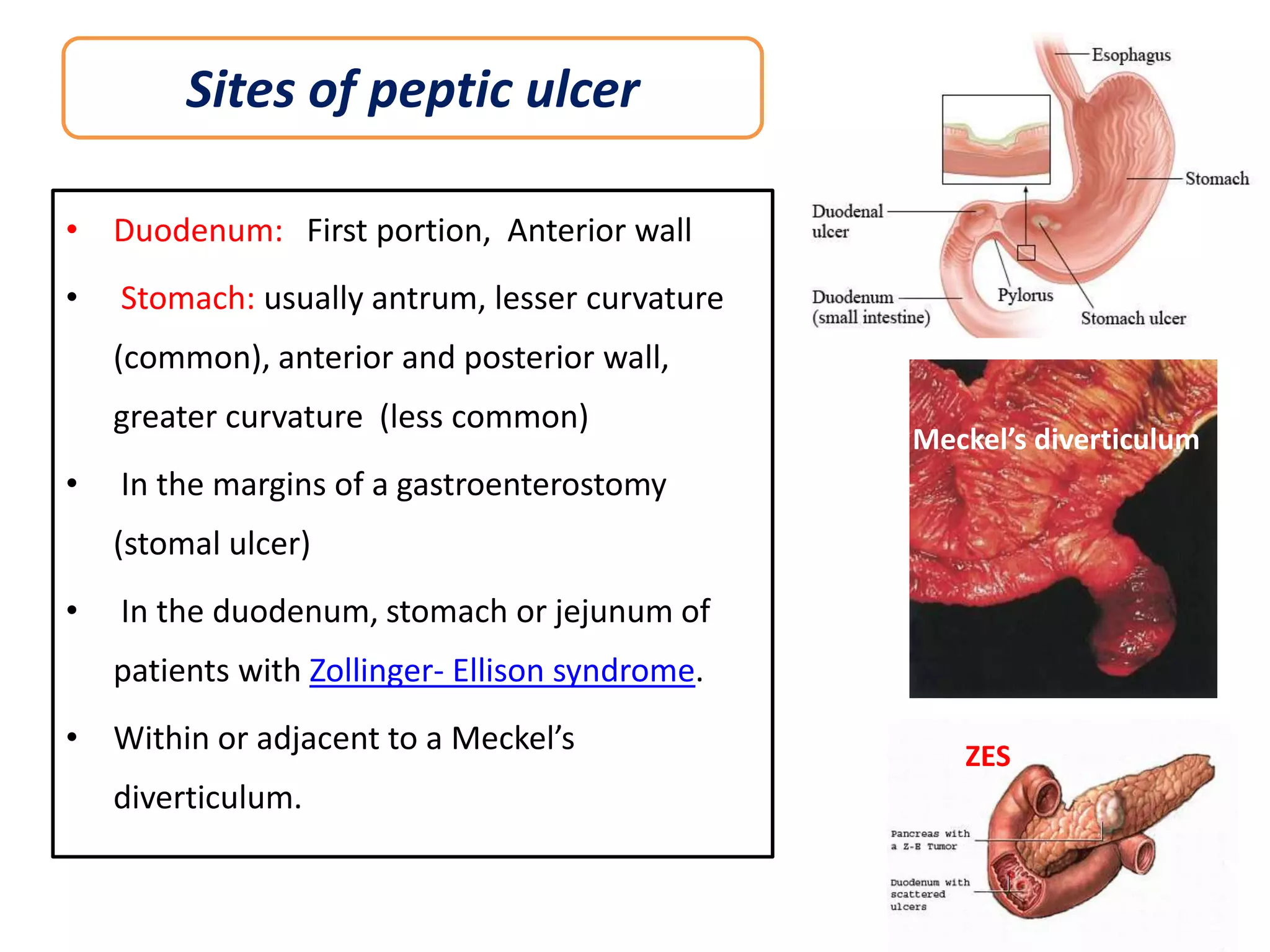
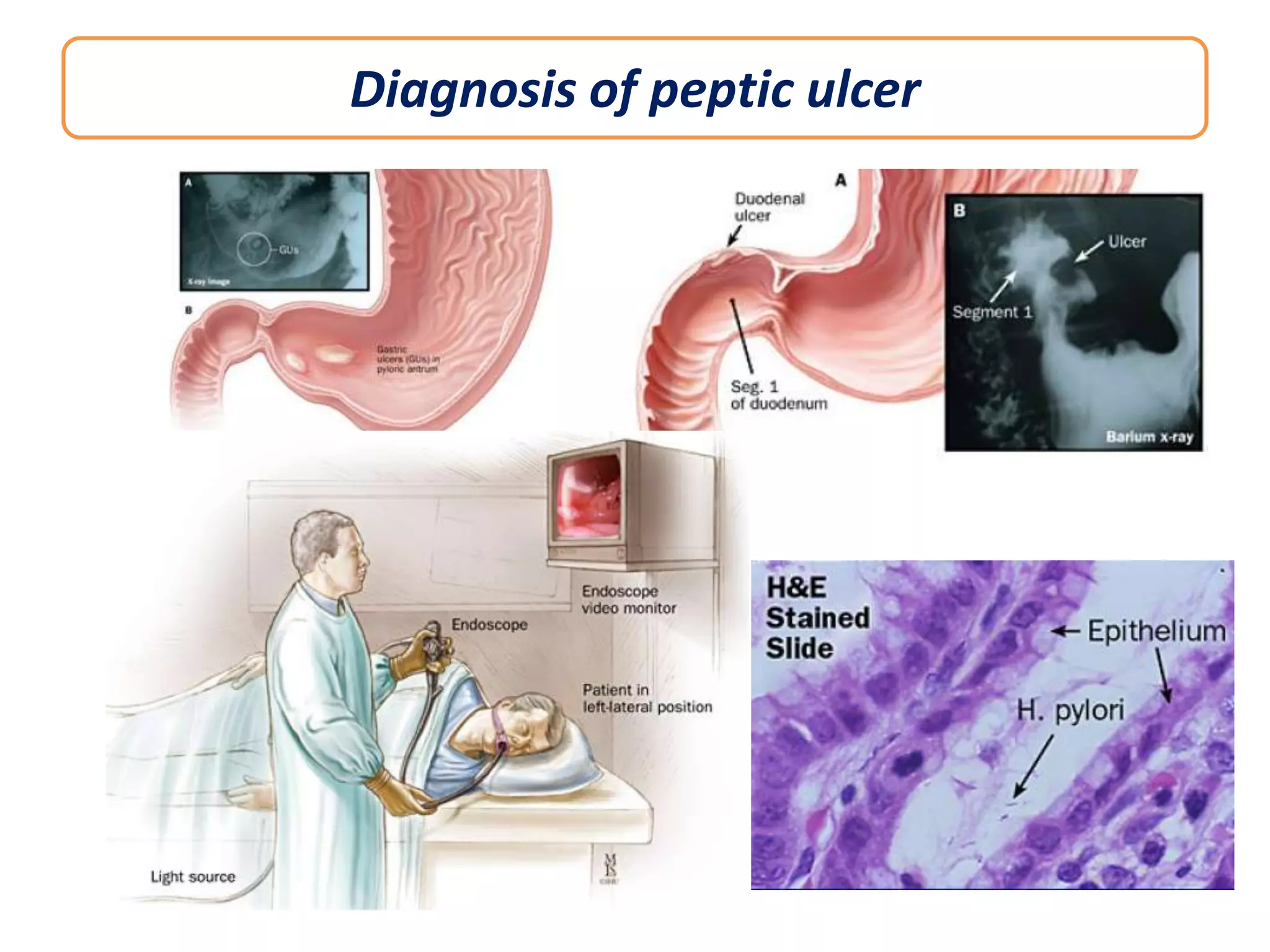
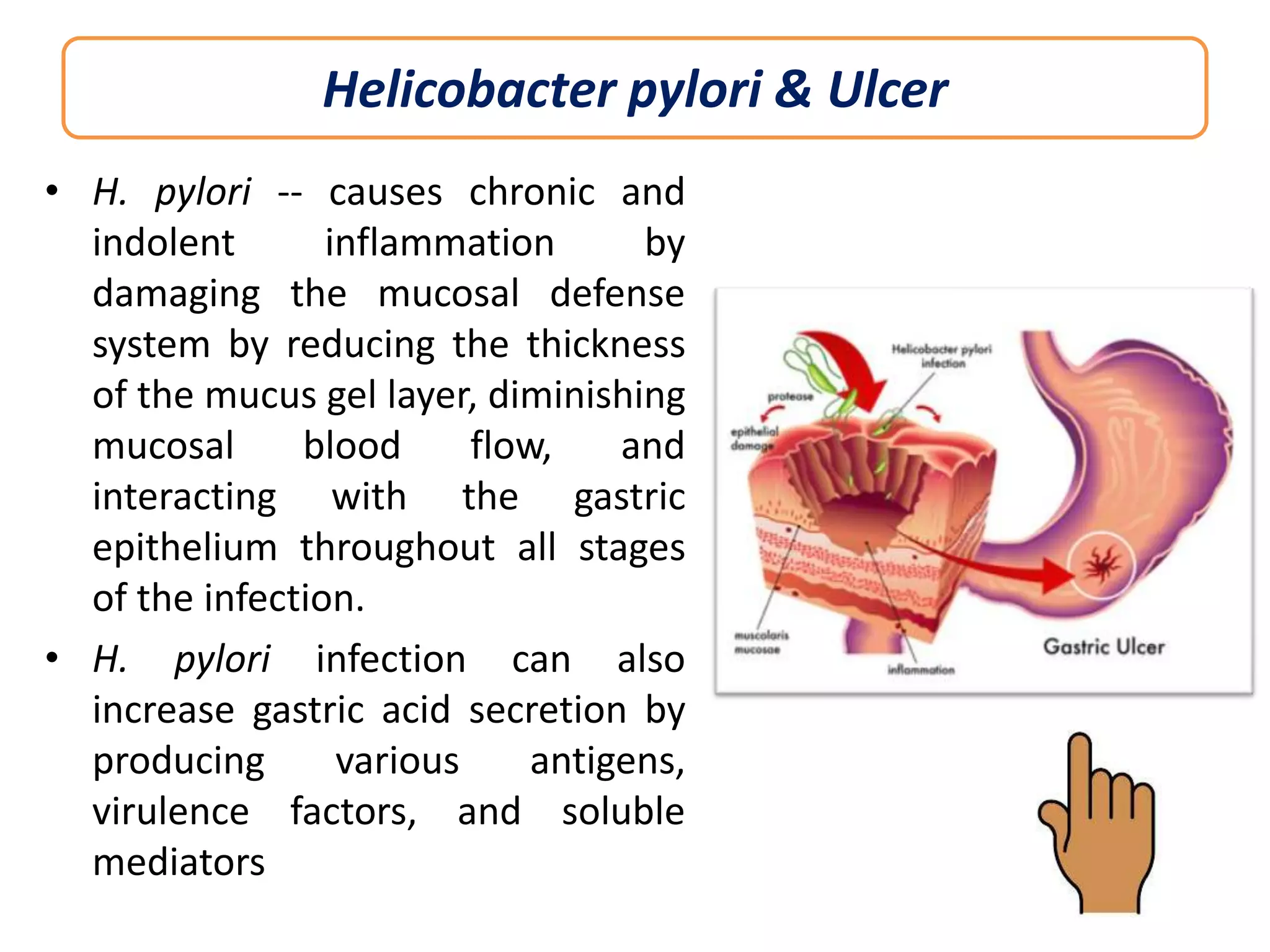
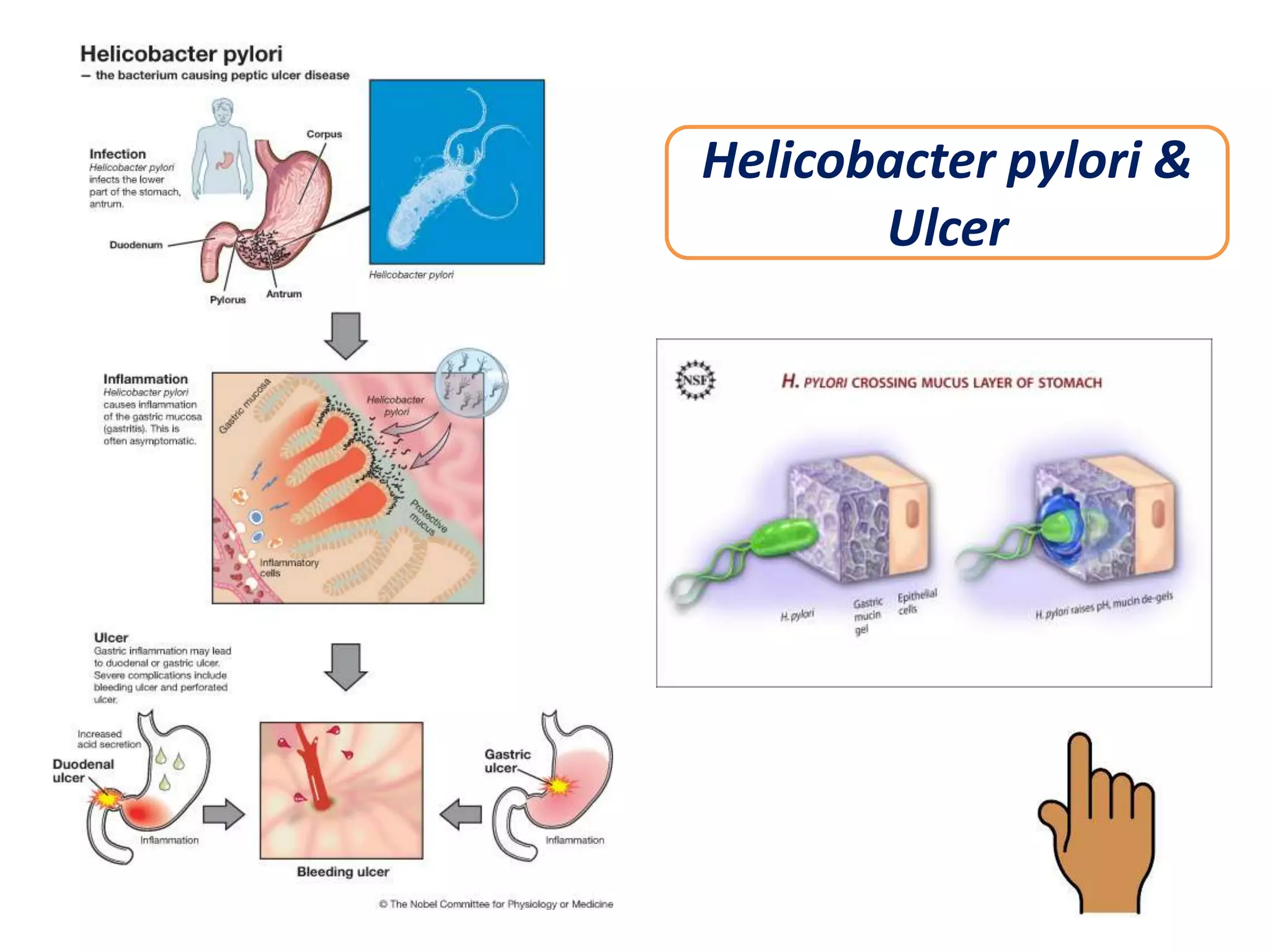
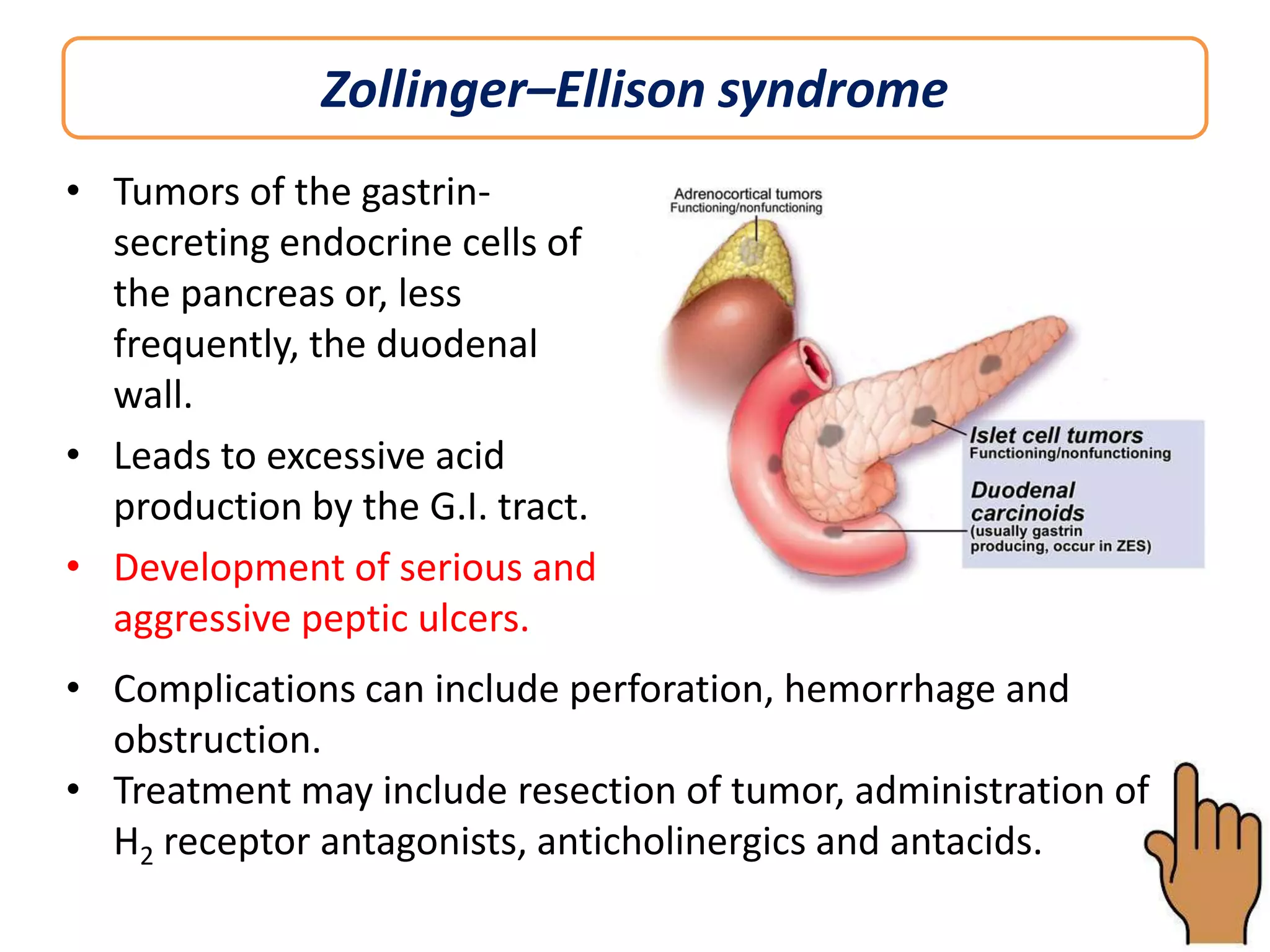
This document discusses peptic ulcers, including their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment. Peptic ulcers are abnormalities in the gastrointestinal tract caused by damage from stomach acid. The most common causes are infection with Helicobacter pylori bacteria and long-term use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Common symptoms include abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting of blood. Diagnosis involves tests to detect H. pylori infection and endoscopy to view the ulcers. Treatment focuses on eradicating H. pylori with antibiotics, reducing stomach acid with proton pump inhibitors or H2 blockers, and protecting the lining with sucralfate.