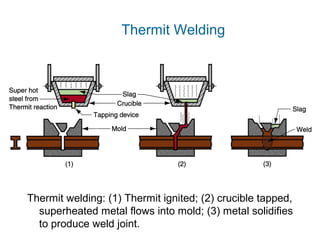
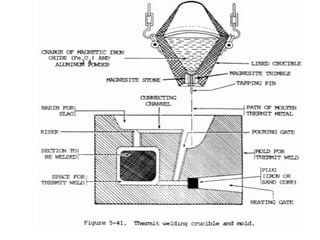
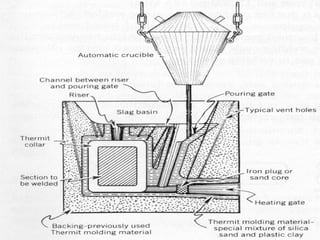
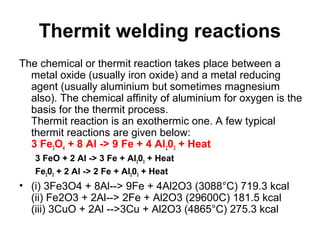
Thermit welding uses an exothermic reaction between a metal oxide and a reducing agent like aluminum to generate intense heat. This heat is used to fuse metal parts together. In the process, a thermit mixture is ignited in a crucible, producing molten metal and slag. The molten metal is poured into a preheated sand mold containing the parts to be welded, fusing them together. Thermit welding is used for large, heavy duty repairs that require high heat, such as welding broken rails or crankshafts.














![• A molding box is then placed around the portion to be
welded and a molding material* is rammed into the box.
Ramming should ensure a tight contact between the
molding sand and the wax.
• The sand mixture must fill the mold completely and be
rammed hard. The molding material should be about 100
mm tick between the wax pattern and the molding box at
all points.
• The mold should be provided with the necessary number of
pouring gates, heating gates and risers depending on the
size of the weld.
• After the ramming has been done, the molder should lightly
rap the gate, riser and preheat opening patterns and draw
them out carefully.
• Wipe away any loose sand that might tend to fall into the
holes]he mould walls and recesses will then need be
trimmed, so that any broken surfaces may be patched,
obstructions in the pouring and other gates removed and
the surfaces efficiently smoothed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thermitweldingnmk-150114025423-conversion-gate02/85/Thermit-welding-nmk-19-320.jpg)





