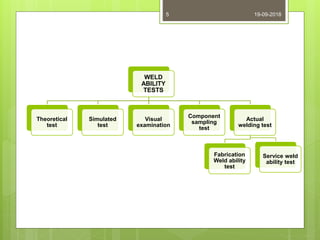
The document discusses weldability, which refers to the ability of materials to be welded into structures that perform satisfactorily in service, focusing on factors like metallurgical compatibility and mechanical soundness. It outlines various weldability tests, their classifications, and the significance of actual welding tests over theoretical or simulated tests to assess material performance under practical conditions. Additionally, it details specific testing methods for both fabrication and service weldability, including hot and cold cracking tests, along with different forms of cracking and their assessments.