Embed presentation
Downloaded 413 times
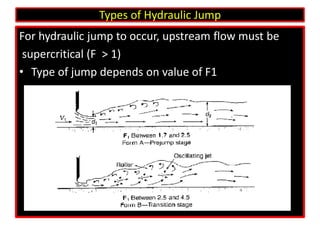




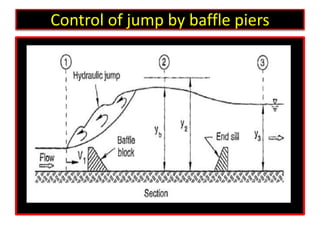
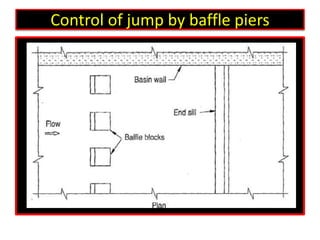


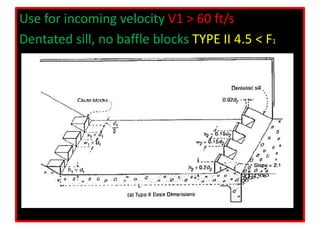
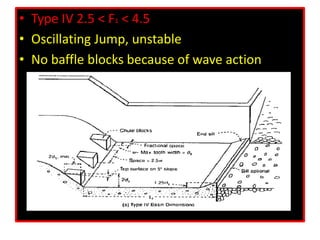
This document discusses types of hydraulic jumps that can occur when upstream flow is supercritical, and describes how stilling basins are used to initiate jumps to dissipate energy without downstream damage. It notes that the "steady jump" type is best for design when the Froude number is between 4.5 and 9.0. Stilling basins use structures like baffle blocks to stabilize the jump position and control the jump. The length and design of the stilling basin depends on factors like the jump length and surface profile which relate to the upstream Froude number and flow velocity.










