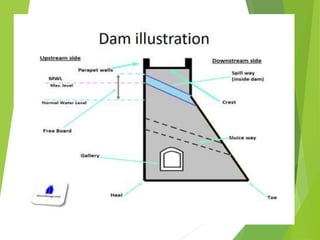
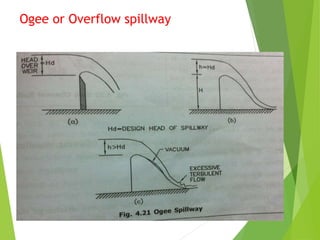
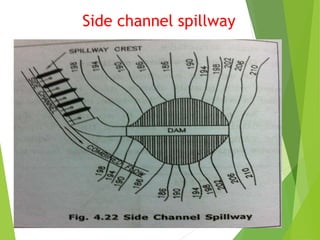
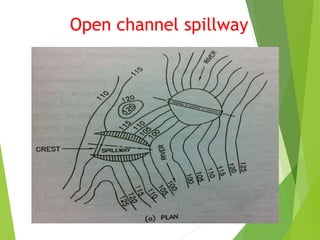
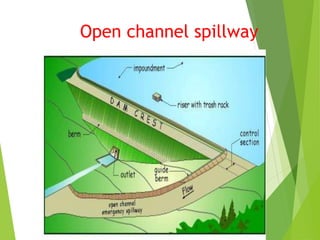
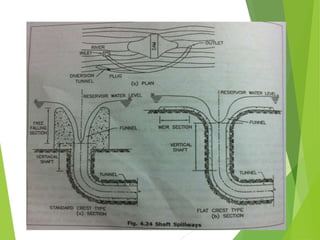
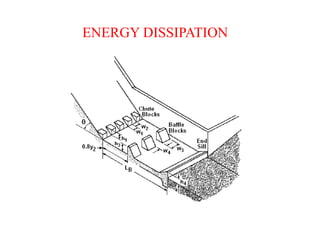
Spillways are structures constructed near dams to safely discharge surplus water from reservoirs. There are several types of spillways classified by their utility and prominent features. Main spillways are designed to pass the entire design flood volume, while auxiliary spillways supplement the main spillway. Emergency spillways activate only during emergencies. Common spillway types include overflow, which guides water smoothly over a curved crest; side channel, which diverts flow through a parallel channel; and tunnel, which conveys flow through a closed channel around the dam. Shaft spillways similarly direct water vertically then horizontally through a tunnel.